(Airway)
(Airway)
In pediatric airways, what age cut-off is recommended for a needle cricothyrotomy instead of surgical cric?
<8-12 years old (also depends on size and anatomy of child)
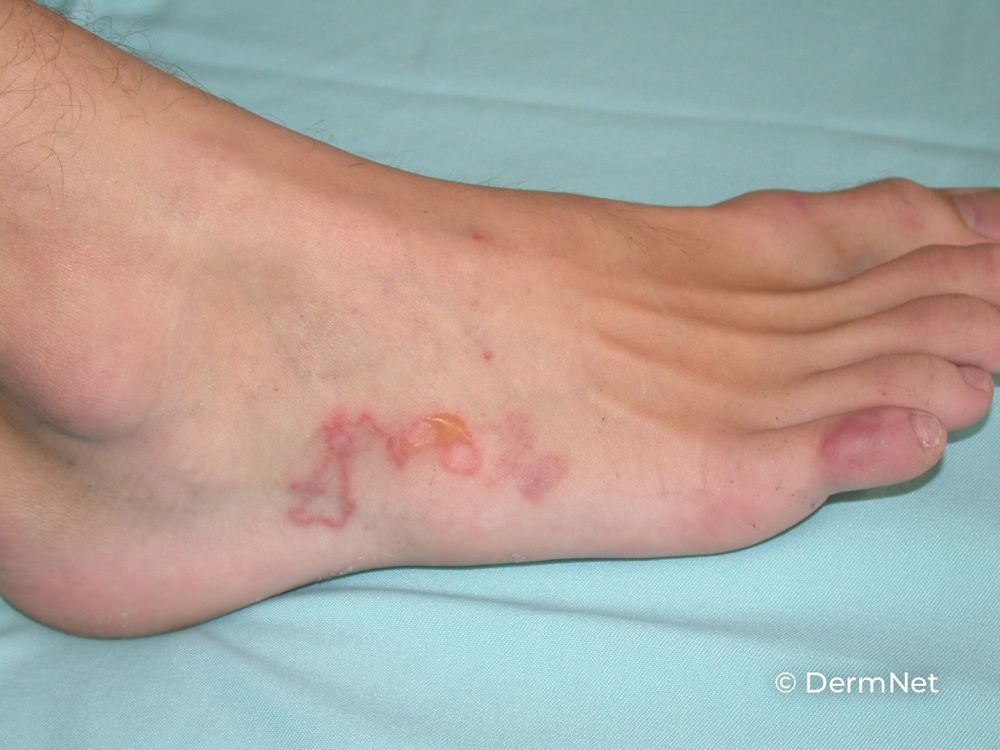
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
A 6-year-old child develops masseter rigidity, rising end-tidal CO₂, and tachycardia minutes after induction with succinylcholine. What is the first-line treatment?
Dantrolene
For acute MH crisis: 2.5 mg/kg IV rapid push, repeat every 5–10 minutes as needed until symptoms subside (up to 10mg/kg)
A patient presents with fever, altered mental status, and has a seizure in the ED. On chart review, this patient has HIV with hx of non-compliance on Biktarvy. What are your first-line treatments?
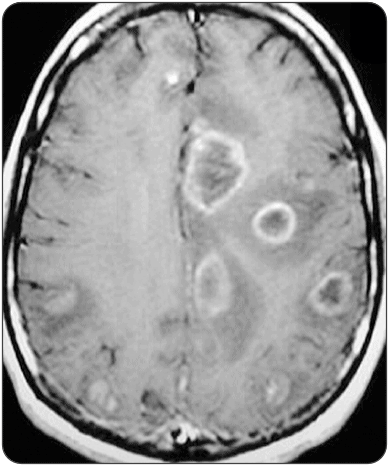
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis
Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine, co-administer with leucovorin to prevent pyrimethamine-induced hematologic toxicity
Florida man presents to your ED with a history of substance use. He states he is Ozzy Osbourne, caught a bat, and bit its head off. He is agitated, diaphoretic, tachycardic. Does not have the bat he decapitated but has blood remnants around his mouth.
What substance did he most likely ingest? What are your next steps?
Substance: PCP or synthetic hallucinogens (bath salts)
Next steps: Scene safety, ABCs, benzos, IV fluids, workup (labs, cardiac monitor, ...), assess for trauma, rabies post-exposure ppx (rabies vaccine series on day 0, 3, 7, 14, and immune globulin), TDaP
What is the equation to determine appropriate ETT size (cuffed tube)?
Age/4 + 3.5
Ex: 12/4 + 3.5 = 6.5
(For uncuffed: Age/4 + 4)

