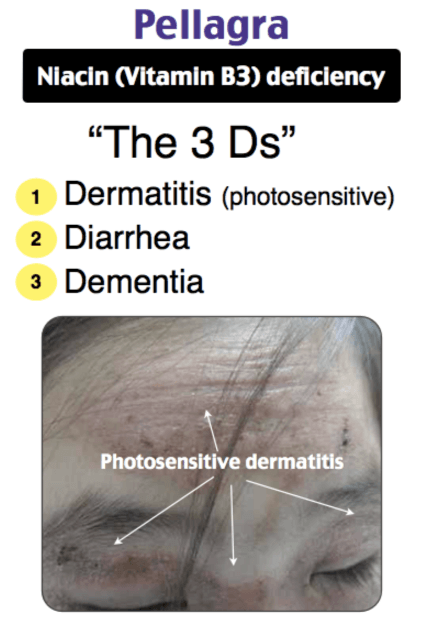
Dermatitis, Dementia, and Diarrhea oh my! This is a vitamin deficiency to cause all three!
Niacin deficiency
-----------
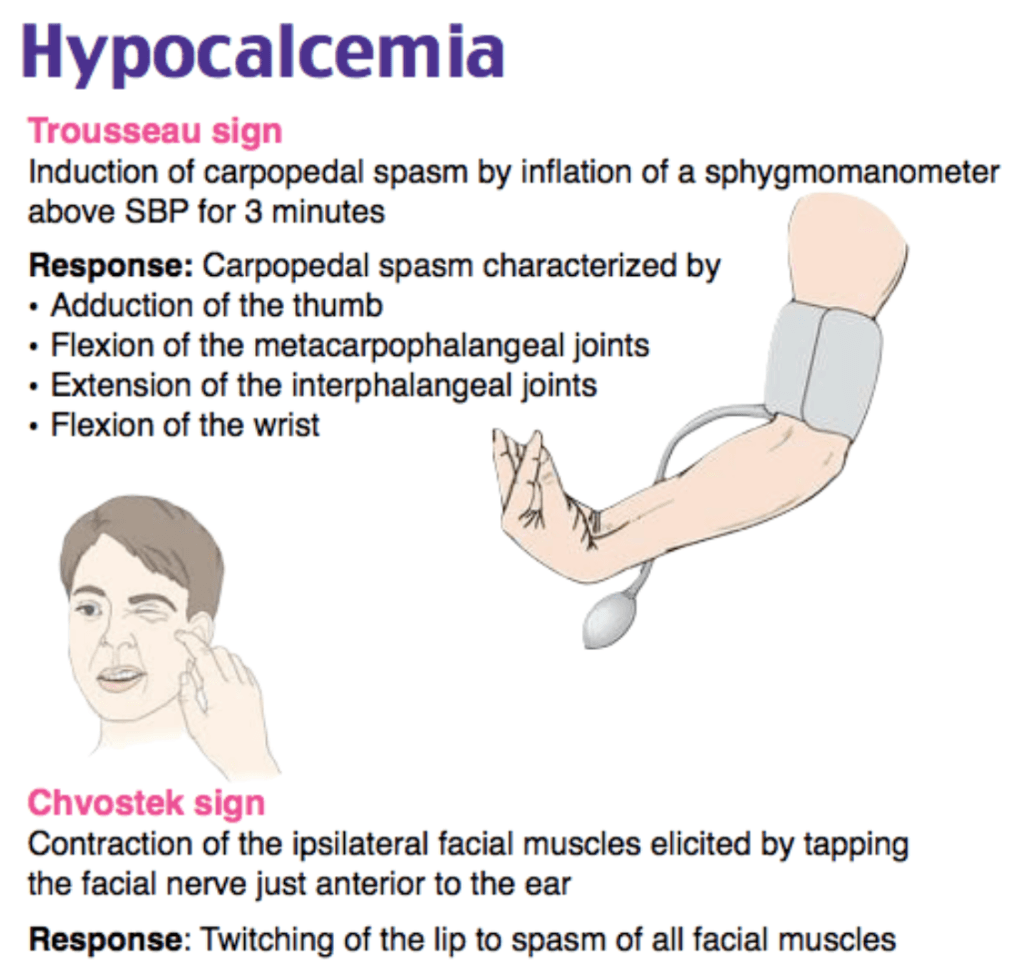
This is the lab abnormality most commonly seen with Chvostek sign.
