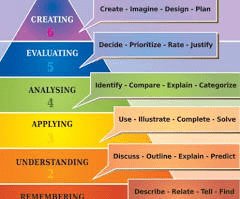
The belief that one's own culture is superior to all others is _______________.
ethnocentricity
An _________ __________ approach identifies and builds on the students’ already existing strengths, experiences, and knowledge.
asset based approach
SLA stands for ________________.
second language acquisition
The question that asks whether students should spend a longer time learning fewer topics or a shorter time on more topics is known as what?
Depth vs breadth
____________________ is the blending and moving between languages as a natural way to think, speak, read, and write, rather than keeping them separate
translanguaging
Give an example of surface culture.
clothing, food, music, language, holidays, art, religion
A ______ ________ approach is a focus on what students lack, rather than what they have; a student's L1 is an obstacle.
deficit based approach
Casual, everyday English is known as _______________________.
BICS – Basic interpersonal communicative skills
What are core concepts?
Foundational knowledge for a given subject; building blocks. i.e. A student must understand what democracy is before learning US history.
Words that translate easily from one language to another are known as _________.
cognates
The unseen values of a group of people is known as _________ __________.
deep culture
What strengths could an ML bring to the classroom?
cultural experiences, languages, differing perspectives, cultural/linguistic bridges, linguistic awareness
Academic English is known as ________________.
CALP – cognitive academic language proficiency
Lev Vygotsky (1978) -The gap between a student’s actual developmental level and the level of potential development under guidance of a teacher or more proficient peers is known as the Zone of Proximal _______________.
Zone of Proximal Development
Culturally _______________ teaching recognizes that culture is a force that forms students’ perspectives of the world
culturally responsive teaching
What might give an ELL culture shock in an American classroom?
a focus on opinions/critical thinking (encouraged to question or challenge ideas), teachers giving students praise, somewhat informal atmosphere, group work
Which phrase(s) best reflects an deficit-based perspective of EMLs?
A. “These students need to catch up to their peers.”
B. “These students bring valuable linguistic and cultural strengths that enhance learning.”
C. “These students struggle because English is not their first language.”
A and C
Explain Krashen's i + 1 theory.
i = input. An effective method for delivering materials is to use language just above a student's proficiency so the material is challenging but graspable.
What two areas of language are output?
input - reading, listening
output - speaking, writing
What kind of assessment is this?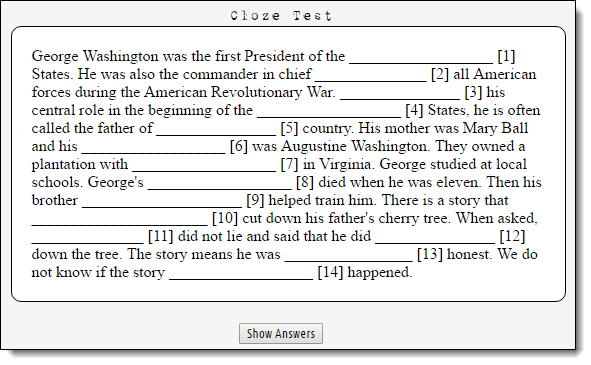
How can you make your classroom a comfortable place for ELLs?
answer
How can a student's background be used as an instructional tool?
answer
What is an affective filter?
Stephen Krashen (1982) proposed the idea of an “emotional filter” that influences how much learning takes place during input; determined by affective factors such as anxiety, motivation, self-confidence, etc.
Selecting standards requires a two-tiered plan.
Describe:
Tier 1 -
Tier 2 -
Tier 1 - essentials goals, skills, and knowledge every student must know
Tier 2 - advanced goals for students who can handle a larger challenge