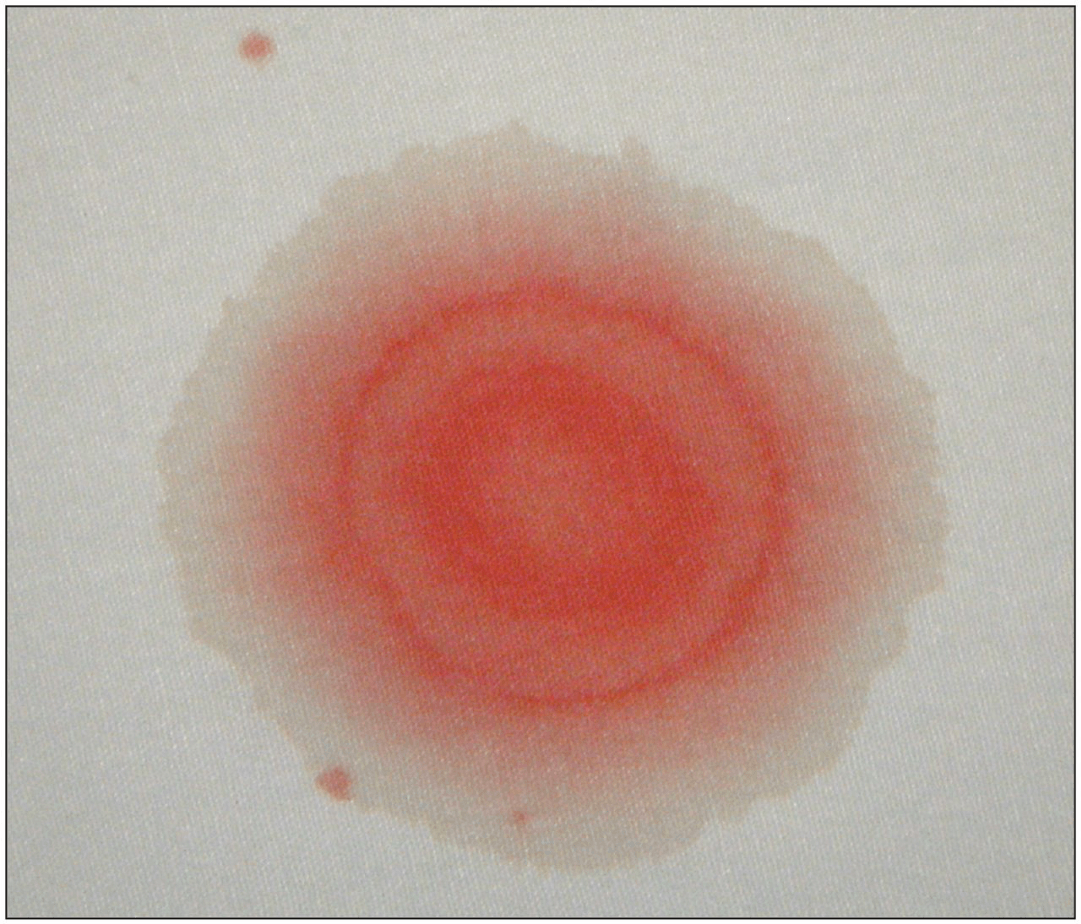
These two techniques are quick ways to determine a CSF fluid leak from the ear or nose.
What is the halo test or glucose check?
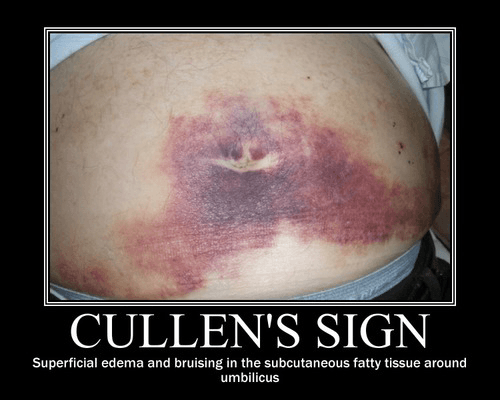
The largest solid organ holding approximately 13% of the human blood supply.
What is the liver?
The largest concern with significant facial trauma.
What is the airway?