Hypocalcemia
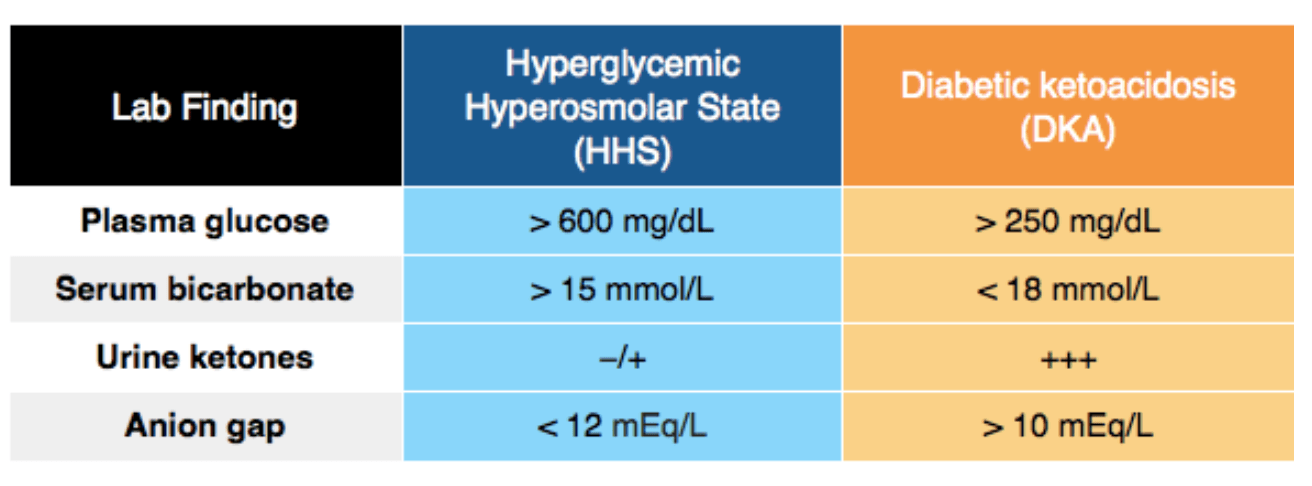
Blood glucose for DKA vs HHS diagnosis
DKA >250 mg/dL
HHS >600 mg/dL
Initial starting dose for insulin therapy in DKA/HHS
0.1 units/kg/hr
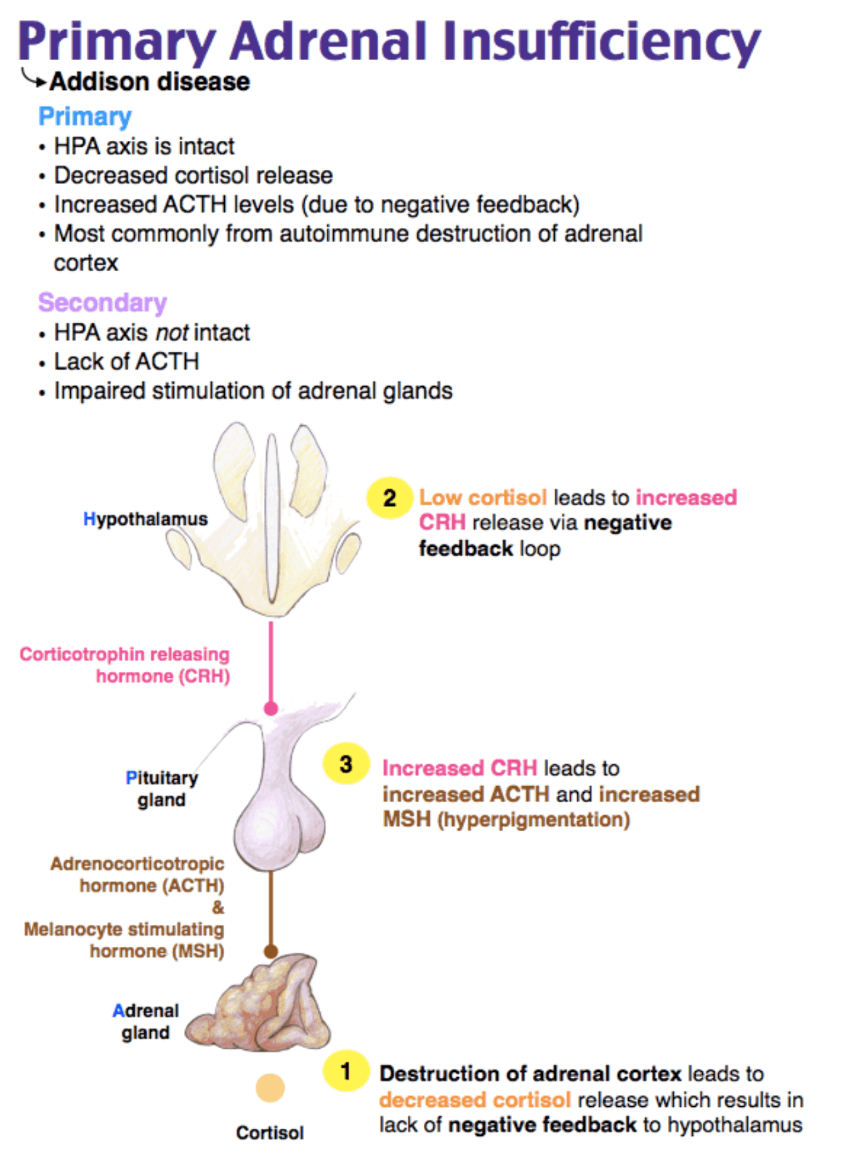
This is the most common cause of acute adrenal crisis in the USA.
