What is an insulator?
Electric charge can be positive or negative: true or false?
What is true?
the flow of electricity will always moved from the ______ pressure area to the _______ pressure area.
What is high to low?
this is a circuit with multiple paths for current to follow.
What is a parallel circuit?
The unit for voltage difference.
What are volts?
A material which does allow electrons to move easily.
What is a conductor?
according to this, electric charge cannot be created nor destroyed.
What is the Law of conservation of charge?
the net movement of electric charge in a single direction.
What is electric current?
this is a circuit with only one path for current to follow.
What is a series circuit?
Lightning is an example of what type of electric exchange?
What is static discharge/ static electricity?
This is the accumulation of excess electric charge on an object.
What is static electricity?
Opposite charges attract and like charges _______.
What is repel?
This type of current is typical in a device powered by a battery.
What is direct current (DC)?
This is an example of a 
What is a fuse?
The units for current (I).
What are amperes (amps)?
This term describes the method which provides a path for a charge to follow so that it prevents a build up of a charge (similar to the pole on top of some buildings to transfer lightning strikes safely to the earth).
What is grounding?
This type of charging happens by the transfer of charge between two objects that are touching.
What is charging by contact?
This type of current is typical in an outlet.
What is alternating current?
the formula for electric power
what is ELECTRIC POWER (watts)= Current (amps) x Voltage difference (volts)?
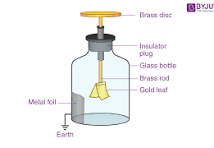 This is an image of one.
This is an image of one.
What is an electroscope?
This is related to the force that causes electric charges to flow.
What is a voltage difference?
This type of charging is the rearrangement of charge in an object due to the influence of another charged object nearby.
What is charging by induction?
the formula for Ohms law
What is current = voltage difference / resistance?
the formula for electrical energy.
What is electrical energy (in kWh)= electrical power (in kW) x time (in h)
What are ohms?
a closed path that an electric current follows
What is an electric circuit?
What is an electric field?
Answers will vary must include the following: carbon rod, paste, chemical reaction, and circuit. Example, "the battery's carbon rod completes the circuit, the electrons are transferred between some of the compounds in a chemical reaction within the paste. The carbon rod becomes positive and the electrons accumulate on the zinc, making it the negative terminal. The voltage difference between these two terminals causes a current through a closed circuit."
The number of volts are typical in an American outlet.
What is 120 v?
AC and DC stand for this.
what is alternating current and direct current?