The two quantities are related by Hooke’s/the Spring Law
What are force and stretch/displacement?
This is the variable that affects kinetic energy the most, because it’s squared in the equation.
What is velocity?
The elastic potential energy stored in a spring that has a spring constant of 675 N/m and is compressed 0.150 m.
What is 7.59 J?
This is the condition required for total energy to be conserved.
What is the total energy transforms within the system, no energy is transferred in or out?
\Delta E = 0
Work is positive when the force and motion point this way relative to each other.
What is the same direction?
The work done by a force over some distance can be found graphically by calculating what?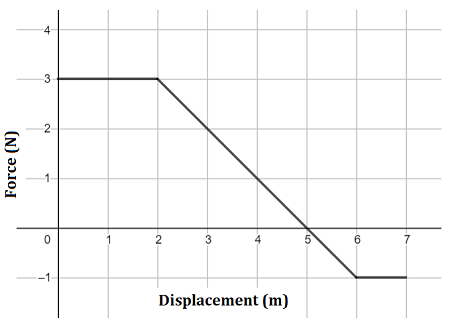
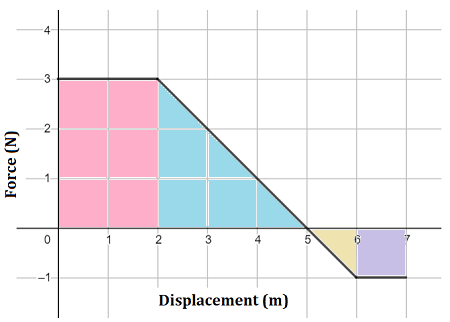 What is area under the Fx vs x graph?
What is area under the Fx vs x graph?
When you plot force vs. stretch for a spring, what does the slope of the line represent?
What is the spring constant k? (it tells us how stiff the spring is (units N/m).)
When speed doubles, this happens to kinetic energy.
What is it quadruples?
What is elastic and gravitational?
The principle that connects work and energy in a system.
What is the work–energy theorem?
The amount of work done by 30.0 N force pushing against a stationary object.
What is none? (0 distance means 0 work done)
The unit used to measure work and all forms of energy in physics.
What is a Joule?
A spring is stretched to twice its original stretch distance. The stored energy changes by this factor.
What is four times as much energy?
If two objects have the same kinetic energy but different masses, the lighter one must have this.
What is a higher velocity?
Raising an object twice as high does this to its gravitational potential energy.
What is it doubles it?
What is 7.67 m/s?
The work done by a 20.0 N horizontal force that acts upon an object for a 5.00 m horizontal displacement.
What is 100 J?
The type of energy that mechanical/kinetic energy is transformed into by friction.
What is thermal energy?
The graph below shows Force vs. Stretch for two different springs, A and B. Which spring has the larger spring constant, and how can you tell?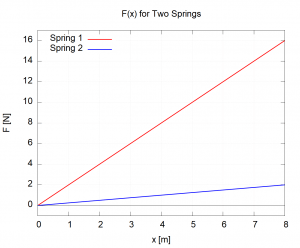
What is spring 1, because the steeper slope means a larger k?
The velocity of a 8.00 kg object that has a kinetic energy of 535 J.
What is 11.6 m/s?
The form of energy that increases as gravitational potential energy decreases during a fall.
What is kinetic energy?
The spring constant of a spring that takes 385 J of work to stretch 0.250 m.
What is 12300 N/m?
A student pushes a cart with 200 J of work, and friction removes 50 J. How much energy becomes kinetic?
Net work =200−50=150 J
This is why a closed system can never truly “lose” energy, even if its motion slows down.
What is because the energy only changes form, staying inside the system?
If a spring is twice as thick but the same material and length, how does k change?
What is, if the cross-section doubles → k doubles
The velocity of a 4.00 kg object that had a net work of 135 J performed on it.
What is 8.22 m/s?
In gravitational potential energy, this variable is relative.. you can choose it to be anywhere, as long as you stay consistent.
What is the zero height point (reference point)?
An object slides across a rough surface and slows to a stop. Describe what happens to the total energy of the CLOSED SYSTEM that includes the object and the surface.
What is the total energy stays constant/is conserved? (yes, even as kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy in the object and surface.. they're all in the same system now!)
The work done by the force of friction if the force of friction is 35 N and the displacement is 2.0 m.
What is -70. J?
When a person jumps on a trampoline, this is what happens to the forms of energy between the lowest point of the jump and the highest point.
What is elastic potential energy converting into gravitational potential energy (through kinetic energy in between)?