This is the operating voltage for most household appliances in the United States.
120V
Describe the charges in this representation of an electrical field.
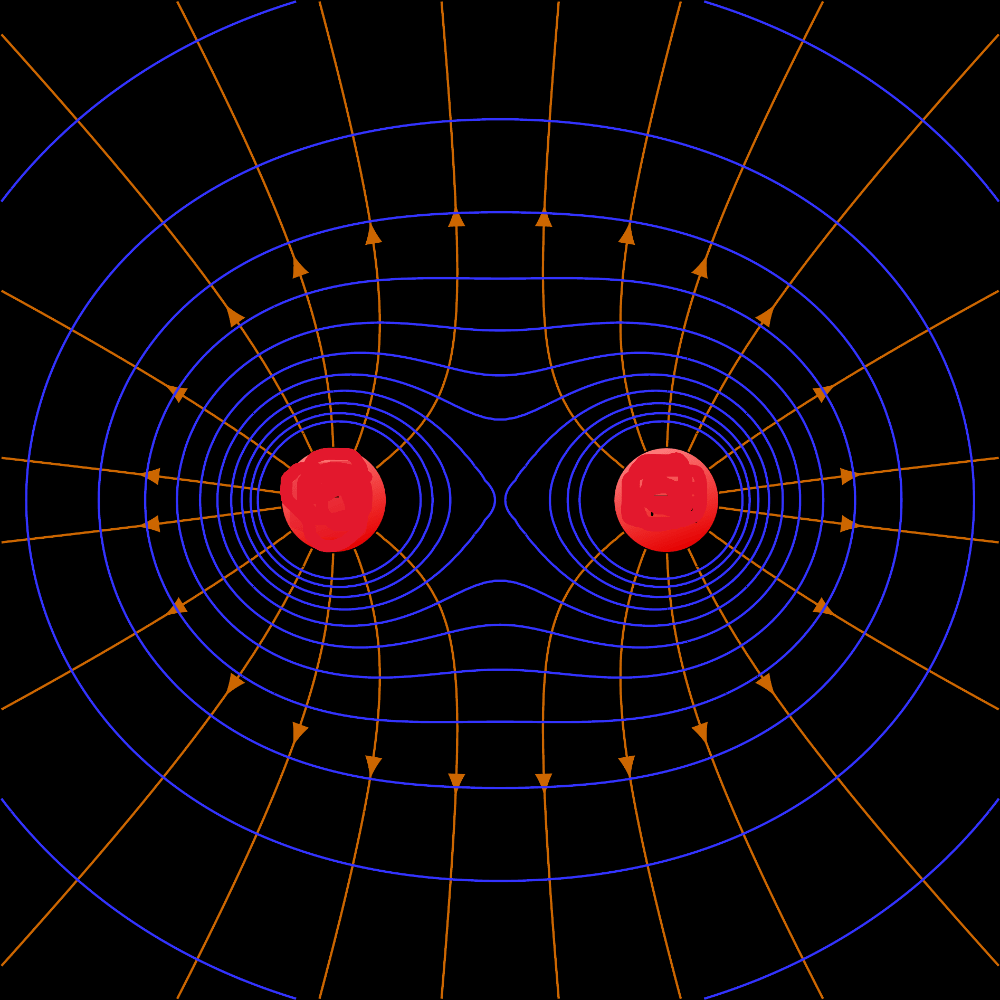
like charges, either both positive or both negative
This device acts as an electromagnet when electric current passes through loops of wire and creates a magnetic field.
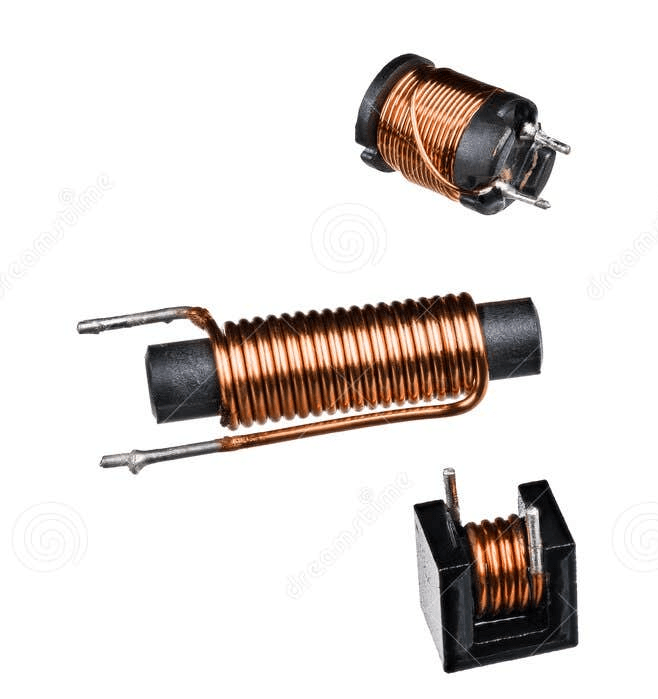
solenoid
This angle is equal to the angle of reflection.