Rapid withdrawal of exogenous steroids in patients on long-term therapy
A 54-year-old man with a history of alcohol use disorder is brought to the emergency department after his family caught him lighting paper on fire in his bedroom. When you confront him about this, he states, “Somebody snuck into my bedroom and lit a fire.” His family informs you that, for the past 6 weeks, he has been acting erratically and telling elaborate lies. He has normal vital signs. The physical exam reveals decreased sensation to light touch up to his ankles bilaterally. He is unable to perform a tandem walk and has a positive Romberg test. Which of the following additional findings is associated with this condition?
- A Bilateral lateral rectus palsy
- B Bradykinesia
- C Small pupils that accommodate but do not constrict with light
- D Tremulousness and responding to internal stimuli
A - Bilateral lateral rectus palsy
------
Patient's confabulation and memory problems = Korsakoff syndrome.
His gait ataxia is the beginning of Wernicke encephalopathy. Ophthalmoplegia = nystagmus, lateral rectus palsy and some pupillary problems. Wernicke = acute thiamine deficiency. Korsakoff happens after accumulated neurologic insults = chronic fx.
This is the best first step in treating the bones, moans, groans, and psychiatric overtones.
What are IV fluids (normal saline)?
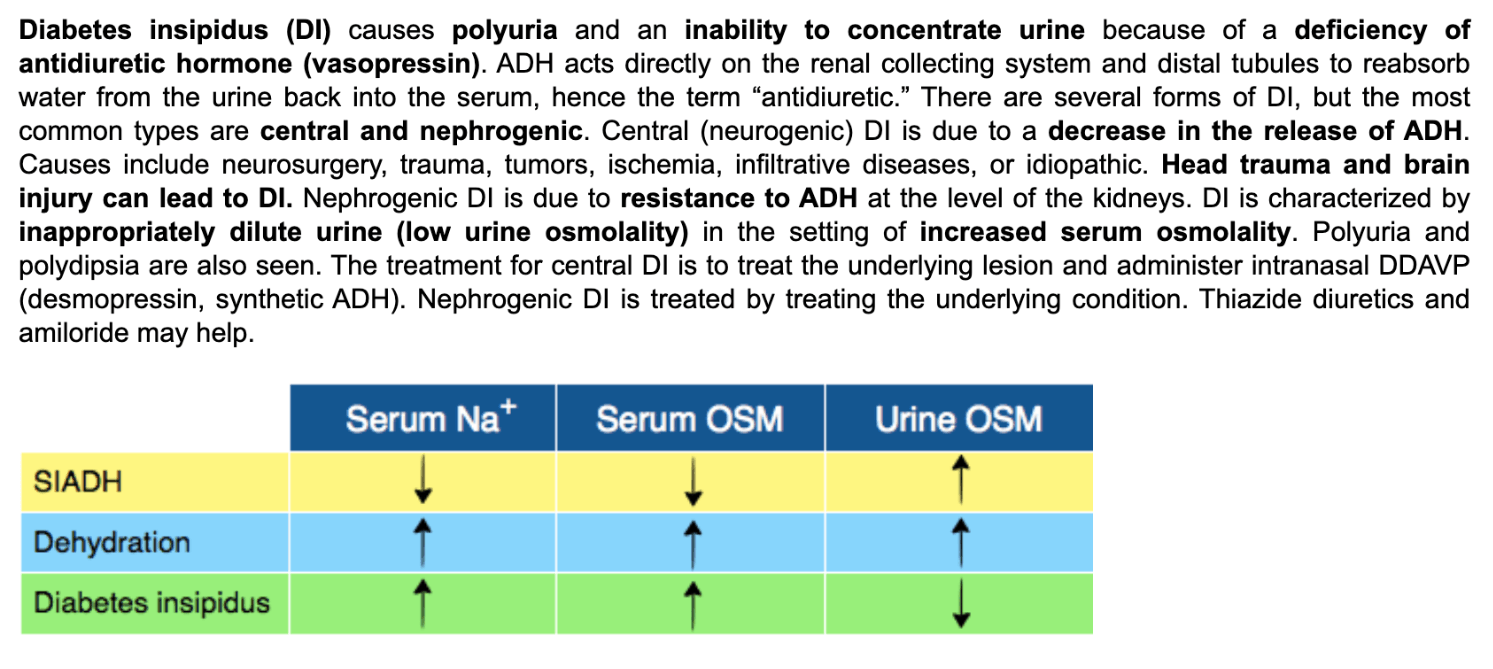
Urine and serum osmolality in diabetes insipidus
DAILY DOUBLE
At which acute salicylate level is dialysis recommended?