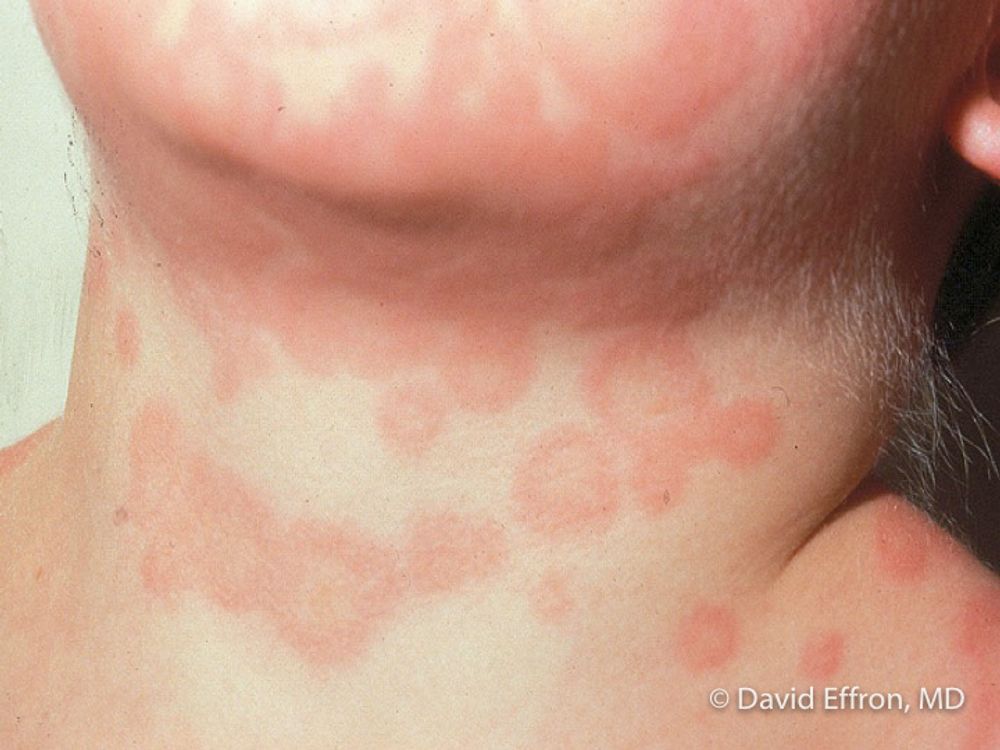
Erythema Multiforme
Skin or mouth lesions that have a pink-red center surrounded by a pale ring border and an outer pink-red ring. The lesions can sometimes be painful or itchy.
Patient has the following symptoms after having dinner at Locals Sushi Bar:
muscle weakness, paresthesias, vomiting, diarrhea, and reversal of hot-cold sensation
Ciguatera, caused by eating reef fish contaminated by a dinoflagellate, Gambierdiscus toxicus, which produces ciguatera toxin

77-year-old man presents with vision loss. He reports seeing flashes of light and then losing vision gradually. Denies pain. Visual acuity is 20/200 in the affected eye. Bedside ultrasound image shown below. What is the diagnosis?

