Lynn just started a new project and immediately created a main() function. They are trying to use cout, but they're getting a red underline and an error saying they cannot use cout. What is one reason why Lynn is having problems?
They forgot to #include <iostream> and/or forgot to using namespace std; at the top of their program.
Akshara has the following code, but it's printing out too many numbers. Why?
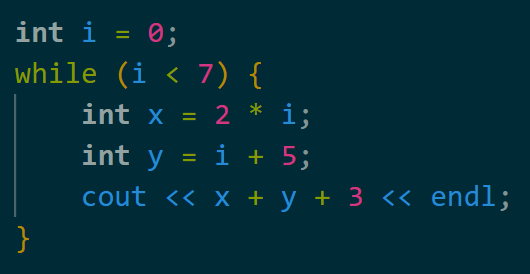
i is never updated, so this is an infinite loop
Keegan wants to write a function that calculates how much money, rounded to the nearest whole number, is leftover after paying for rent, groceries, entertainment, etc. What should the return type of the function be?
int
Christine has function that prompts the user for input and returns either true or false. Suppose she wants to write a program that asks the user for a number n and then runs that function exactly n times, regardless of whether the function returns true or false. Which loop should she use?
for loop
Since we want to run the function exactly n times, we want to use a count controlled loop, which for loops are better for
True or false: If the requires clause of a function says n > 0, then I should check if n <= 0 and print an error message if it is.
False. Do not check requires clauses. You may lose points on FRQs if you do this.
What is the value of x after the code is run?
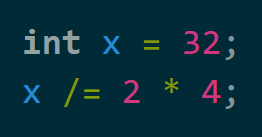
4
In the +=, -=, etc operators, we first compute the expression on the right side then use that value to modify the variable on the left. Therefore, [x /= 2 * 4] is NOT equivalent to [x = x / 2 * 4], but it is equivalent to [x = x / (2 * 4)]
Rakesh wants to write a loop that prints numbers from 0 to n (inclusive) where n has already been defined and initialized earlier. However, his implementation below isn't working. What is causing the issue, and how would you change exactly one line of code to fix it?

The ++i increments the variable before it is printed, so this implementation actually prints 1 to n + 1 (inclusive). To fix this, we should replace ++i with i++ so we increment i after printing its value.
Makayla has a function with declaration void print_announcement(); but she is unsure how to use it to print the announcement. She came up with four options below, which option(s) will work?

Only option D will work
Shalini has a function that prompts the user with an addition problem and returns true if the user enters the correct value (false otherwise). Suppose Shalini wants to write a math game where users try to get as many of these addition problems in a row. Which loop should she use?
while loop
Since problems are prompted as long as the user enters correct answers, this calls for an event controlled loop, which while loops are better for
Which option(s) below are valid ways to cast x to be a double?

All of them are valid
List all lines with errors that prevent the program from compiling, and explain what the error is.

4. no return type
9. cannot declare variables in a function call
10. >> instead of <<
Victoria is writing a program that asks the user for a number n and prints n^2 if n < 10 or n + 10 otherwise. Victoria's current implementation below is buggy, but she knows square(n) correctly returns n * n. What is the issue?

When n >= 10, we do n + 10, but we don't update the value of n.
What is the value of x that is printed?
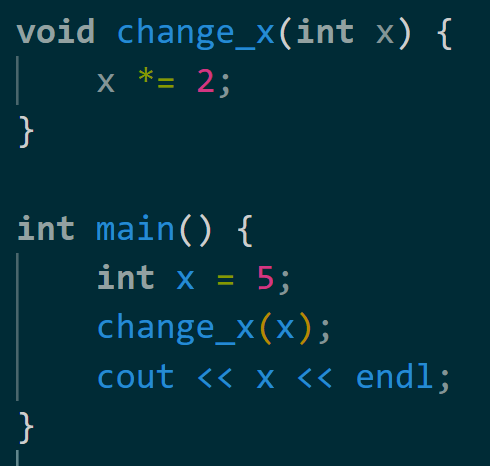
5
When we pass a variable into a function, it makes a copy of that variable, so the x in the function is a different variable than the x in main(). Therefore, x *= 2 does not modify x in main().
What prints?
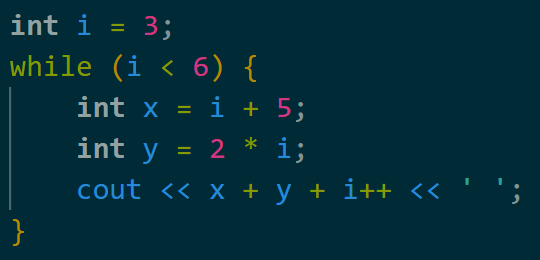
17 21 25
Since x + y + i == 4 * i + 5 and i can only be 3, 4, and 5.
Which option(s) evaluate to true?