>100 mg/dL
Which of the following laboratory results is consistent with Addison disease?
- Decreased ACTH and cortisol levels
- Decreased ACTH level and increased cortisol level
- Increased ACTH and cortisol levels
- Increased ACTH level and decreased cortisol level
Increased ACTH and decreased cortisol.
-----
20 something patient with flushing, tremors, vision changes, and BP of 240/110. Has right flank pain. States her symptoms completely resolve, then suddenly start up again.
Best 1st line anti-hypertensive.
bonus points: 2nd line? 3rd line?
1st: phentolamine (alpha blocker)
2nd: labetalol (beta blocker)
3rd: nicardipine (calcium channel blocker)
4th: aren't they in the ICU already?
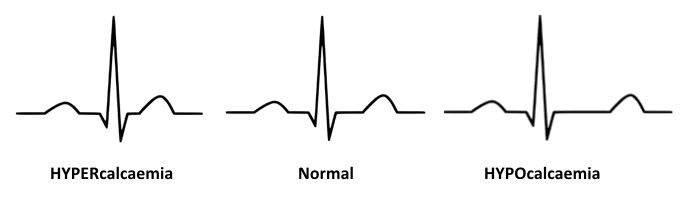
This ECG finding is found with hypocalcemia
prolonged QT interval
An 85-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes presents with confusion and lethargy. His serum glucose is 1,227 mg/dL. Which of the following represents the average fluid deficit of a patient with this disease process?
--------
HHNC - hyperosmolar hyperglycemia nonketotic coma)
* Severe hyperglycemia induced dehydration
* higher mortality than DKA
* elderly patients using psych meds, or handicapped and unable to get oral rehydration
*serum glucose >600
*serum osm >315 mg/dL
*minimal to no ketosis
*pH >7.25
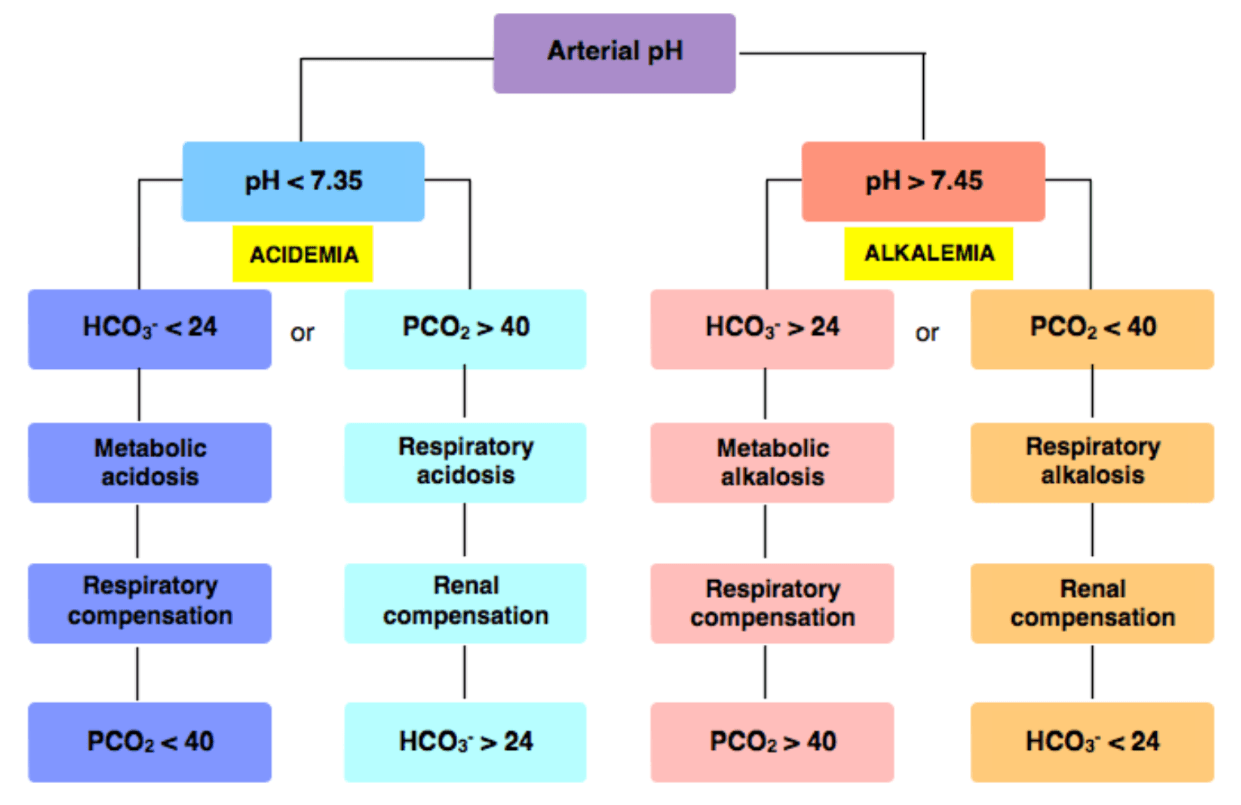
pH 7.1
HCO3 15
PCO2 30
Primary acid base?
