A general term for electrical phenomena, much like gravity has to do with gravitational phenomena
What is electricity?
Any material that has free charged particles that easily flow through it when an electrical force acts on them.
What is a conductor?
This is the process responsible for the wood's sticking to the balloon

What is polarization?
This is stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object
What is potential energy?
An electrical device (in its simplest form, a pair of parallel conducting plates separated by a small distance) that stores electric charge and energy.
(Hint: this is similar to a battery)
What is a capacitor?
The study of electric charges at rest (not in motion, as in electric currents)
What is electrostatics?
A material that does not contain free charged particles and through which charge does not easily flow.
What is an insulator?
A molecule electrically polarized in its normal state (without the influence of an outside charge). H2O (water) molecules, for instance, are an example of this.
What is a dipole/electric dipole?
The picture on the left is an example of what kind of energy? The picture on the right?
Left: mechanical potential energy; Right: electric potential energy
Charge transferred in clothes in a clothes dryer is an example of...
What is charging by contact (friction)?
This is the fundamental rule that underlies all electrical phenomena (hint: it has to do with particles)
Like particles repel, opposite particles attract
A material with properties that fall between those of a conductor and an insulator and whose resistance can be affected by adding impurities.
What is a semiconductor?
An aura of force that exists between things that are not in contact with each other - this can be gravitational or electrical, for example
What is a force field?
The energy a charged object possesses by virtue of its location in an electric field.
What is electric potential energy?
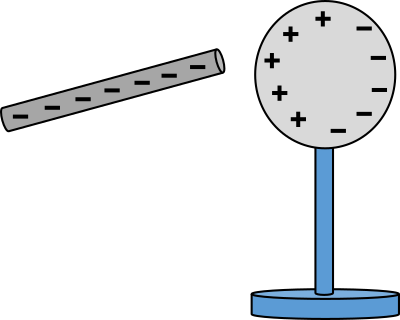
This is an example of . . .
(Hint: I'm not looking for polarization)
What is charging by induction?
"Electric charge is neither created nor destroyed. The total charge before an interaction equals the total charge after."
What is this law called?
Law of conservation of charge
The redistribution of electric charges in and on objects caused by the electrical influence of a charged object close by but not in contact.
What is charging by induction (induction)?
This is the process where positive and negative charges within a neutral object separate slightly due to the influence of an external electric field.
What is charge polarization?
This is the unit of electric charge. One of these is equal to the total charge of 6.25 X 10 ^18 electrons.
What is a coulomb (C)?
What is charging by induction?
Atoms and ions are different for this reason
Atoms usually have zero net charge; ions have net charge - ions are positively or negatively charged
Metals are good conductors for this reason
Metals contain free charged particles
An aura surrounding charged objects—a storehouse of electrical energy.
What is an electric field?
The electric potential energy per unit of charge, measured in ____; often called _____.
The electric potential energy per unit of charge, measured in volts; often called voltage.
The nucleus of an atom is _____ charged.
positively