the attractive or repulsive force between two electrically charged objects
Electrostatic Force
Doses not transfer a charge on contact
Insulator
Electric current that only flows in one direction
Direct Current (DC)
Two things that are needed for an electric current to flow
1. Closed circuit
2. Source of electrical energy
Make this by wrapping a copper wire around a nail or bolt and attach the ends of the wire to a battery
Electromagnet
Likes charges do this
Repel
May transfer some charge on contact
Semiconductor
Electric current that changes direction periodically
Alternating Current (AC)
Electrons only have one path to flow through; one part goes out everything goes out
Series Circuit
Copper wire surrounded by magnets when spun really fast turns mechanical energy into electrically energy
Generator
Opposite charges do this
Attract
Transfers a charge on contact
Conductor
Rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region
Electric Current
Multiple paths for the current to flow through; one goes out the others might not go out
Parallel Circuit
This machines contain sharp blades that when spun they then start spinning the generator. One is pictured below
Turbine
Example of static electricity
Nylon Clothes
Rubbing a Rod with a Cloth
Television Screen
Winter Wear
Photocopier
Rub balloon against your hair
Charged Comb
Example of a material that will transfer a charge on contact
Cooper wire, humans, water, etc
Example of an alternating current
Home and office outlets
Refrigerators, Dishwashers, and the like
Electric Motors
The following is an example of what type of circuit
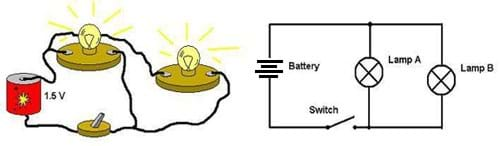
Parallel Circuit
We use both nonrenewable and renewable resources to spin a turbine. What is an example of each one
Nonrenewable: Oil, Gas, Coal, Nuclear
Renewable: Water, Wind, Sun
The name of the machine that she is touching
Van Der Graaff
Example of something that will not transfer a charge on contact
Plastic, rubber, paper, etc.
Example of a direct current
Cell phones
Flashlights
TVs (AC goes into the TV, which is converted to DC)
Hybrid and electric vehicles
This is an image of what kind of circuit

Series Circuit
Explain the process of how you get electricity in your home. Give as much detail as possible starting with how the power plant generates electricity to how it ends up in your home.
1. A resources uses steam to move a turbine
2. The turbine spins a generator
3. The generator with its copper wire and magnets when spun creates an electrical charge
4. That charge is then sent to a transformer that turns up the voltage
5. It is then carried over long distances by transmission lines
6. Enters into a substation or neighborhood transformer where the voltage is turned back down
7. Distribution line carries the electricity to the house where another transformer may turn the voltage down again before it enters the house