What is: Metabolic Acidosis
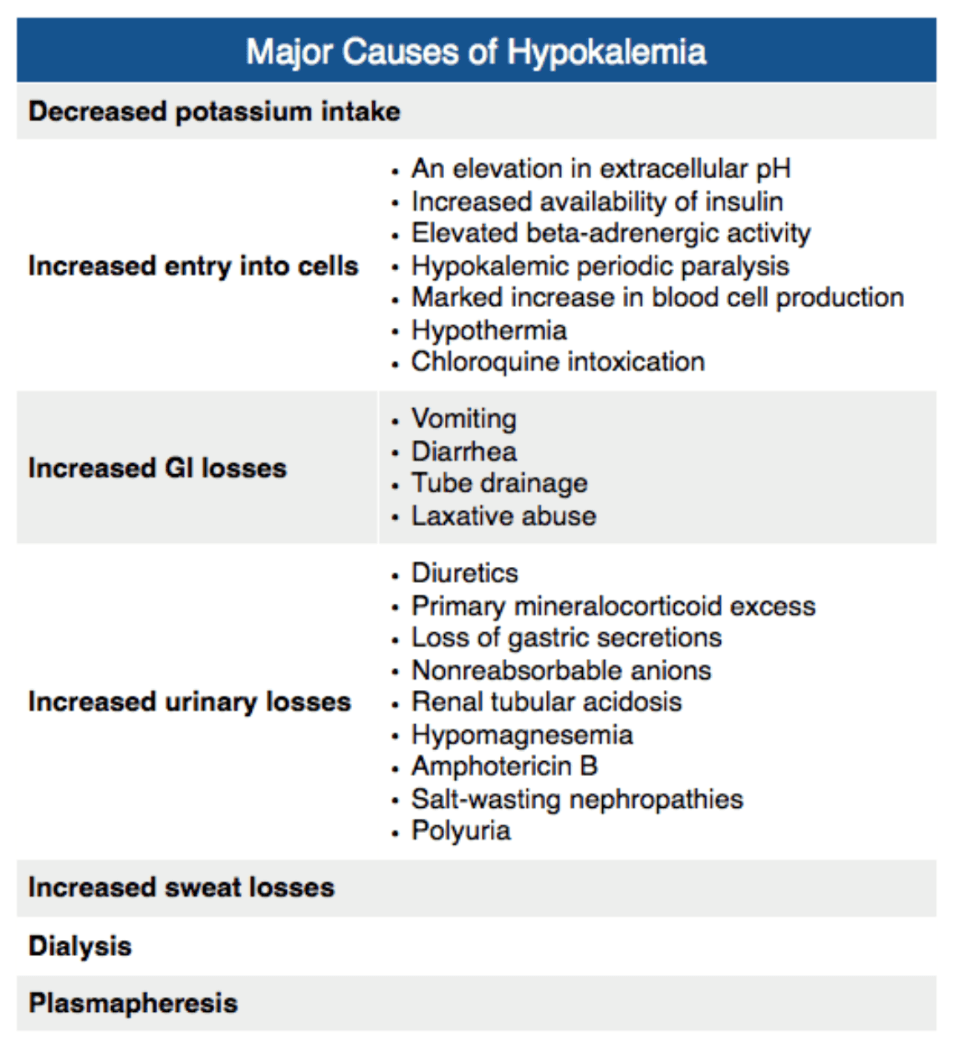
"Everytime I replete the potassium, it's just not going up and it's really frustrating!"
What is the most common reason for refractory hypokalemia?
Hypomagnesemia
Weight appropriate dosing of benzos given without resolution.
POC Na is 118. 3% hypertonic is given and the seizure stops. Which fluid do you give next?
* 0.45% saline infusion
* 0.9% saline infusion
* 3% saline infusion
* fluid restriction
0.9% saline infusion
Electrolyte derangement in Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Hypocalcemia
Phosphate released and binds (nom noms) to the calcium -> leading to hypocalcemia.
These bound complexes can cause kidney damage, hence aggressive IV hydration is necessary.
Which of the following set of serum laboratory values is more consistent with a hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state?