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1pQpor9DtPVIBqPjZH9hTlgCLpaiv1KY8
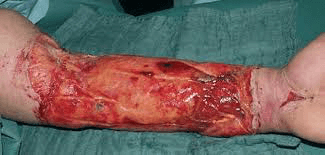
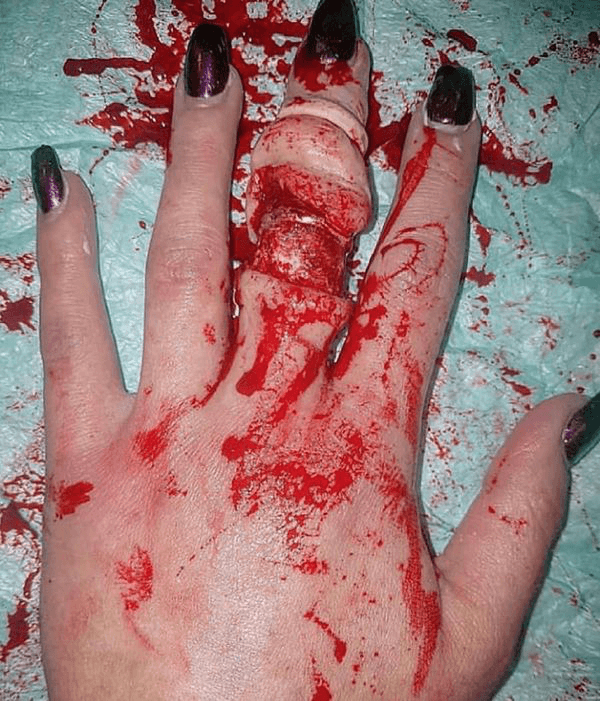
An injury in which soft tissue is completely tore off, or hanging by a flap.
What is an avulsion?
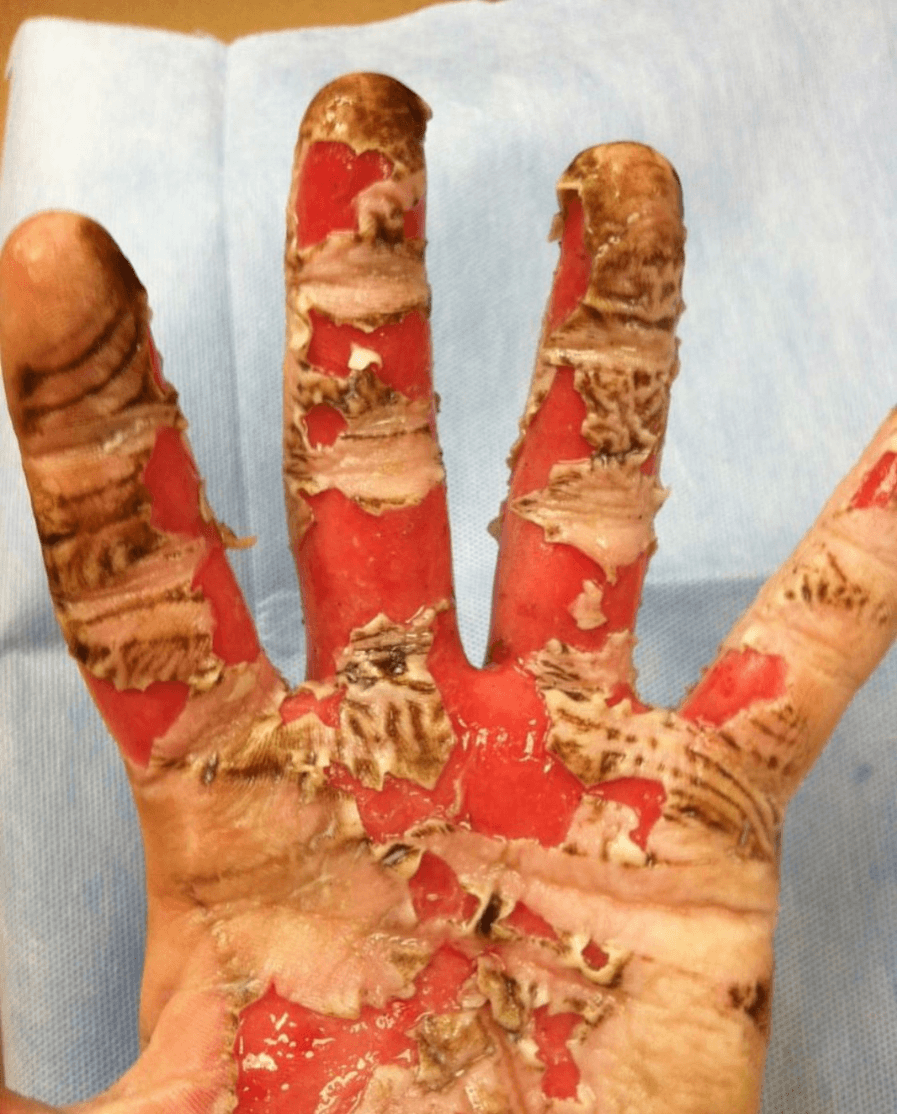
Four types of burns.
