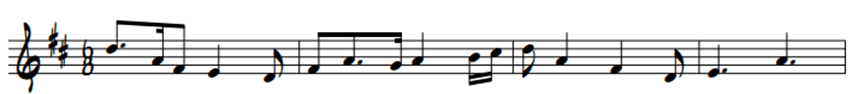4 musical features made popular by the Mannheim orchestra
Mannheim crescendo/rocket/roller/sigh/birds/grand pause/energised rhythm/sudden cresc and dims/Mannheim climax
The year this work was first performed
What is 1795?
The era of music this was composed in.
What is (early) Romantic?
The group of composers that defined 20thc music.
Two different techniques strings players can use when playing.
What are pizziccato/arco/spiccato/col lengo/sul tasto/sul pont
[answer] was an early classical style that originated in France.
What is style galant?
[answers] are the five tempo markings used throughout the piece. (There are 2 tempo markings for mvmt 1)
Mvmt 1: Adagio and Allegro
Mvmt. 2: Andante
Mvmt. 3: Allegro
Mvmt. 4: Spiritoso (allegro also accepted)
True/false: The coda is the longest section of movement 1.
What is false? (It is the exposition.)
The composer "Les Six" and other 20thC composers wrote their music as a response to...
What is French/German romantic music and composers (Wagner, Debussy, etc;)
...is the definition of a Neopolitan 6th.
A chord built on the flat 2nd degree of the scale
(e.g. Db would be a Neopolitan 6th in C major)
4 commonly used structures in the Classical Era of music and 2 ways structure changed in the Romantic era.
What are binary, rondo, ternary, sonata, sonata-rondo, minuet and trio, and theme and variation?
What is introduction of symphonic tone poem/5 movement symphony/less use of sonata form/any other relevant answers/Beethoven replaced minuet with scherzo/cyclic form
[answers] are 3 Haydn characteristics used in the piece
What are whole orchestra trills/whole orchestra pauses/use of sonata form/monothematicism/any other relevant answers
The time signatures at the start of each movement.
What Are...?
Mvmt 1: 6/8
Mvmt 2: 4/4
Mvmt 3: 3/4
Mvmt 4: 4/4
3 characteristics of 20thc French music.
What are short works/melody more important than harmony or counterpoint/avoid overly legato and expressive music/any relevant answers
The super special chord here is a...

What is a German augmented 6th?
3 Romantic composers who wrote in a more traditionally classical style and 3 who did not.
Traditional - Brahms, Schubert, Mendelssohn, Schumann, Dvorak (mostly)
Less traditional - Wagner, Liszt, Strauss, Berlioz, Bruckner, Tchaikovsky, Mahler
1 interesting harmonic feature per movement.
What are:
Mvmt. 1 - N6 chord, circle of 5th descending sequence
Mvmt 2 - Interrupted cadences, diminished chords, fanfare figure
Mvmt 3 - Tertiary modulation, Bb+ chord, German augmented 6th
Mvmt 4 - Drone, harmonic sequence, circle of 5ths
The definition of the word antiphonal and significance it has to Mendelssohn's Italian Symphony.
What is a musical idea that is played between 2 groups? This writing used in mvmt 1 with the flutes and violins playing in oscillating 3rds.
Poulenc's 4 stylistic periods
What are "Les Six"/Satie influenced, neoclassical, neoromantic, and religious?
Dictation time!!!
-6/8
-D major
-4 bars
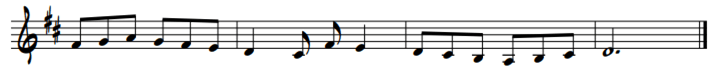
The amount of eras Beethoven's style can fall into and a feature of each era.
3 eras
Early (Symphony 1) - Haydn influenced/sonata form
Middle - Mixed forms (sonata-rondo)/more modulation/more important development section/minuets now labeled as scherzos/5 movements in Symphony 6/
End - (Symphony 9) - huge orchestration/inclusion of choir and bass solo/fugues used (mvmt 4)
Sing the main theme from each movement.
[insert singing here]
The texture in the beginning of movement 2 and significance this has to the influence behind this movement.
The monophonic texture resembles chant, which Mendelssohn would have encountered during his travels in Rome.
Who are
•Schubert – The song cycle “Winterrise” was an early influence of Poulenc’s and could be why he used many major-minor alternations
•Satie – Satie ignored musical influences of the time and his pieces tended to be sparse, charming (say some), and witty
•Debussy
•Ravel – Flowing melodies, eclectic style, not conforming to “musical fashion” at the time
•Stravinsky – unexpected harmonic turns and dissonances
Dictation time!!
-6/8
-D major
-4 bars