- Glucose 390 mg/dL, pH 7.1, 1+ urine ketone, bicarbonate 10 mEq/L
- Glucose 450 mg/dL, pH 7.0, 2+ urine ketone, bicarbonate 8 mEq/L
- Glucose 510 mg/dL, pH 7.35, 1+ urine ketone, bicarbonate 18 mEq/L
- Glucose 520 mg/dL, pH 6.9, 3+ urine ketone, bicarbonate 5 mEq/L
Glucose 510 mg/dL, pH 7.35, 1+ urine ketone, bicarbonate 18 mEq/L
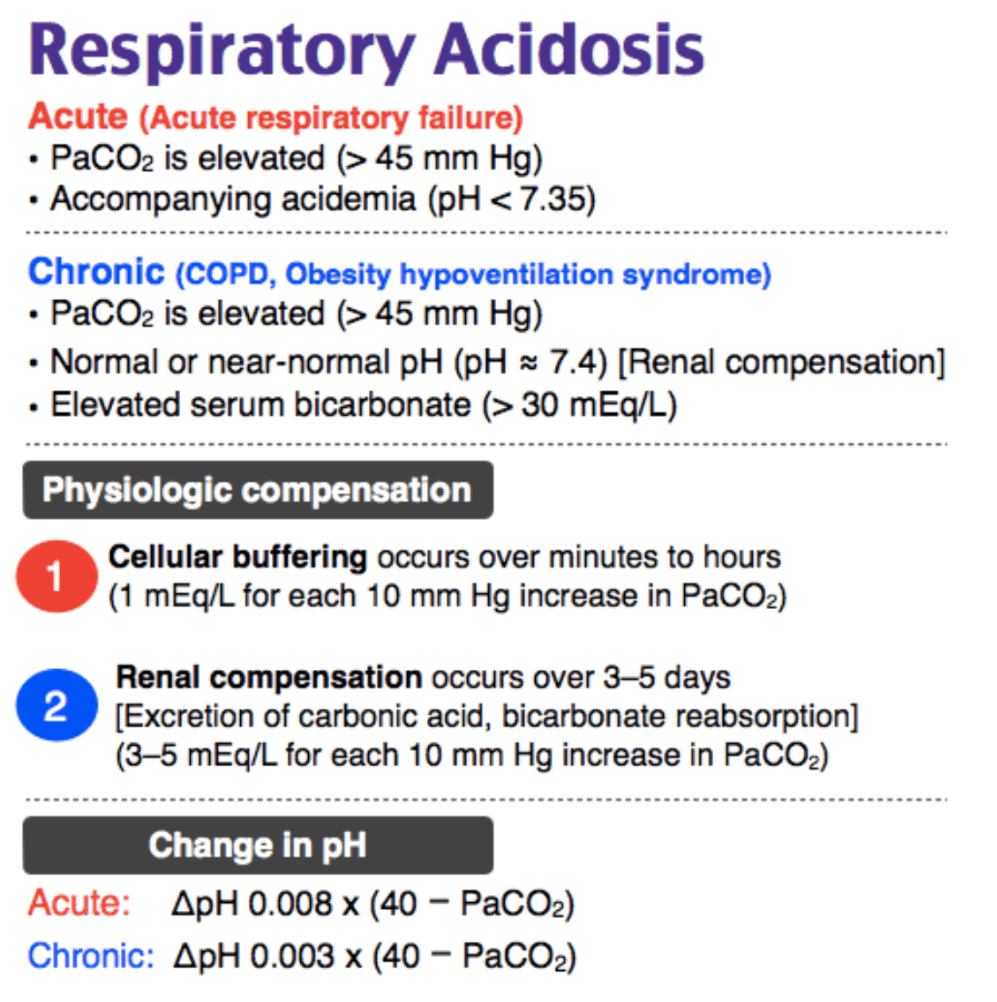
A 70-year-old woman with hypertension and COPD presents with shortness of breath. On evaluation, she appears tachypneic with increased work of breathing. Her breath sounds are notable for diffuse wheezing. She reports no fevers, productive cough, headache, nausea, or vomiting. She is started on ipratropium and albuterol. Which of the following would be expected on an initial ABG?
- pH 7.25, PaCO₂ 80 mm Hg, HCO₃ 30 mmol/L
- pH 7.30, PaCO₂ 75 mm Hg, HCO₃ 14 mmol/L
- pH 7.37, PaCO₂ 90 mm Hg, HCO₃ 10 mmol/L
- pH 7.43, PaCO₂ 60 mm Hg, HCO₃ 28 mmol/L
pH 7.25, PaCO₂ 80 mm Hg, HCO₃ 30 mmol/L
COPD'ers have a chronic respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation. An exacerbation is an *acute* rise in the PaCO2 on top of the previous acid base disturbance.
