Friends bring in a young high school student who is apneic and unresponsive. They tell you they were just ‘partying a little’ and their friend collapsed. Her vitals are as follows: HR 128, RR 4, BP 100/70, Temp 98F and O2 Sat 82% on room air. On physical exam, she is unresponsive with pinpoint pupils.
Opioids
Apnea
Hypoxia
Miosis
Unresponsiveness
Flash pulmonary edema (rare)
Antidotes
Pralidoxime and Atropine
Plant Sources of Toxicity
Jimson weed (Devil's trumpet)
Amanita mushroom
Sources of Toxicity Sympathomimetic Toxicity
Over-the-counter cold agents (containing ephedrine)
Street drugs (e.g., cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine, Synthetic cannabinoids, Bath salts)
illicit designer drugs (“ecstasy”)
Wintergreen
- Methyl Salicylates
A young college student is brought in by his friends after being found confused at a party. His friends tell you that he was just dumped by his girlfriend. His vital signs are as follows: HR 122, RR rate 18, BP 120/80, Temp 100.8F, O2 Sat 98% on room air. He is mumbling and picking at his clothes. On exam, his pupils are 8mm and his skin is flushed, although he is not sweating. You noted his bladder is full.
Anticholinergic
- Dry as a bone: anhidrosis (esp axillae, mouth)
- Hot as a hare: anhydrotic hyperthermia (may become severe w/ agitation)
- Red as a beet: cutaneous vasodilation
- Blind as a bat: nonreactive mydriasis (often delayed 12-24hr)
- Mad as a hatter: delirium; attention deficit; hallucinations; dysarthria; lethargy
- Full as a flask: urinary retention
- Tachycardia (HR 120-160) and decreased/absent bowel sounds
Sources of Toxicity
Organophosphates found in:
- Pesticides (e.g. malathion, diazinon)
- Chemical weapons (e.g. Sarin, nerve agents)
- medications (e.g. neostigmine, edrophonium)
Name 2 Medications That can lead to toxicity
- Atropine
- Lomotil toxicity
- Antihistamines
- Antidepressants
- Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) toxicity
- SSRIs
- Antipsychotics
- Muscle relaxants
- Anti-Parkinsonians
Treatments for sympathomimetic toxicity
sedation, hydration, and treatment of complications such as rhabdomyolysis and hyperthermia.
Fruity
- Ketoacidosis
- Isopropanol
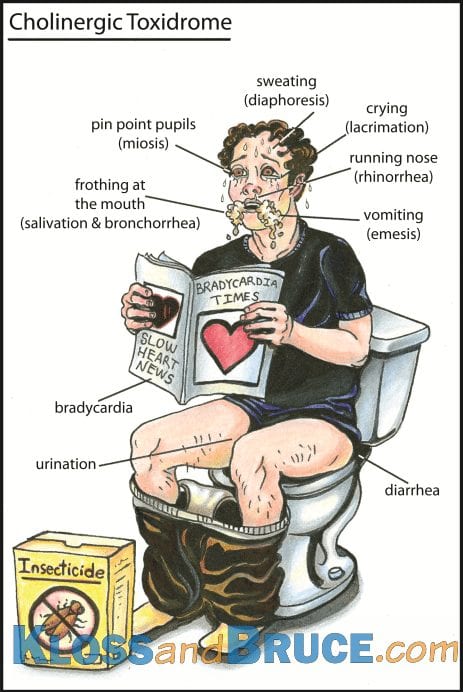
A migrant worker is found wandering on a deserted road. She is confused, sweating and wheezing. You notice that she has been incontinent. Her vitals are as follows: HR 36, RR rate 24, BP 100/68, Temp 98F, O2 Sat 96% on room air.
Cholinergic Toxidrome (organophosphate exposure).