Only option D is true
The following code doesn't compile. Why?
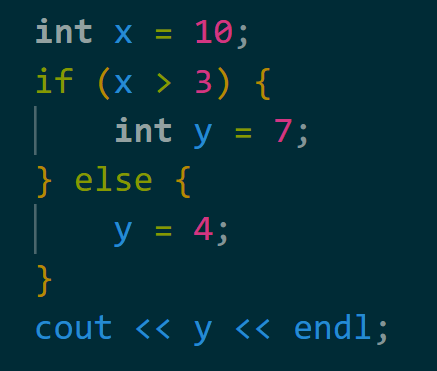
The scope of y is only in the body of code in the if statement but before the else statement; that is, y can only be used:
if (x > 3) {
[HERE]
} else {
[NOT HERE]
}
[NOT HERE]
The following function takes advantage of the fact that integer division effectively rounds down the result of x/y, but it has a bug. Give a value for x and y that would expose the bug.

Any x that is a multiple of y would expose the bug. If we specifically pick x = 10 and y = 5 then ceil_divide(x, y) outputs 3, which is not 2 rounded up to the nearest whole number.
What should go in the blank if we have a function char get_first_initial(string name); that returns the first initial of the name passed in?
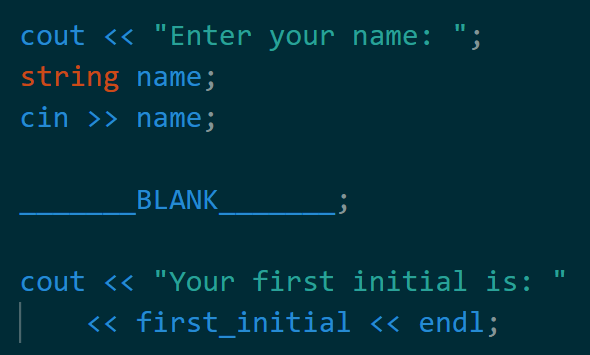
char first_initial = get_first_initial(name);
What should go in the blanks to print:
A B C C C A B B C C A B B B C
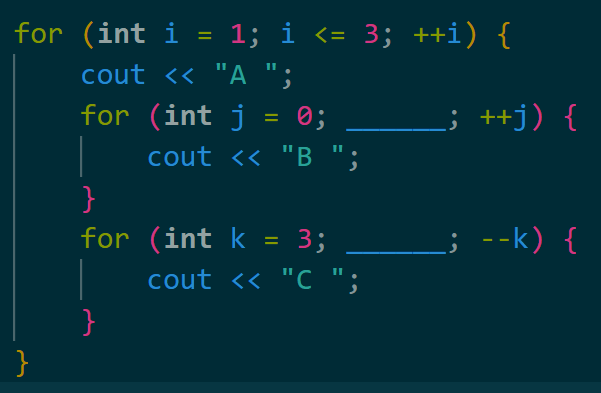
j < i and k >= i
Which letters are printed?
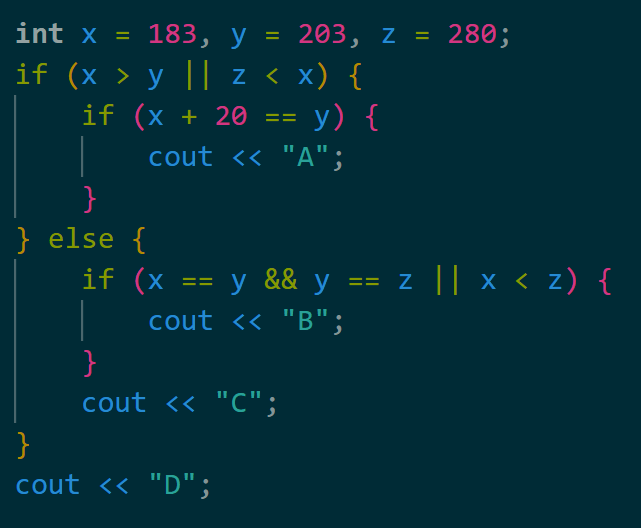
B, C, and D