angle of incidence
This occurs when one object's vibrations match the vibrations of another object and thereby intensify a sound; such as a tuning fork over a bottle.
resonance
This symbol represents this electrical part in a circuit that are used to control current and/or voltage in the circuit.
resistor
This instrument uses electrostatic induction to detect electric charge.
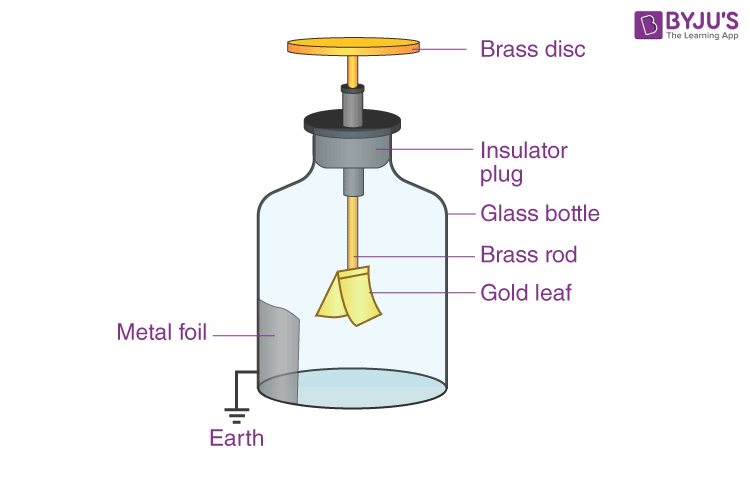
electroscope
In this device, the polarity of a stationary magnet switches, to attract and repel the fixed magnets on a rotor, causing the rotor to spin.
electric motor
If you are nearsighted, you may need this kind of lens to correct your vision.
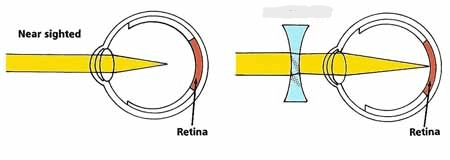
concave
This bending of light is why the moon will appear orange during the lunar eclipse on Friday morning.
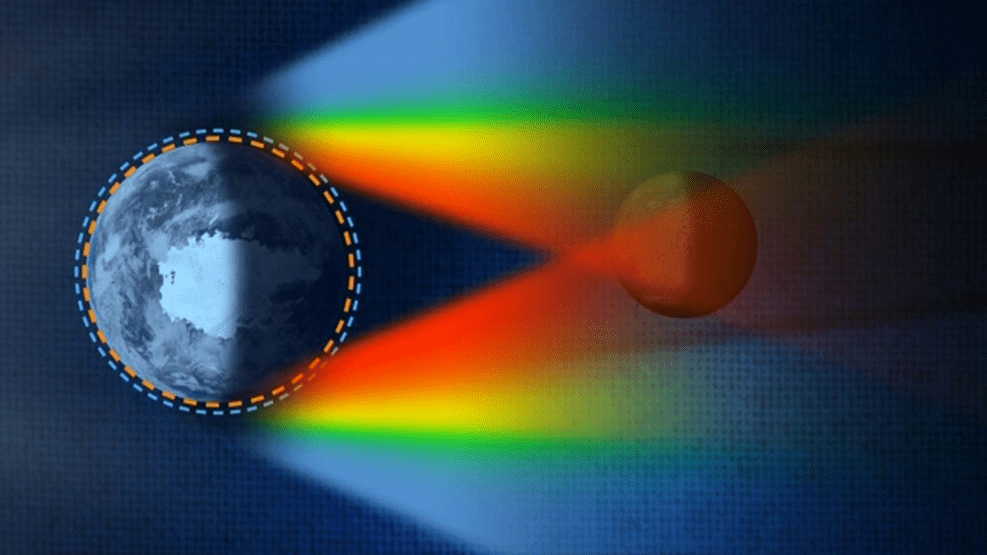
refraction
This is the inventor who invented the first chemical battery in 1800.
