The way of wiring components so the current must split up and flow through one or the other.
What is parallel?
A measuring device that ideally has zero resistance
What is an ammeter?
This is the unit for potential difference. It is equivalent to J C-1
What is the volt?
This is a type of material that does not allow charge carriers to flow.
What is an insulator?
The device that dissipates electrical energy as thermal energy due to collisions of the charge carriers.
What is a resistor?
The rate of flow of electric charge. It is a vector quantity.
What is electric current?
This type of electric cell can be recharged.
What is a secondary cell?
This the unit for electric field strength.
What is N C-1 or V m-1?
The work done per unit charge to move charge completely around a circuit.
What is emf or electromotive force?
The name of the insulating material placed between the two conductive plates of a capacitor
What is the dielectric?
The ratio of potential difference across to the current flowing through a conductor?
This is a type of circuit that outputs a fraction of the input potential difference.
What is a potential divider?
The unit of electric current multiplied by time in its honorary form.
What is the coulomb?
The ratio of electric charge on one side to the potential difference across both.
What is capacitance?
This is a device that has a proportional relationship between the potential difference across it to the current flowing through it provided the temperature remains constant.
What is an ohmic device?
This is the law that electric charge comes in a smallest size package, the elementary charge (e).
What is the quantization of electric charge?
The symbol is this:
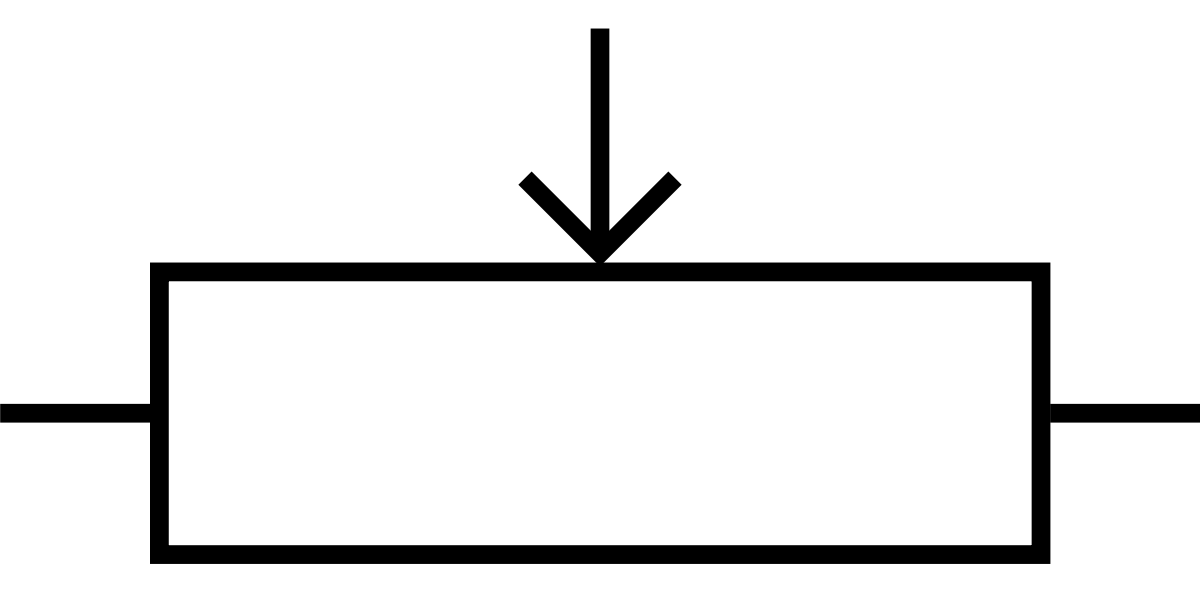
What is a potentiometer?
The unit for capacitance times resistance in its fundamental form.
What is the second (s)?
This is the constant that describes the ease of the electric field in a vacuum. It is used to calculate the effect of a dielectric on capacitance.
What is the permittivity of free space or a vacuum.
What real cells have that causes the potential difference available to the external circuit to be lower than the EMF when a current is flowing.
What is internal resistance?
This is the percent to which a fully charged capacitor is discharged to in one time constant (t=RC).
What is 36.8%?
The electric field between these is uniform in strength (but not really at the edges).
What are two oppositely charged parallel plates?
The unit for k, coulombs constant.
What is N m2 C-2?
The work done per unit charge to move a positive test charge from infinity to a point in an electric field.
What is electric potential?
The change that is made to this circuit to cause the lamp to dissipate more power.
What is decrease the resistance of the variable resistor?
(or decrease the temperature)