What are thermal burns, electrical burns, chemical burns, radiation burns?
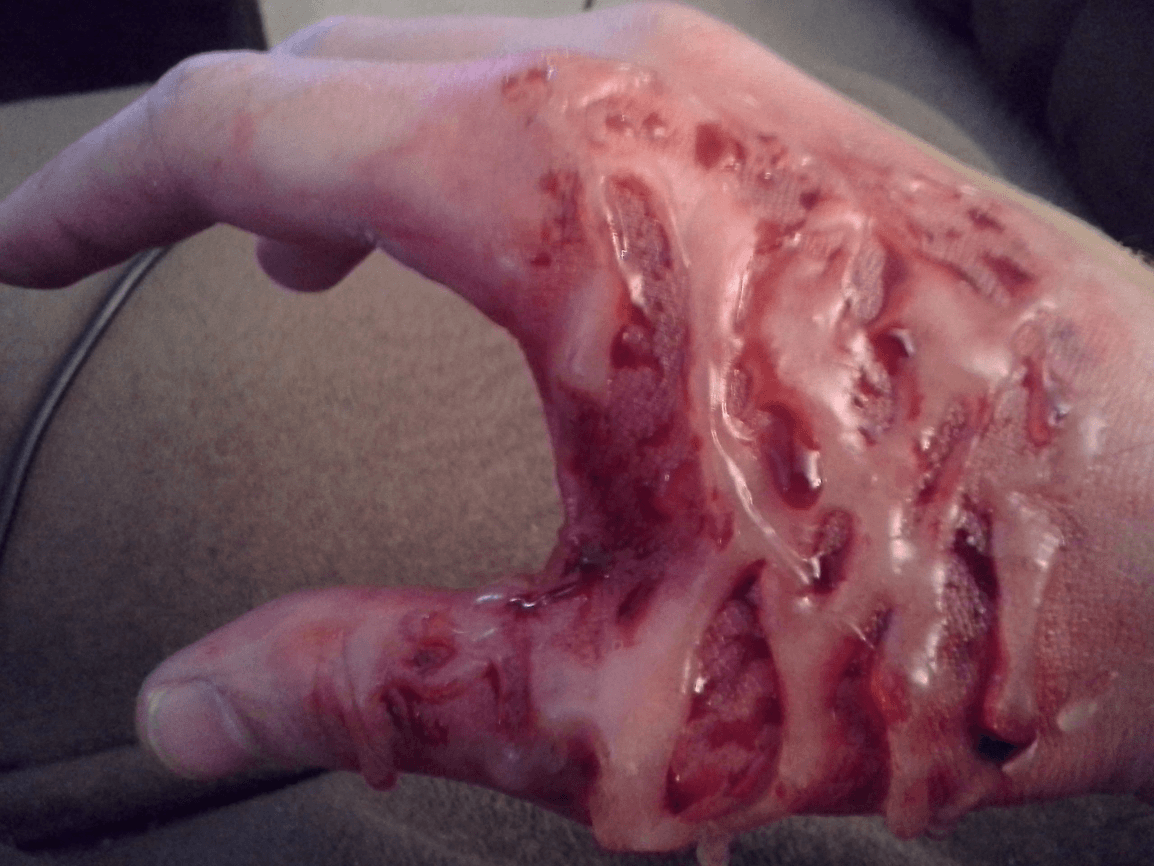
Alkali = liquification necrosis
This is when the anterior fontanel closes.
What is 10-24 months.
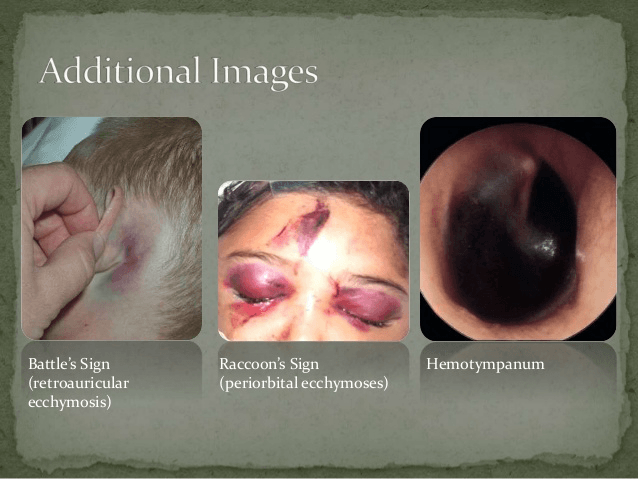
Raccoon eyes, battle signs, ottorrhea/rhinorrhea, and hemotympanum.