Retinal detachement
Be aware of Mac on vs Mac off (the macula is located on temporal side relative to optic disc).. Mac on is emergent

A Florida man presents to your ED after being found unconscious as he surfaced from the water by bystanders on a boat. He is wearing scuba gear that he borrowed from his friend, although he has no scuba license. One minute later patient loses pulses and bystanders start CPR. (Answer 2 of the 3 questions for full points) What is the likely diagnosis? Is this an injury during descent or ascent from the dive? What is the best position for patient to be in while first responders resuscitate him?
Arterial Air Embolism
Injury from rapid ascent
Supine

Descent: Middle/inner ear barotrauma, sinus barotrauma, mask squeeze, dental barotrauma
At depth >100ft: Nitrogen narcosis (AMS)
Ascent: Pulmonary barotrauma, arterial gas embolism (AGE), pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, decompression sickness (DCA I "the bends" joint pain and rash, DCS II "the chokes, the staggers" neuro deficits), middle/inner ear barotrauma
In emergent intubation situations, who would most likely benefit from pretreatment with atropine?
Bonus 100 points for the dose (mg/kg)
Vagal-induced bradycardia from laryngoscopy is more pronounced in younger infants, so atropine can be considered for all intubations in children < 1 year of age. Succinylcholine can cause bradycardia in young children, so atropine can be considered in intubations using a single dose of succinylcholine in a patient < 5 years and in all children who need multiple doses of succinylcholine.

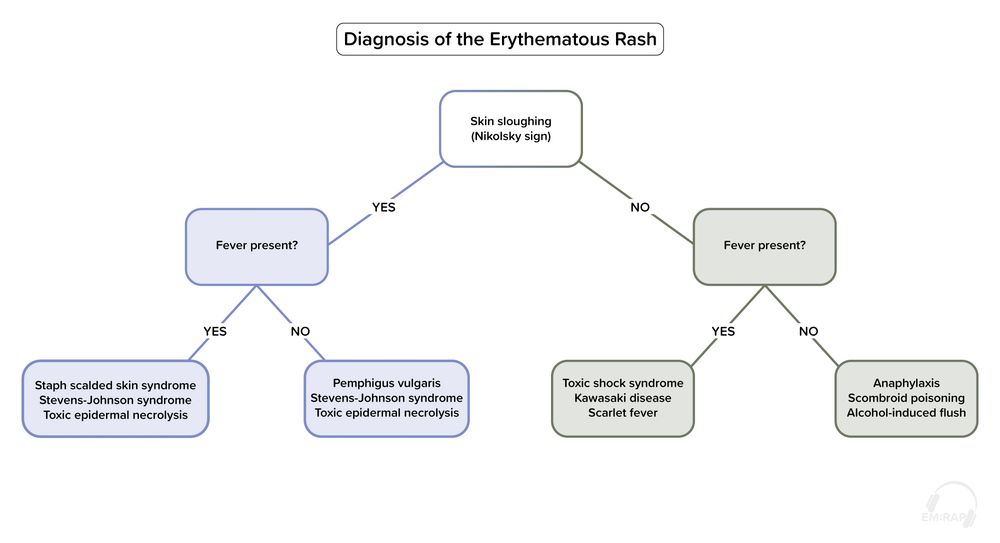
3 ddx for this erythematous rash:
+ Nikolsky sign
- Fever
*Hint for -100 points*
Pemphigus vulgaris
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
*Hint: also involve mucosa*
How to tell between NMS and serotonin syndrome?
(Tell me the exam findings they have in common and one that can tell them apart)
Both: AMS, hypertonia/rigidity, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension
SS: CLONUS
* Notes:
SS caused by SSRIs, MAOIs, TCAs, Amphetaminesh, St. John's Wort; tx: cyproheptadine
NMS caused by Antipsychotics (less frequently can also be caused by withdrawal from dopamine agonists like levodopa); tx: stop offending agent, benzos, or restart dopamine agonist if NMS caused by withdrawal of it
What is the name for this injury?
Galaezzi fracture-dislocation (Distal Radius fx with distal ulnar dislocation)

