A character or a group of characters that oppose the story’s main character.
Antagonist
When a character faces resistance from a outside force.
Ex: the wilderness
Character vs. Nature
The author's attitude or feelings toward the subject they are writing about.
Tone
An obvious or extreme exaggeration used for effect.
Hyperbole
Isaiah's pediatrician prescribed him an antibiotic.
Is the word "him" a direct object or indirect object?
indirect object
A character who shows little to no change in their personality, perspective, or outlook from the start of the story to the end.
Static Character
The most common type of conflict. Two characters are in conflict with each other's ideas, actions, or beliefs.
Character vs. Character
The time and place of a story.
Setting
Repetition of the beginning sounds in a group of words.
Alliteration
What is the dictionary definition of a word called?
Denotation - its denotative meaning
The main character of a story.
Protagonist
When a character is in conflict with their internal emotions and feelings and or a decision that they need to make.
Character vs. Self
Author leaves hints or clues to suggest events that will occur later in the story.
Foreshadowing
Comparing two unlike things without using like or as.
Ex. Her eyes were stars that lit up the night.
Metaphor
Which is a thesis statement?
a. Taking a year off before college makes high school graduates better students because they are more mature, experienced, and focused on their studies.
b. The following paper discusses how taking a year off after high school affects students who plan on attending college or technical school.
A.
A character who changes throughout the story usually as a result of overcoming a problem. Usually a main character.
Dynamic Character
When a character is in conflict with a larger group, community, or culture.
Character vs. Society
Contrast Subjective and Objective P.O.V.
When using Subjective P.O.V., the author shares their feelings and opinions.
Ex. Not having recess SUcks!
When using Objective P.O.V., the author sticks to the facts only.
Ex. We have recess during fourth period.
A figure of speech that makes reference to a well known person, event or place that may be real or imagined. Ex. Brenda had a smile that rivaled that of Mona Lisa.
Allusion
Which sentence is more formal?
a. During Homecoming Weekend, everyone is invited to come to a fancy dinner and other events at the college.
b. During Homecoming Weekend, former students are invited to attend a banquet and other events at the college.
B.
Who was the protagonist in The Watsons Go to Birmingham?
Kenny Watson
Which one of the types of conflict is the only type that shows internal conflict?
Character vs. Self
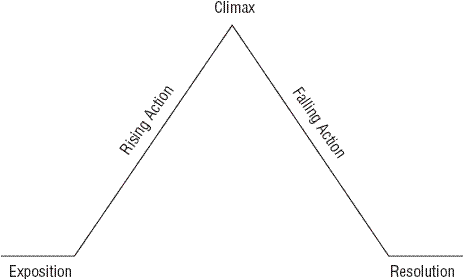 Which part of the plot would the conflict most likely be introduced?
Which part of the plot would the conflict most likely be introduced?
Rising Action
When two opposite ideas are put together for effect.
Ex. act natural
Oxymoron
Contrast a transitive verb and intransitive verb.
A transitive verb has a direct object and an intransitive verb does not have a direct object.