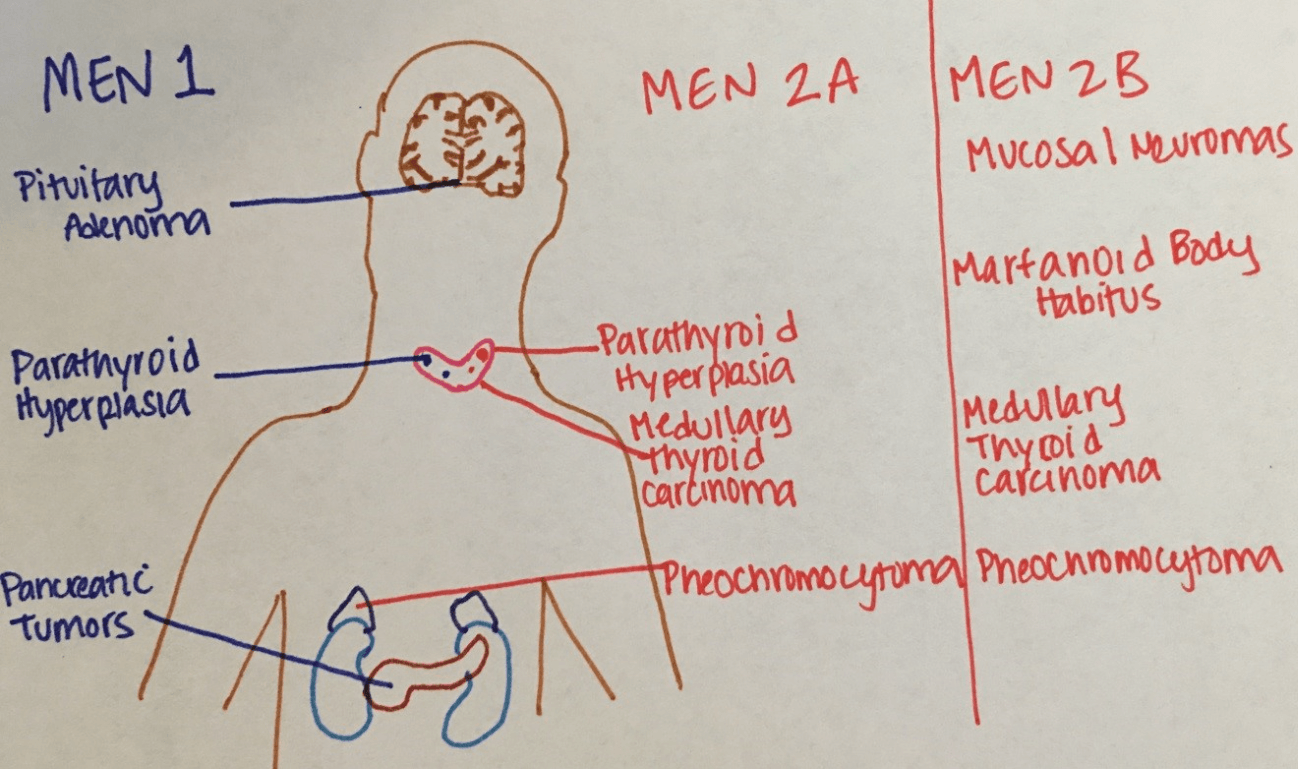
A 19-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with complaints of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia. His blood pressure is 185/95 mm Hg despite taking three antihypertensive medications. His mother had multiple “tumors” surgically removed in her twenties after experiencing similar symptoms. This condition is associated with a neoplasm in which of the following organs?
- A Lung
- B Pancreas
- C Pituitary
- D Thyroid
D - Thyroid
------
These symptoms are characteristic of a pheochromocytoma. Given his family history, he likely has multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 2A or 2B, which are both associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma. Pheochromocytomas classically present with the triad of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia. Diagnosis is made by urinary and plasma fractionated metanephrines and catecholamines. However, pheochromocytomas can present as part of the MEN type 2A or 2B. MEN 2A presents with medullary thyroid cancer, parathyroid neoplasms, and pheochromocytoma. MEN 2B present with medullary thyroid cancer, mucosal neuromas, and pheochromocytomas.
Correct order for reversing a storm

Mortality Rate of storm? ~75%
21yF s/p baby 5 days ago. Baby doing well, but can't breastfeed anymore. Feeling more shaky and craving sugar. Wants more salty things to eat. Pregnancy complicated by post partum hemorrhage, EBL "minimal".
Vitals: 90/50, afebrile, HR 62, RR 10
Labs:
Na 125
K 5.5
Glucose 50
What is the diagnosis?
What caused it?
Sheehan Syndrome
Post-partum Hemorrhage
A middle-aged man with a history of diabetes and hypertension presents with nausea, vomiting, and shortness of breath. His laboratory testing is remarkable for a leukocytosis, ketonemia, and an anion gap acidosis (pH of 7.13). The EM resident caring for this patient is surprised to find that the blood glucose is 121 mg/dL.