Florida man presents to your ED complaining of abdominal and rectal pain. He states that last night he did cocaine and chugged multiple Four Locos and does not really remember what he did afterwards. CTAP shows rectal foreign body which appears to be a hollow plastic tube.. next steps?
On rectal exam, you are able to feel this object but unable to retrieve it. If you tried without any meds, consider giving an anxiolytic to relax the patient. Or consider procedural sedation (preferably propofol) and can use rectal retractor/speculum. If this fails, call surgery.
(based on experience, not ITE related)
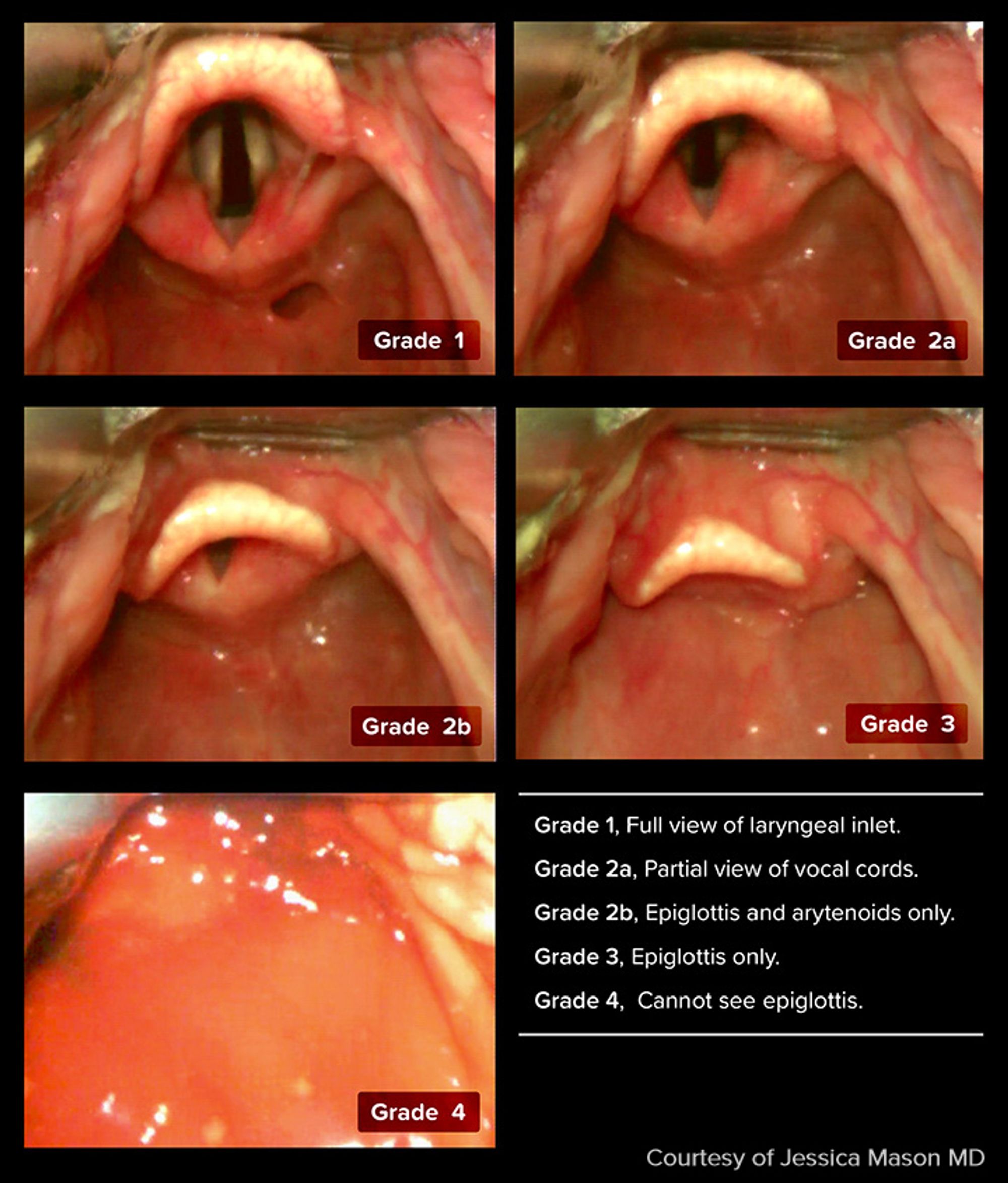
In the Cormack–Lehane system, what does a Grade III view represent?
Epiglottis only.
Which organisms are responsible for cause Type I vs Type II necrotizing fasciitis?
Type I: Polymicrobial: mix of gram-positive cocci, gram-negative rods, and anaerobes (common in diabetic pts)
Type II: Group A Strep (or MRSA) in healthy individuals.. can be caused by trauma/surgery
Less common:
Type III: Vibrio vulnificus (seawater exposure)
Type IV: Fungal (immunocompromised pts)
Which tox ingestion causes an anion gap metabolic acidosis + osmolar gap, can lead to renal failure, and is treated with fomepizole?
Ethylene Glycol
2nd line if fomepizole not available: ethanol infusion
Additional considerations: Thiamine (100mg IV daily) + pyridoxine , sodium bicarb , HD

