Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot make their own food; they are also called this because they must consume other organisms for energy
What are consumers?
Each level on a energy pyramid or food web is called a ________ __________
What is a trophic level?
Number 4 on this diagram of the water cycle, water leaves the atmosphere in the form of rain or snow
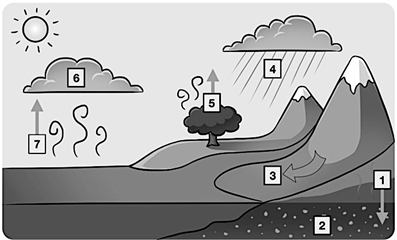
What is precipitation?
Letter A of the carbon cycle diagram, factories release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere
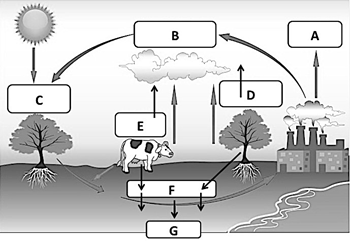
What is burning fossil fuels?
Nitrogen gas (N2) makes up this % of the Earth's atmosphere
What is 78%?
Plants get their nitrogen from the soil. Animals get their nitrogen from this activity
What is eating plants?
In this food web, there is the food chain:
algae-->minnow-->bluegill-->raccoon
The bluegill is this level of consumer
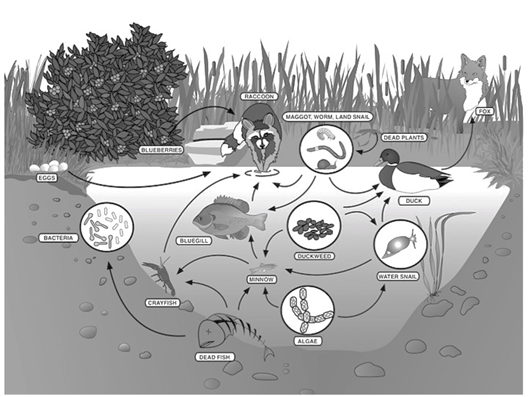
What is secondary consumer?
The aphids are this trophic level
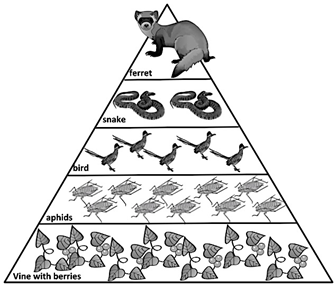
What are primary consumers?
Number one on this diagram of the water cycle, water seeps into the ground to become groundwater
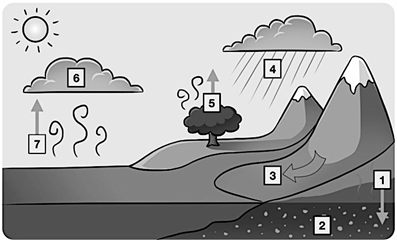
What is percolation?
Letter C on this diagram of the carbon cycle, where plants take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere
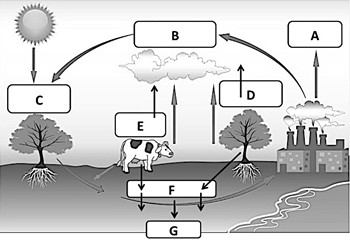
What is photosynthesis?
Bacteria A is called this, and it converts nitrogen from the atmosphere into ammonia
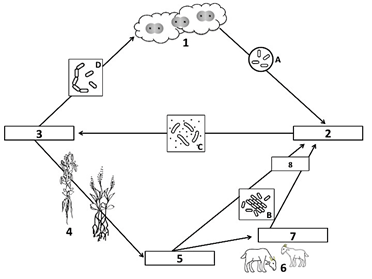
What is nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Number 1 of the Nitrogen Cycle, found in the atmosphere
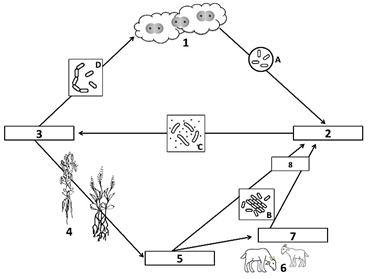
What is N2, or atmospheric nitrogen gas?
The raccoon eats blueberries, eggs, and fish. Because it eats both plants and animals, it is classified as a __________
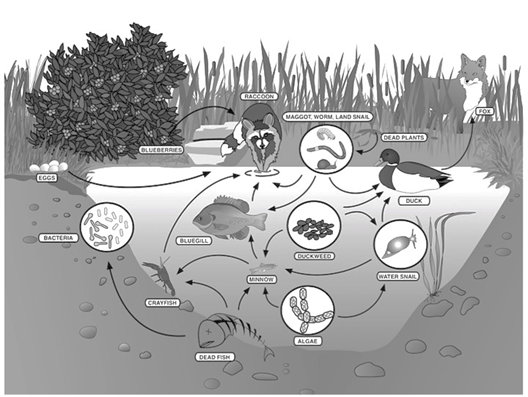
What is an omnivore?
The snakes are at this trophic level
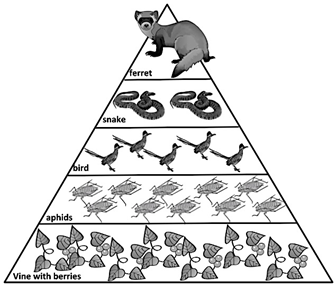
What is tertiary consumer?