- SLUDGE(M) = Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Diarrhea, GI pain, Emesis, Miosis
- DUMBELLS = Diarrhea, diaphoresis, Urination, Miosis, Bradycardia, Bronchorrea, Emesis, Lacrimation, Lethargic, Salivation
Patient with cholinergic toxicity presents in significant respiratory distress and requires intubation. This medication should be avoided. Why?
Succinylcholine should be avoided because it is degraded by AChE and may result in prolonged paralysis.
Why would you choose to use sedation as treatment option?
Sedation
- Decreases the risk of hyperthermia, rhabdo, traumatic injuries
- Benzos are agents of choice
- Repeat boluses every 5-15 minutes as needed to halt seizures and provide adequate sedation
What complication can be avoided with aggressive hydration in sympathomimetic toxicity
renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis
Bitter Almonds
Cyanide
Sources
- Weapon or intentional toxin
- Tobacco Smoking
- Foods: Fruits, seeds and pits
- Prunus Seeds (plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots and almonds)
- Lima beans
- Cassava plant roots (staple in some parts of world)
- Smoke Inhalation (Structure fires)
- Especially plastics (acrylonitrile)
- Industrial use Hydrogen cyanide
- Nitroprusside metabolite
Antidote: Hydroxycobalamin
- Can also use amyl nitrate or sodium nitrite but need sulfur donor also (i.e., sodium thiosulfate)
A young college student is brought in by EMS after becoming combative at a concert. He is very agitated with an altered mental status and requires restraints. His vitals are as follows: HR 138, RR 24, BP 154/92, Temp 101.2, O2 Sat 98% on room air. Physical Exam reveals mydriasis, flushed skin, sweating and agitation.
Sympathomimetic
● Tachycardia
● Hypertension
● Mydriasis
● Diaphoresis
● Hyperthermia
● Agitation
Nicotinic Effects of Cholinergic Toxicity
- MTWThF (days of week) = Mydriasis/Muscle cramps, Tachycardia, Weakness, Twitching, Hypertension/Hyperglycemia, Fasciculations, Seizures, Somnolent
When is Cholinesterase inhibition (physostigmine) indicated?
severe agitation or delirium (esp if unresponsive to benzos)
A 16 year old is brought to the ED after being caught getting "high" with inhalants in the locker room at school. On history, you find that he has chronically been abusing inhalents. What is the most severe acute complication and long term complication of inhalant abuse?
Acute = arrthymias Chronic = encephalopathy
Garlic
Mnemonic: TOADS-P smells like Garlic
- Thallium
- Organophosphate Toxicity
- Arsenic Poisoning
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
- Sulfur Mustard
- Phosphite
16 year old male is BIB EMS due to stumbling around as if drunk. He complains of coughing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. He denies alcohol use. He also complains of nausea, headache, dizziness, and lightheadedness. His BP is 136/80, irregularly irregular HR of 98, RR 26 , T 99.8. His sclera are moderately injected. There are mild expiratory wheezes but no rales. Frequent ectopic beats are noted. Soon after presentation, he has a seizure. Initial lab findings include a metabolic acidosis, hypokalemia, hematuria, and proteinuria. What ingestion is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Toluene
Chronic abuse "sniffing" of hydrocarbons such as toluene can cause cans DEPRESSION, CARDIAC DYSRHYTHMIAS, and distal tubular acidosis.
This can occur 24-96 hours after acute cholinergic crisis
Intermediate Syndrome
- Syndrome that occurs 24-96 hours after acute cholinergic crisis
- Proximal muscle weakness, cranial nerve palsies
- Can last for days - weeks
- May require mechanical ventilation
When is Cholinesterase inhibition (physostigmine) contraindicated?
- Contraindicated in QRS>100 or Na blockade signs (R' in aVR) and in narrow angle glaucoma
- Relatively contraindicated in asthma or ileus
What treatment is contraindicated in TCA toxicity and why?
Cholinesterase inhibition (physostigmine)
- associated with cardiac arrest
Gasoline
Hydrocarbons