The unit for wavelength
What are meters
The number of valence electrons an atom generally needs to be considered "full"
What is 8
The longhand electron configuration for Germanium (Ge)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2
One of the many properties of metals
What is good conductor of heat and electricity, malleable, ductile, and lustrous (shiny)
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion
What is ionization energy
The variable that increases along with frequency.
What is energy?
The total number of electrons a p-type orbital can hold
6
The Lewis Dot structure for Nitrogen (N)

The element that is not a member of the alkali metal family
What is Hydrogen
The element with the larger ionic radius out of the following: Al or P
What is P
The distance between two peaks of a wave
What is wavelength
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
Only 2 electrons can fill any given orbital and must have opposing spins
Identify the following orbital diagrams as correct or incorrect. If incorrect identify which rule is broken.
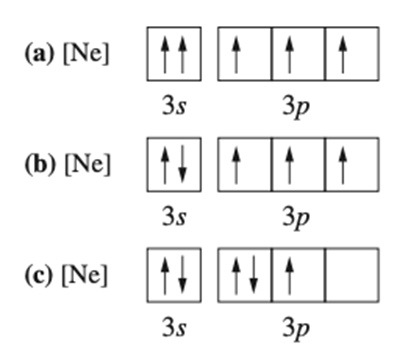
a) incorrect - Pauli Exclusion Principle
b) correct
c) incorrect - Hund's Rule
The element in group 8 and period 5
What is Ruthenium (Ru)
The element in the alkali metal family with the highest electronegativity
What is Lithium (Li)
The variable that increases as wavelength decreases according to the speed of light equation.
What is frequency
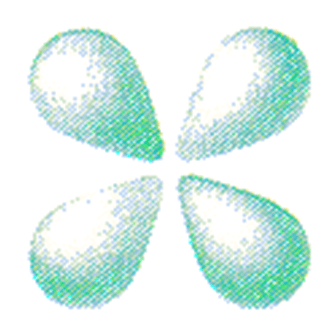
What is a d-type orbital
The noble gas configuration for the +1 ion of silver.
[Kr] 4d10
The family with a full valence shell
What is the Noble Gas Family
The following elements in order of increasing ionization energy: Mo, I, Rb, Ag, Sn, Zr
What is Rb, Zr, Mo, Ag, Sn, I
The energy of a photon whose wavelength is 527 nm
3.77 x 10-19 J
The number of electrons a half-full f-type orbital would hold.
7 electrons
The shorthand electron configuration, Lewis dot diagram, and shorthand orbital diagram of Vanadium (V)
[Ar] 4s2 3d3

What is the metalloid family
The following elements from smallest to largest: Cl, Ta, Zn, Ba, Si, Cr
Cl, Si, Zn, Cr, Ta, Ba
