
sinus tachycardia
no p waves, QRS complexes irregularly irregular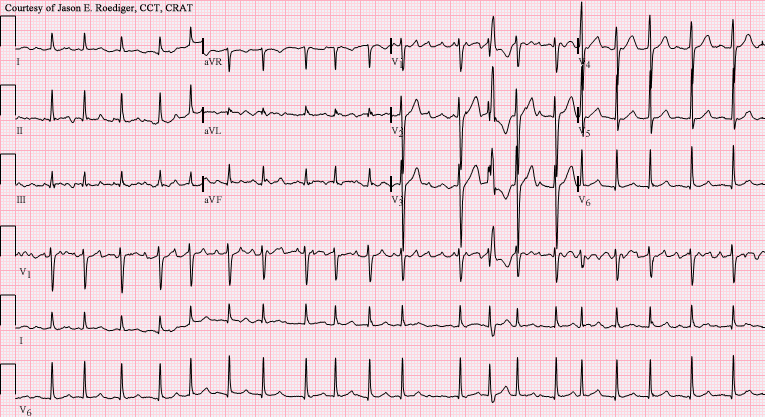
atrial fibrillation

PVC - bigeminy
+/- fever, shortness of breath, chest pain
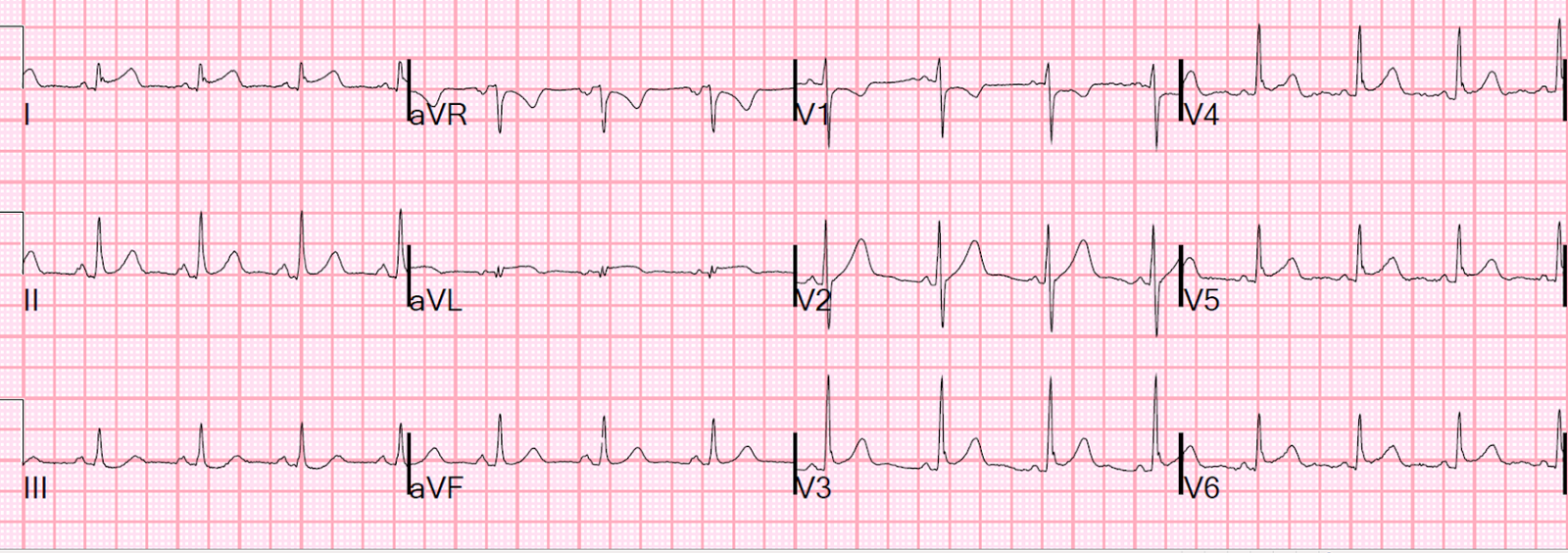
myocarditis

left ventricular hypertrophy - large R waves in V6 and deep S waves in V1
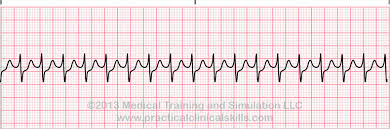
SVT
ventricular fibrillation

hyperkalemia
Wolff Parkinson White syndrome - delta waves and shortened PR interval

right ventricular hypertrophy- large S wave in lead 1, Larger R waves in V1 and deep S waves in V6
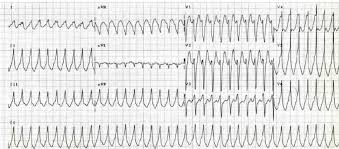
Ventricular tachycardia

atrial flutter

prolonged QT - long QT syndrome, hypocalcemia
pain worsens with deep breath or laying flat, improves with leaning forward; friction rub on exam
pericarditis

left atrial enlargement- notch in p wave "p-mitrale"

Sick sinus syndrome - SA node doesn't fire properly causing tachycardia or bradycardia

Torsades de pointes

second degree heart block - mobitz type 2, can lead to sudden cardiac death
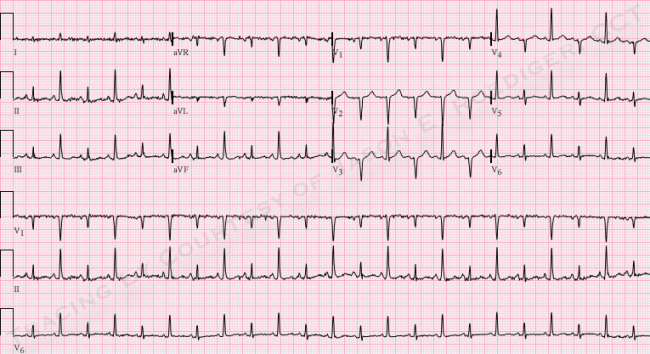
pericardial effusion - electrical alternans (every other QRS has varying amplitude) or low voltage QRS
right atrial enlargement - peaked P waves


junctional tachycardia (accelerated junctional rhythm) - narrow QRS, no P waves; a form of SVT characterized by involvement of AV node with generation of impulses from a focus in the region of AV node due to an AV disassociation

Brugada syndrome - elevated ST and inverted Twave in V1-V3; sodium channelopathy

3rd degree heart block

pulmonary embolus - S1Q3T3 sign (prominent S wave in lead1, Q wave and inverted T wave in lead3); reflects acute pressure and volume overload of right ventricle because of pulmonary hypertension; present in 15-25% of PE

hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - LVH (deep S wave V1 and large R wave V6), tall R waves in septal leads and deep S waves in lateral leads