These words indicate first person voice, second person voice, and third person voice.
First: I, me, my, ours, we
Second: You, yours
Third: they, he, she, people
This is what A.R.M.S stands for and it represents Revising in the Writing Process.
Add - information/details
Remove - information/details
Move - paragraphs or sentences
Substitute - change overused/confusing words
This is the first thing you do if you do not understand a task.
Re-read the directions, T.A.P the prompt
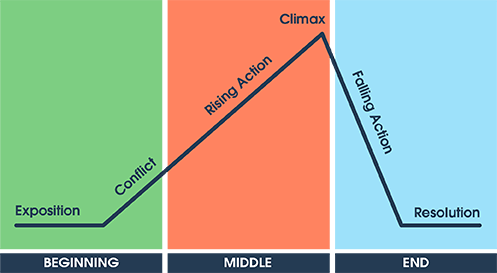
This is the series of events that create a story and move it from beginning, to the middle, to the end.
A plot
These are the text features you look for when you "preview" a text before reading.
These are the elements of informative writing.
facts, details, direct language, thesis statement, 3rd person voice, sequencing, NO opinions
This is what C.U.P.S stands for and it represents the Editing step of the Writing Process
Capitalization
Understanding
Punctuation
Spelling
This is what you might do if you read a text and you find it hard to focus or follow along.
Ask for scratch paper to fold into squares to write a mini-main idea for each paragraph.
Annotate (Pink, Green, Yellow, Blue)
Underline the most important sentence in each paragraph
This is when a character of a story changes throughout a story as a result of the events of the story.
Character Development
This is what you look to find for each paragraph of an informative text to identify a central idea and pre-write for a summary.
The mini-main idea of each paragraph
These are elements of narrative writing.
dialogue, descriptive language, plot
This is the order of paragraphs in an argumentative and informative essay.
Introduction paragraph
Body Paragraph #1
Body Paragraph #2
Conclusion Paragraph
This is what you might do if you are struggling with a topic or skill during a lesson.
Ask to be stamped for PACE
Ask a question during the lesson
These are the characteristics of literary texts.
Plot, theme, exposition, setting, characters, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, conflict
These are the characteristics of an informative text.
facts and text features such as table of contents, pictures, captions, bold print, and glossary
These are elements of argumentative writing.
Claim, persuasive language, sequencing, third person voice
This is the step you should take to attack any writing prompt to better understand the prompt/directions before beginning your writing.
T.A.P the prompt
This is what you might do if you are given a writing prompt.
T.A.P the prompt
pre-write and create a thinking map/graphic organizer
These are examples of literary texts
poetry, drama, fiction, narrative, short story
These are examples of informative texts.
text books, news articles/paper, reports, biography, reports
This is the "purpose" of a writing prompt.
to inform
to narrate
to argue/convince
This is the step you take before writing to organize your ideas and outline your paragraphs using short sentences, symbols and thinking maps.
Pre-writing
This is what you might do if you want to reach (or grow past) grade level reading and writing in class to be ready for the SBAC and 7th grade.
1. participate in class
2. do your iReady homework
3. ask to come to PACE
4. have a growth mindset when things get hard
This is the order of plot elements from beginning, to middle, to end. (Think: Plot Map)
Exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution
It helps take a bigger text more understandable and identify the most important parts.