What type of ankle fracture is this? What additional imaging needs to be obtained with this injury?
Bonus 100 points if you can name the additional fracture(s) that is/are associated with this

Weber C
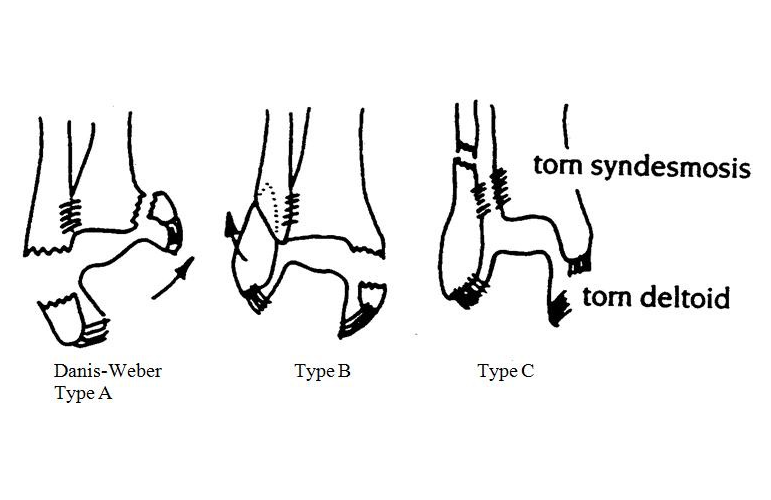
BONUS:
ALWAYS GET IMAGE OF PROXIMAL FIBULA, or else you'll miss Maisonneuve and Dupuytren’s fractures.
Maisonneuve and Dupuytren’s fractures are Weber C spiral fractures of the proximal third and middle third of the fibula respectively. Mechanism of injury: external rotation.

(Medial ankle injury with medial clear space widening associated with Masonneuve fracture.)
Florida man presents to your ED after a Miami EDM festival in July, he complains of dizziness, headache, nausea, muscle cramps, edema. His friend says he had a syncopal episode, no head strike. On exam, no head trauma, neurologically intact, vitals show tachycardia, hypotension, temp of 103F. What is the most likely dx?
Heat exhaustion

Congratulations.. you got a foundations style question
60-year-old male presents to the ED with a muffled voice, difficulty breathing, hemoptysis
Sxs occurring on and off for several months but more persistent over the past 3 weeks
Appears ill, pale, diaphoretic, respiratory distress, inspiratory stridor, towel in hand with bright red blood
HFNC, 2 large bore IVs
1g IV TXA, 500mg neb TXA given to temporize bleed
10mg IV dexamethasone
fentanyl, zofran
Neb rac epi
No blood thinners
VS improved, respiratory status improved, bleeding slowed down
go with pt to CT
extensive drinking and smoking hx
on CT hypo pharynx is extremely narrowed due to mass
AWAKE INTUBATION. No paralytics! Use ketamine or dexmetetomadine
video intubation won't be successful due to blood and even DL is high risk for making this friable mass bleed more. fiberoptic intubation would also be tricky due to how narrow the space is, the ETT will likely get stuck or make the mass bleed more. Bagging the patient won't be useful. Supraglottic airway also useless.
While in the ER, had extremely close monitoring with preparedness to do emergent surgical cric at any given time. But they got him to the OR in time for an emergency awake tracheostomy with light sedation
Name palpable (2) vs non-palpable (3) petechial rashes in a febrile/toxic patient
Palpable: Meningococcemia, RMSF
Non-palpable: DIC, Endocarditis, TTP