Number 6 on the water cycle diagram, water in the atmosphere changes from a gas to a liquid and forms clouds
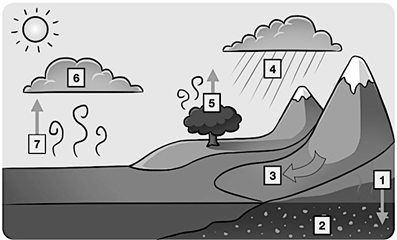
What is condensation?
Photosynthesis allows autotrophs to make their own food, and it also removes this from the atmosphere and releases oxygen
What is carbon dioxide?
or
CO2
Bacteria C turns ammonia into nitrates so that plants can use it
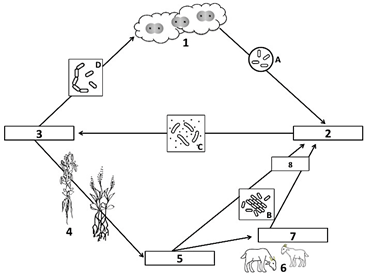
What is nitrifying bacteria?
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and ammonifying bacteria turn nitrogen into this compound, shown as number 2 on the diagram
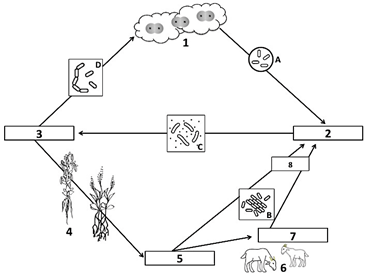
What is ammonia (NH3)?
This class of heterotrophs cause decay by breaking down dead matter and returning nutrients to the ecosystem. An example is mushrooms
What are decomposers?
The raccoon is at this trophic level
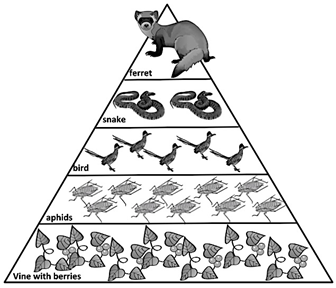
What is quaternary consumer?
Number 7 on this diagram is the changing of water from a liquid state to a gas state
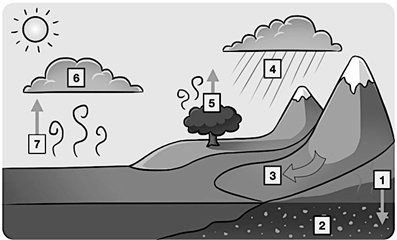
What is Evaporation?
Letter E and D on the carbon cycle, when plants and animals release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere
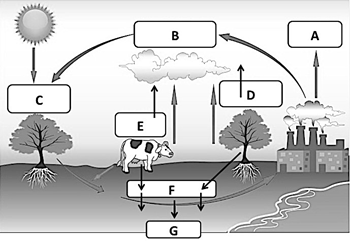
What is respiration?
Bacteria D turns nitrates back into nitrogen gas, which returns to the atmosphere
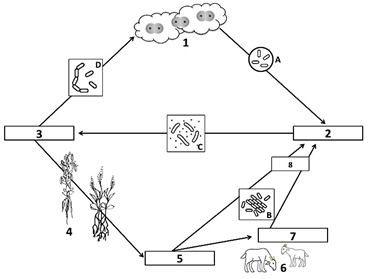
What is de-nitrifying bacteria?
Number 5 on the diagram, nitrates are absorbed by plants in order build these
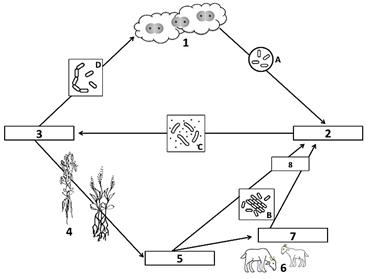
What are plant proteins?
Name the three producers in this food web
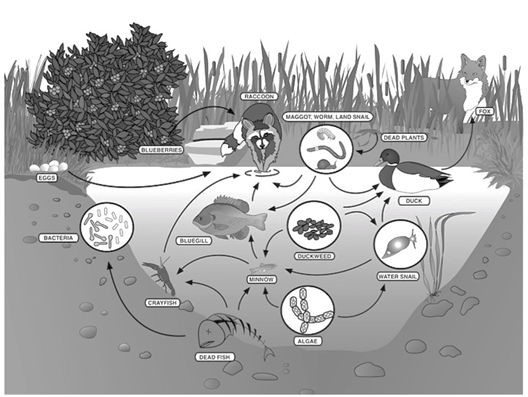
What are blueberries, algae, and duckweed?
This much food energy is transferred up each level of the energy pyramid
What is 10%?
Number 5 on this diagram of the water cycle, water is released into the atmosphere from the leaves of plants
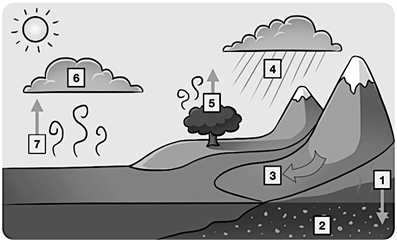
What is transpiration?
Name 2 human activities that release carbon into the air
What are burning fossil fuels,
cutting and burning trees,
mining
These 2 processes result in the production of ammonia in the nitrogen cycle
What are nitrogen fixation AND ammonification?
The absorption and incorporation of nitrogen into plant and animal compounds
What is assimilation?