What is a basilar skull fracture?
I am Beck's Triad.
What are muffled heart sounds, hypotension, and JVD.
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1gu83vi6tIFQhy1JuQ7Lg00H4mpsdQBxq
Is a globe rupture a surgical emergency?
Yes!
Large risk for infection and permanent loss of vision,
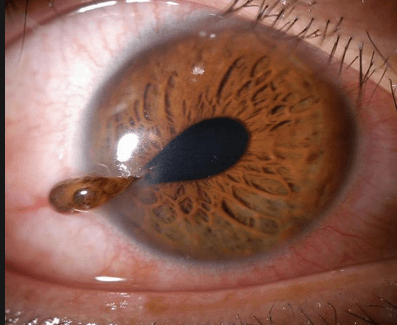
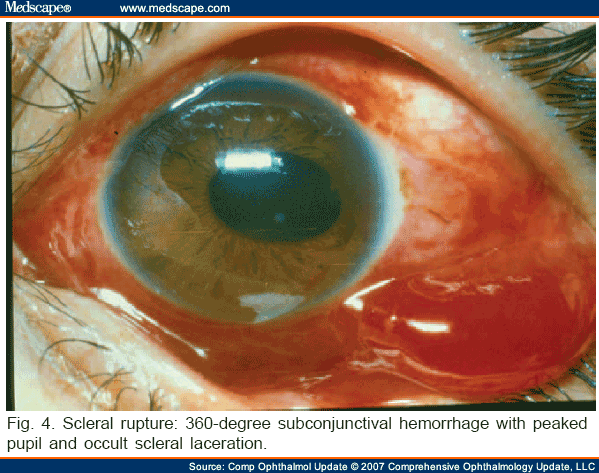
True or false?
If a tourniquet is applied, you will not feel a distal pulse.
False!
A tourniquet should be applied tight enough to stop the bleeding, it does not necessarily mean a distal pulse will not be felt.
What percentage of TBSA should we consider transportation to a burn facility?
What is greater than 15-20% TBSA.
In regards to hemorrhagic shock, this population compensates their blood pressure until they lose approximately 45% of their total blood volume.
What are pediatrics?
If the patient has transient loss of consciousness, we should be concerned for this.
(unconscious, alert, unconscious)
What is an Epidural brain bleed?
Arterial bleed, between the dura and the skull.
Contralateral motor deficit: Motor deficits/pupil fixation will be noted on the opposite side that the brain bleed is on.
What is a ruptured diaphragm?
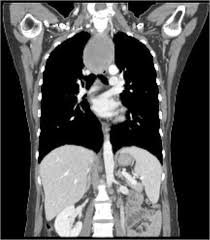
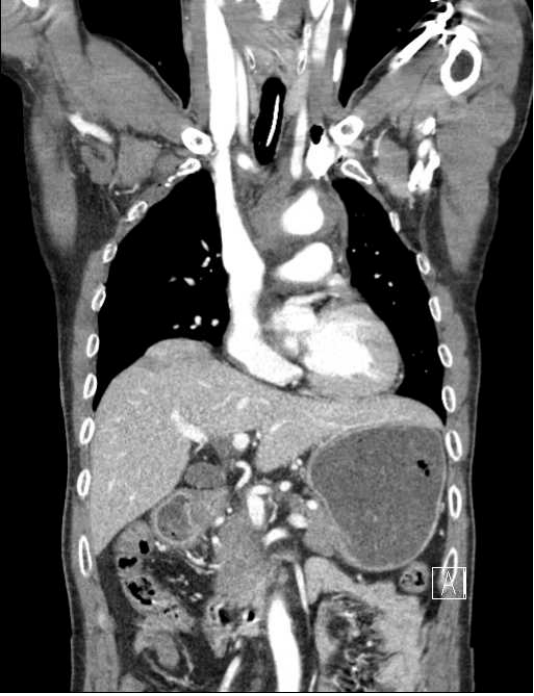
You are the EMS care provider for a patient in who was involved in a traumatic motorcycle accident without a helmet on. Pt is unresponsive but has a pulse at this time. As you perform your pupil check you witness the left pupil "blow." This is indicative of this type of injury.