Which home medication is likely responsible for this presentation?
- Metformin
- Glipizide
- Liraglutide
- Canagliflozin
Canagliflozin
---------
This entity is known at euglycemic DKA and it is increasingly recognized for an association with a newer oral diabetic medication class, SGLT2 inhibitors. They all end in -flozin.
Mechanism: SGLT2 inhibitors may lead to a decrease in either endogenous or exogenous insulin, and an increase in glucagon production. Really though, it's a bit unclear.
Take-Home Points
- DKA is not defined by an absolute blood glucose.
- Obtaining a urine sample for ketones and a blood gas early in the ED course is extremely important in all diabetics, especially those who are Type 1 and those on SGLT2 inhibitors.
- The treatment of euglycemic DKA is essentially the same as traditional DKA: hydration, replace electrolytes, insulin.
Stress dosing steroids for pediatric patients.
- For small-sized kids (neonates to 3 years old), give 25 mg IV/IM (or think of a quarter)
- For medium-sized kids (3-12 years old), give 50 mg IV/IM (or think of a half-dollar)
- For large-sized kids (12+ years old), give 100 mg IV/IM (or think of a dollar coin).
--------
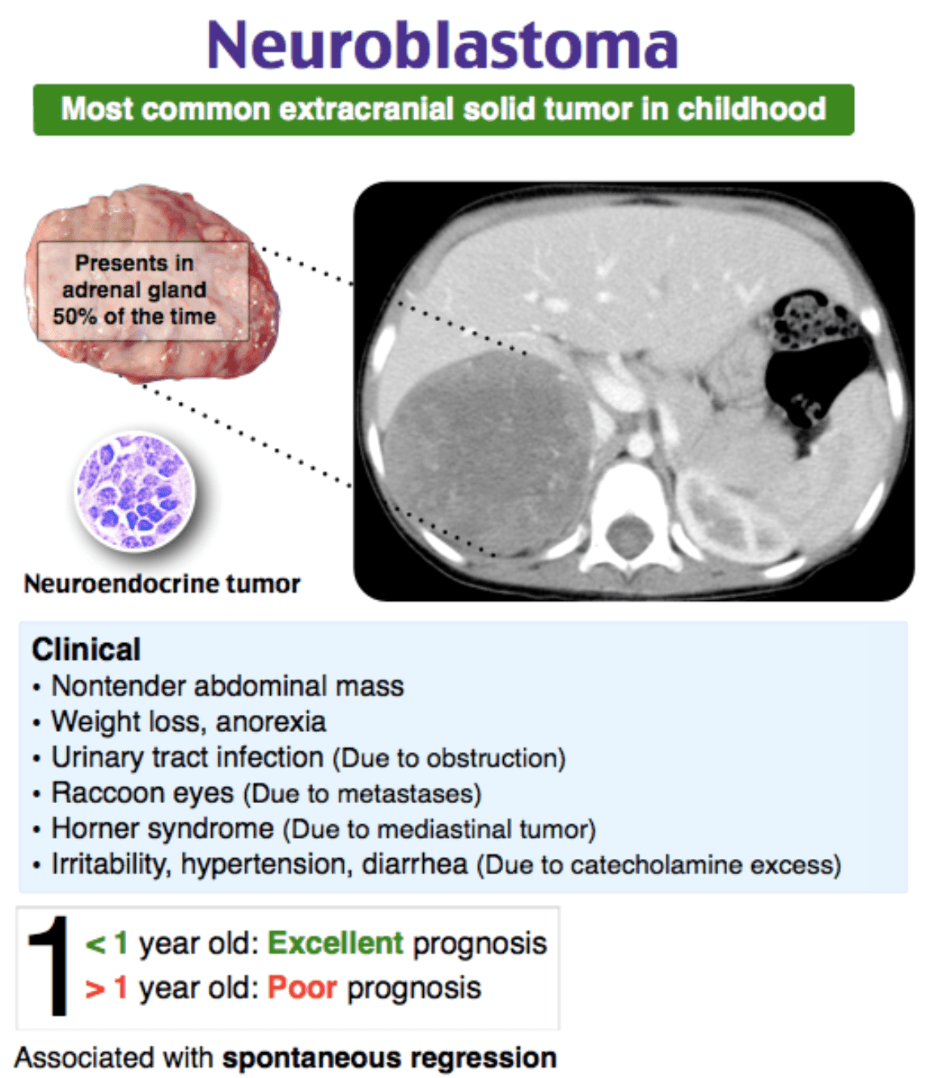
3 year old boy
* painless abdominal distension
* periorbital ecchymosis and edema
* no recent trauma
* non-tender irregular abdominal mass
What is the diagnosis?
neuroblastoma