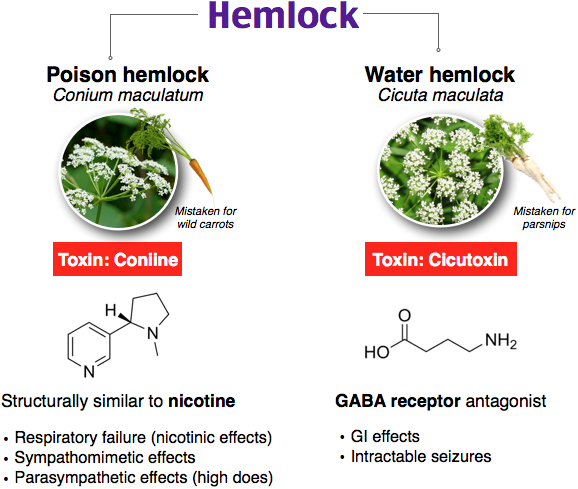
A patient presents to the ED via EMS after a suicide attempt. EMS deny any drug paraphernalia around him, patient only had a cup of tea on the table next to him. He is diaphoretic and anxious. Vitals are 99.5°F (37.5°C), BP 135/85, HR 110, RR 12, SpO2 99% on room air. Pupils are 4 mm and ERRL. EKG only shows sinus tachycardia. He suddenly develops generalized tonic-clonic seizure-like activity.
Which of the following is the most likely cause?
Foxglove, Hemlock, Oleander, Juniper
Hemlock (see below)
Foxglove and Oleander: cardiac glycosides similar to digoxin. Toxic effects are similar to digoxin toxicity, including cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension, and cardiogenic shock.
Juniper: herbal medication often used to treat urinary tract infections and kidney stones. It causes kidney toxicity in overdose.
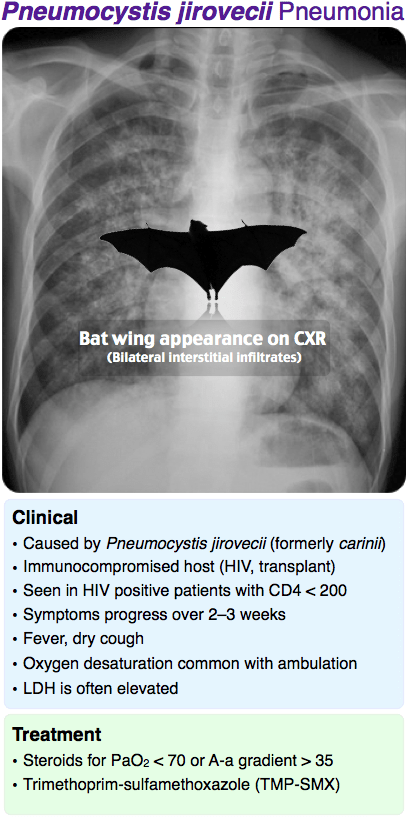
Patient with hx liver transplant (on immunosuppressants) presents to the ED due to worsening dyspnea, fever, dry cough for the past few weeks. You get a CXR and CT Chest:

A and B are images before treatment, C and D are images after treatment. What was/were the treatment(s) that was/were given?
This is Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP/PCP)
Treatment: TMP-SMX (steroids if PaO2<70 or A-a gradient >35)
A Florida man presents to your ED with burning pain of right arm and chest after attempting to catch a pretty sea creature that reminded him of his ex-girlfriend.

What are 3 things from the options below that should be avoided?
Freshwater, urine, ice, heat, alcohol, 4-5% acetic acid/vinegar solution
Freshwater, urine, ice, heat, alcohol, 4-5% acetic acid/vinegar solution
Avoid treating with fresh water, alcohol, methylated spirits, or urine as these have shown to increase nematocyst firing.
4-5% acetic acid/vinegar solution should be applied to the injured area for at least 30 seconds. For minor envenomations ice recommended but heat may actually work better.