What is brain herniation?
Uncal Herniation is a midline shift of the brain
Central herniation, the brain is trying to leave the skull through foramen magnum.
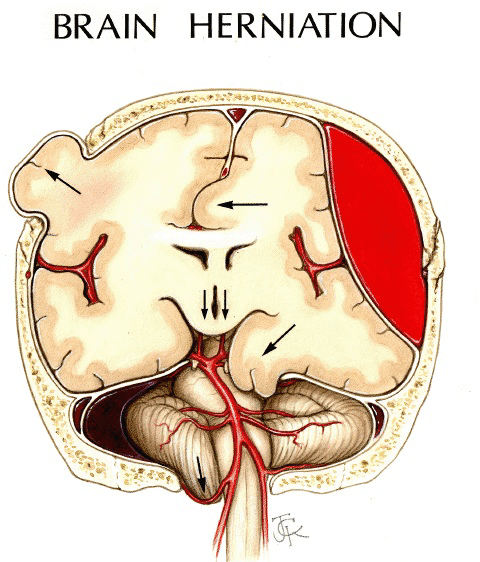
This should always be check for in any GSW patient.
What is an exit wound?
True or False?
AC current is more dangerous than DC current in reference to electrocution.
True!
AC is more dangerous as it causes tetany, which can result in the person tightening their grip on the source of electrocution.
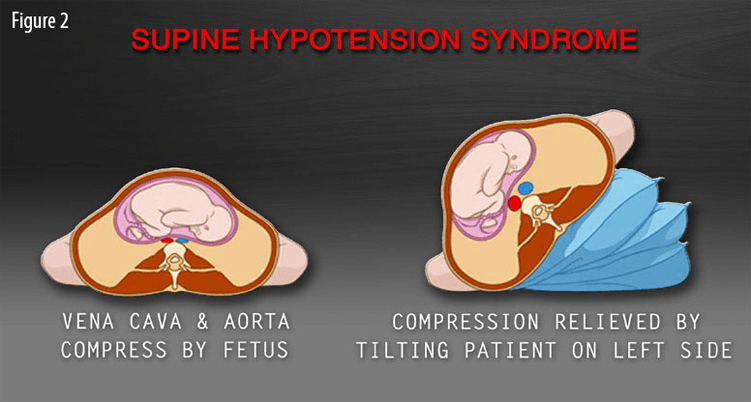
If a pregnant trauma patient is hypotensive while laying supine, doing this noninvasive intervention could improve circulation.
What is tilting the patient on her left side?
Describe the pathophysiology of Cushing's Triad.
Increased systolic blood pressure (also widened pulse pressure) to increase cerebral perfusion
Bradycardia due to a vagal response triggered by the cardiac baroreceptors
Abnormal or irregular respirations due to the respiratory center of the brain being affected by the increased ICP.
Pt involved in a high mechanism head on MVC. Pt exhibiting pallor, unequal upper extremity pulses, and crepitus over the first and second ribs on the left.
This is the likely phenomenon.
What is aortic disruption?
Most frequently seen in rapid acceleration/deceleration injuries.
75-90% mortality rate on scene.
This is the position that the patient should be in with any type of significant eye injury.
What is raising the head of the cot to approximately 30 degrees?
In a traumatic PNB, the patient's EtCO2 is reading 24 mm Hg. This is simple intervention to attempt to normalize this EtCO2 reading?
What is warming the patient?
Ex: Warmed IV fluids, blankets, increase ambulance temperature.
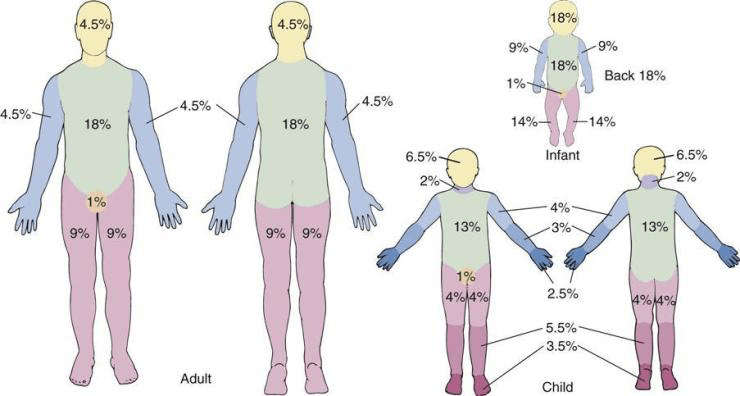
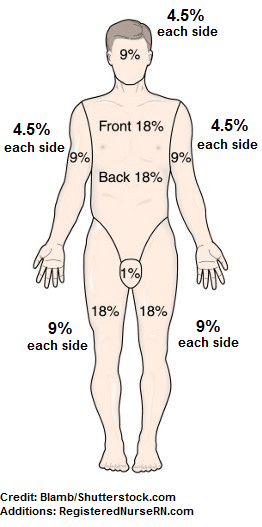
The percentage of TBSA burned with burns noted to the entire RUE, chest, and abdomen.