Alessandro Volta
Magnetic declination describes the difference between these two north poles.
magnetic north and geographic north
These electromagnets are made from materials that do not lose any energy as heat, making them useful for MRI machines and magnetically levitating trains.
superconducting magnets
Sunglasses that block UV rays have low this for that wavelength of light.
transparency
Sound waves are this type of wave.
longitudinal or compression wave
The relationship between current, voltage, and resistance is described by this law.
Ohm's Law
This device is used for storing electrical charge and electrical energy, and in a circuit, is usually placed in series with a resistor and a battery.
capacitor
Moving a magnet inside a coil of wire to create an electric current produces this phenomenon.
electromagnetic induction
This point (in red) is the point through which all rays that were parallel going into the mirror pass, after they are reflected by a spherical mirror.
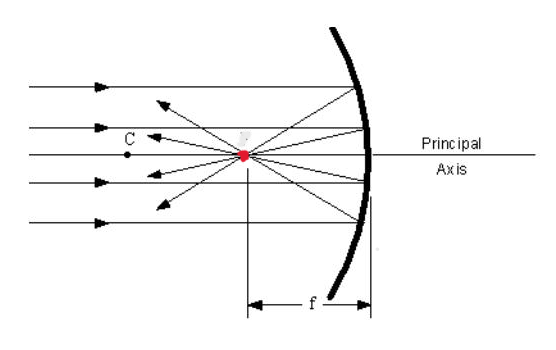
focal point
This property of waves allows them to bend around obstacles.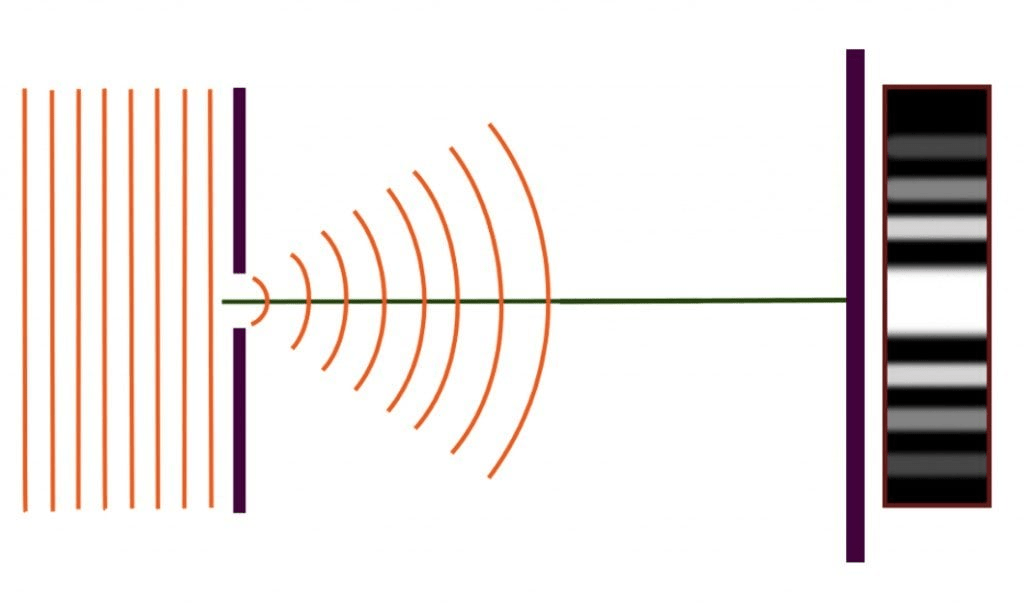
diffraction
This law says that the total amount of electrical current entering and leaving a junction of a circuit must be equal.
Kirschhoff's current law
The reason you are safe inside a car during a lightning storm is NOT because of the rubber tires, but because the metal shell of the car acts as this device, redistributing electric charges around the exterior, so that the interior remains safe.
Faraday cage
According to the right hand rule, where is the north pole of this electromagnet?
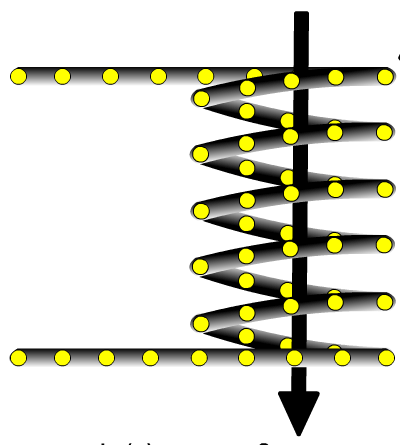
at the bottom
If you move 4 times the distance away from a light source, the light intensity will decrease by this much.
16 times
This process, in which the crests and troughs of inverse cancel each other out, is what makes noise canceling headphones work.
destructive interference