What general trend is observed in atmospheric CO₂ levels from 2000 to 2020?
The carbon dioxide level is increasing at a fairly constant rate.
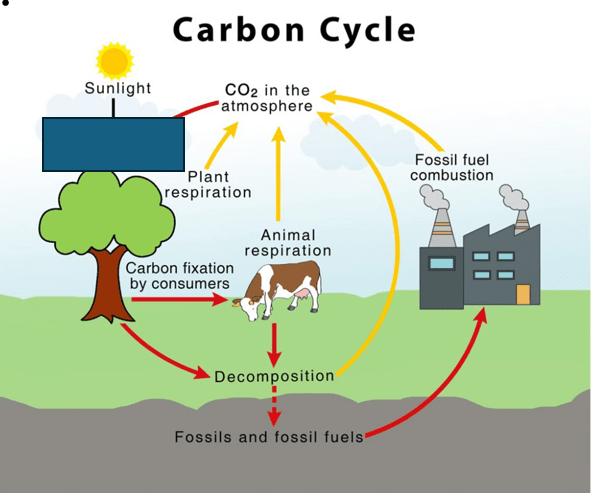
What process is missing?
Photosynthesis
Effect :Eutrophication and algae blooms
what is the cause?
Cause: Use of synthetic fertilizers →
Which human activity is most responsible for disrupting the nitrogen cycle?
A. Deforestation B. Use of fertilizers C. Burning fossil fuels D. Overfishing
Which human activity is most responsible for disrupting the nitrogen cycle? B. Use of fertilizers

What actions can individuals take to reduce their carbon footprint?
If a line graph showed declining populations of top predators, what would most likely increase in response?
The prey would increase consuming most of the producers (grass, plant) until carrying capacity is met.
90 percent of the energy is lost as heat during body processes, only 10 percent of the energy is available to be used at the next level.
What is the 10 percent rule?
Where does the other 90 percent go?
Cause: Deforestation → How does this impact the carbon cycle?
Effect: ? How does this impact the carbon cycle?
It causes increased concentrations of atmospheric Carbon dioxide.
An increase in atmospheric CO₂ is most likely to directly result in
A. Eutrophication B. Global warming C. Acid rain D. Ozone depletion
An increase in atmospheric CO₂ is most likely to directly result in:B. Global warming
Incorporate green spaces, establish wildlife corridors, institute storm water runoff for watering gardens
How can urban planning be adjusted to minimize disruption to ecosystems?
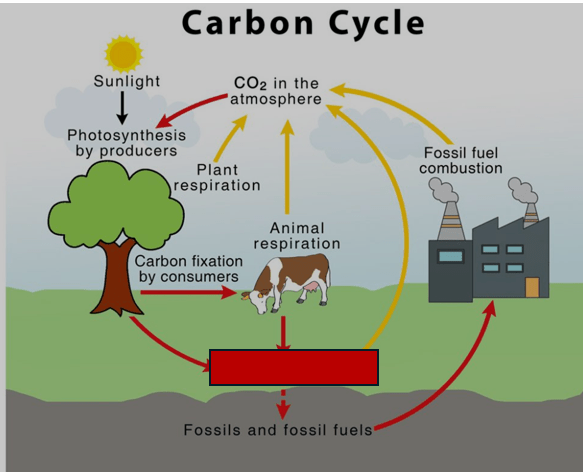
What process is missing between animals and the soil?
What is decomposition?