What is 27%?
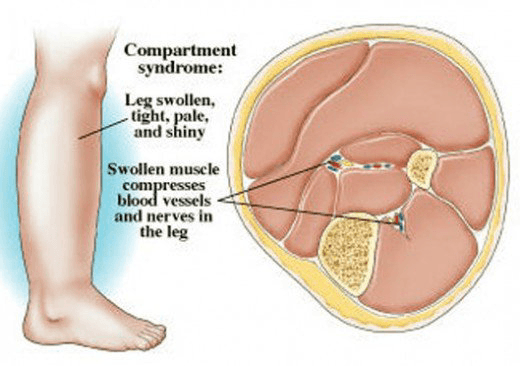
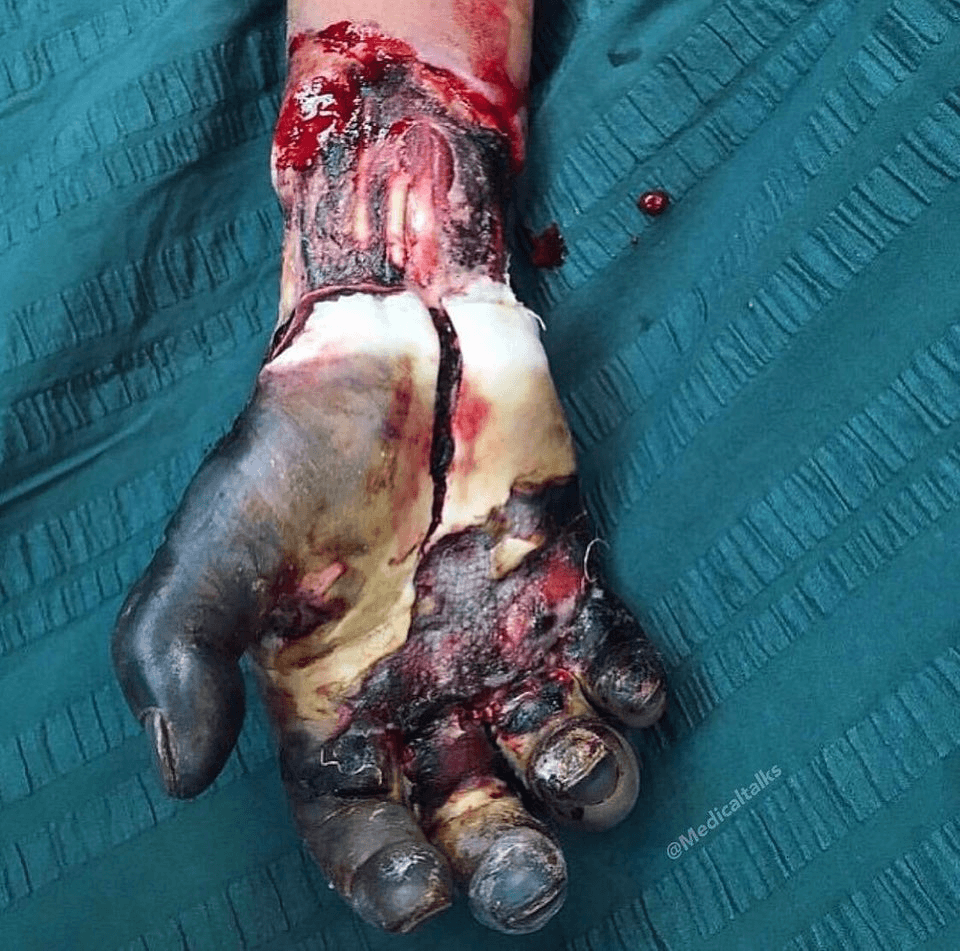
What is compartment syndrome?