What is the first-line class of medications for OCD?
SSRIs
(or TCAs with CBT)
A patient presents combative with HTN and tachycardia. Admits to smoking crack. First line treatment?
Benzos
Describe the symptoms of opiate withdrawal.

Which is more likely to indicate an organic etiology over primary psychosis for the patient's symptoms: visual or auditory hallucinations?
Visual hallucinations → think delirium, drug intoxication, or withdrawal, not primary psychosis.
What is the (mostly) pathognomonic exam finding for serotonin syndrome?
Myoclonus
QT interval prolongation and the development of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (torsades des pointes)
What is the first step in management of a combative or aggressive patient?
Verbal de-escalation
A patient who has been chronically taking oxycodone was found unresponsive. EMS administered Narcan in route. He arrives with BP 200/100, HR 122, diaphoretic, and agitated. What is the best medication to alleviate his symptoms?
Clonidine
Alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that may be administered to blunt some opioid withdrawal symptoms, such as tachycardia, hypertension, anxiety, restlessness, and dysphoria.
A 14 yo F p/w her parents due to their concern for anorexia. Over several months, she has reported loss of appetite and has had a 20 pound weight loss. She has thin hair and is sweating, saying she always feels hot. Vitals notable for HR of 120. Her parents would like her evaluated by psychiatry. Which two tests are most likely to change ED management/disposition?
Pregnancy test, TSH
Which SSRI is most likely to precipitate SSRI withdrawal and why?
Paxil (paroxetine) - shortest half-life, metabolized quickly, and lacks active metabolites
23 yo w/ h/o substance use disorder pp/w 7 months of feeling on edge, difficulty concentrating, muscle aches, & intermittent palpitations with episodes of derealization and feeling dizzy. Exam and labs are unrevealing. Which class of meds are the best first-line agents to treat the most likely disease?
Serotonergic antidepressant (SSRIs/SNRIs)
35 yo F p/w diffuse abdominal pain, fatigue, & intermittent headaches. Has 6+ ED visits over the past 8 months with similar concerns, including chest pain, joint pain, & nausea. Extensive workups, including CTs, labs, EKGs/stress tests, have been unremarkable. She says symptoms significantly interfere with her daily life and job performance, & she would really like an answer this time. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Somatic symptom disorder

What distinguishes delirium tremens from simple alcohol withdrawal?
Time of onset and agitation/hallucinations
Withdrawal = onset 6–24 hr after last drink; tremor, anxiety, tachycardia, hypertension
Delirium tremens = 48–96 hr after last drink; agitation, hallucinations, autonomic instability
A patient with a fib on Eliquis p/w behavior changes. He lives alone and was last seen 3 days ago. His daughter is requesting psych evaluation due to verbal abusiveness. Which two studies are most likely to affect ED management/disposition and should be obtained.
CTH, UA
A patient p/w AMS. BP 80/40 and HR 180. EKG is shown. Best first treatment?

Sodium bicarb
TCA OD = sodium channel blockade
For each buzz phrase, give the diagnosis:
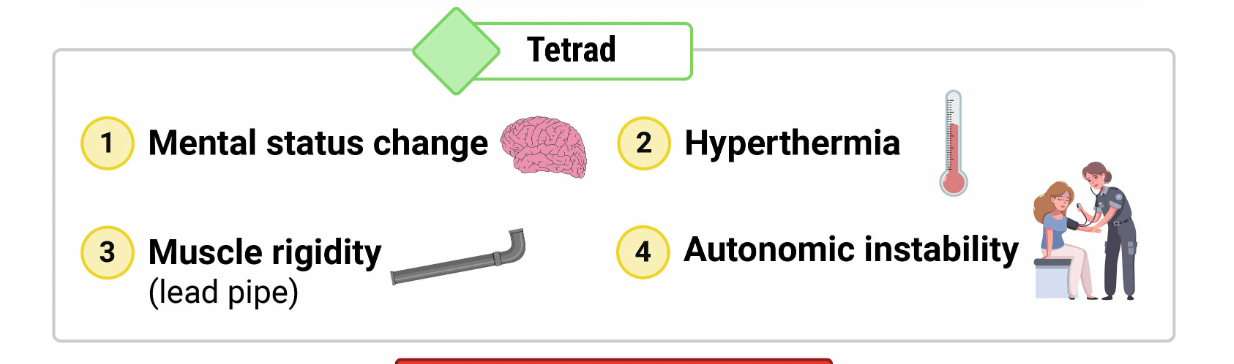
Lead-pipe rigidity
Hyperreflexia + clonus
Tremor + ataxia + confusion
Visual hallucinations + tremors + autonomic instability
Lead-pipe rigidity --> NMS
Hyperreflexia + clonus --> Serotonin syndrome
Tremor + ataxia + confusion --> Lithium toxicity
Visual hallucinations + tremors + autonomic instability -->DTs
Name one personality disorder for each of the clusters A-C.
A - odd/eccentric. Schizoid, schizotypal, paranoid.
B - dramatic/emotional. Histrionic, antisocial, borderline, narcissitic.
C - anxious/fearful. Avoidant, OC, dependent.
What is the correct order of dextrose and thiamine administration for alcoholics? Why?
Thiamine before dextrose
Alcoholics are already thiamine deficient. Administering a glucose load without sufficient thiamine dramatically increases the demand for the remaining thiamine stores as the brain begins to metabolize the sudden influx of glucose. This rapid depletion of limited thiamine reserves can trigger acute neurological deterioration, leading to cell death and the onset of Wernicke's encephalopathy/Korsakoff syndrome.
A patient with anorexia is boarding and awaiting placement. She suddenly develops SOB and pedal edema. Which electrolyte abnormality do you most expect to see?
Hypophosphatemia
Can lead to weakness, paresthesias, AMS, and decreased cardiac function, which may manifest as heart failure.

Pt with h/o bipolar disorder p/w vomiting. Vitals normal, but she is confused. Lithium level is 5.6 mEq/L and creatinine is 1.9. What is the best next step in management?
Dialysis

Describe the pharmacology of buprenorphine.
High-affinity partial mu agonist = binds tightly to the receptor, displacing or preventing other opioids from binding to it. It only has partial activity at this receptor, so does not give the same high, thus curbing overuse. If buprenorphine is administered to a patient who is actively intoxicated with opioids, it may displace the currently bound opiate and precipitate withdrawal.
Describe the difference between schizotypal, schizoid, and schizophrenia.
Schizotypal and schizoid = PDs.
Schizotypal = demonstrate eccentric behavior but maintain an overall firm grip on reality
Schizoid = doesn't desire relationships, demonstrates emotional coldness, indifferent to praise/criticism
Schizophrenia = >6 mo of psychosis, pt can't tell what's real or imagined
What is unique about phenobarbital's mechanism of action that makes it particularly effective in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal?
Inhibits glutamate receptors
The barbiturate phenobarbital differs from alcohol and benzodiazepines in that it uniquely inhibits the excitatory glutamate receptor, reducing agitation and seizure potential.
An 85 yo pt presents from geri psych unit with AMS. He is afebrile. His exam is notable for profound confusion and flushed skin. No focal deficits, nuchal rigidity, or trauma. Labs including UA and CTH are normal. What other information may yield this patient's diagnosis?
Med list
Name the tetrad of NMS.