What are the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle?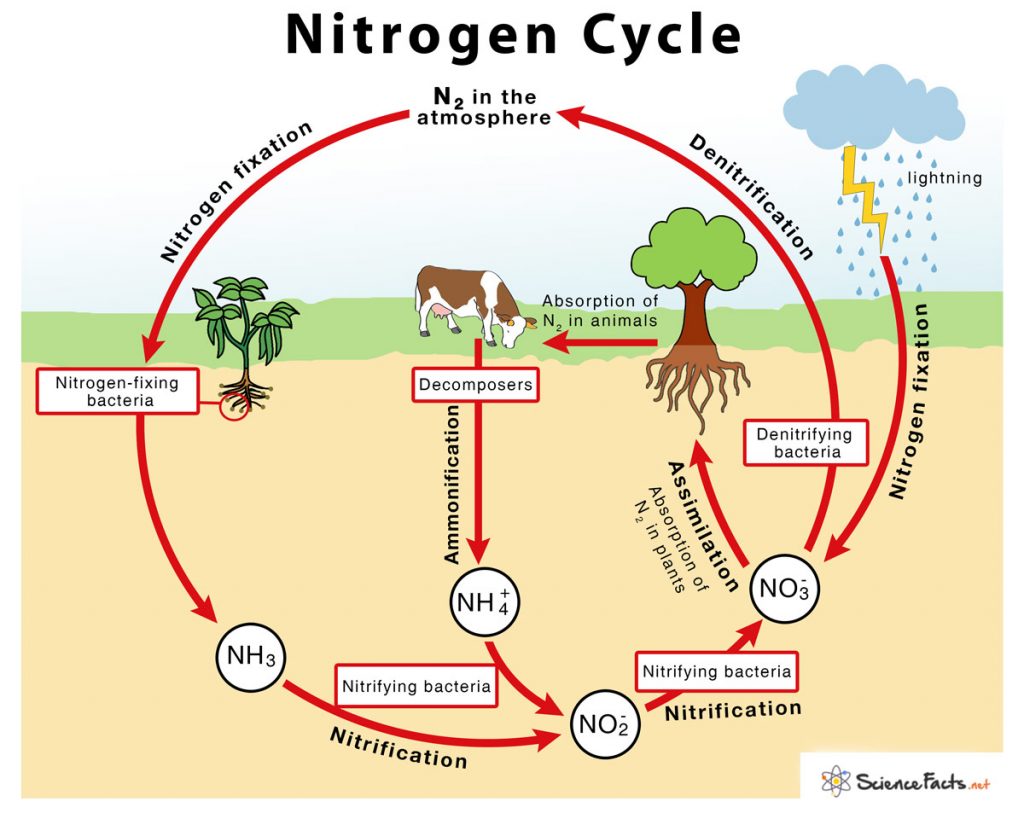
Bacteria fix nitrogen by removing it from the air to make usable by plants and animals and also return nitrogen back to atmosphere.
Cause: Overfishing → how can this destabilize a marine food web?
Effect: ? How could this destabilize a marine food web? Overfishing would cause lack of food in the upper trophic levels due to lack of prey and could cause overpopulation of organisms that consume fish.
The carbon cycle includes all of the following processes EXCEPT:
A. Photosynthesis B. Respiration C. Combustion D. Nitrogen fixation
The carbon cycle includes all of the following processes EXCEPT:D. Nitrogen fixation
Different species often perform similar functions within an ecosystem (e.g., pollination, nutrient cycling). If one species is lost, others can take over its role, maintaining ecosystem functions and stability. This concept is known as functional redundancy.
Why is biodiversity important to ecosystem stability?
If a trophic pyramid is missing its producers, what would happen to the levels above?
All levels above the producers will die as well.
Design a food web using at least 6 organisms from a freshwater ecosystem.
FISH, AQUATIC PLANTS, SNAILS, DRAGONFLIES, CRAYFISH, FROGS, BIRDS
Design a food web using at least 6 organisms from a freshwater ecosystem. AP-D-C-S-F-B
Cause: Increased CO₂ emissions →
Effect: ? What feedback loop might accelerate climate change?
Which of the following would best model a stable ecosystem?
A. Only predators and prey B. Balanced producers, consumers, and decomposers C. A system with only producers and herbivores D. A food chain with no top predator
Which of the following would best model a stable ecosystem? . Balanced producers, consumers, and decomposers
- accidental ingestion: mammals, mistake plastic debris for food.
- Bioaccumulation of Toxins: Plastics can absorb harmful pollutants (like heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants) from the water.
Discuss one major environmental consequence of plastic pollution.
Analyze a graph showing biodiversity loss over time. What conclusions can be drawn about ecosystem stability
Fewer species means fewer roles filled (predators, pollinators, SEED DISPERSERS, decomposers, etc.).
With fewer “backup” species, losing even one organism can destabilize food webs.
A HUGE DECREASED STRATED AROUND THE TIME OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION.
 The biomass decreases at each trophic level.
The biomass decreases at each trophic level.
How does biomass decreases at each trophic level in a pyramid of biomass?
Cause: Urbanization → Examples?
Effect: ? What impact does this have on local biodiversity?
Implementing crop rotation can improve soil nutrients and reduce pest populations without the need for
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides
- Reduce Synthetic Fertilizer Use:
- Crop Rotation and Cover Cropping:
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technology to apply fertilizers more efficiently and only when necessary can minimize nitrogen runoff and optimize crop uptake.
Describe how human activity can be adjusted to restore the balance of the nitrogen cycle.
