The Specialty that manages prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of dental pulp and periradicular tissues that surround the root of the tooth.
Endodontics
The Subjective exam: chief complaint, character/duration of pain, painful stimuli, biting and pressure sensitivity.
What is Diagnosis
What is Working Length & the Goal?
What is the Distance from occlusal reference to the apical point of canal instrumentation/obturation that coincide with the apical constriction of the canal.
The Standard of Care for Endodontic treatment is...
What is:
Using a Rubber dam
The button on the Promark motor that is used for calibrating the motor & contra-angle before every RCT
What is the CAL button
The AAE formally incorporated in 1955 with 568 members... How many years has that been?
What is 75 years.
Tooth will display symptoms of lingering pain. Incapable of healing, indicating root canal therapy or extraction as only tx option.
What is Irreversible pulpitis
The 3 major objectives to access opening...
What are:
- Attaining straight-line access to canals
- Conserving tooth structure
-Unroofing the pulp chamber to expose orifices and remove pulp horns
The use of this Electronic device ensures 95% accuracy to reach apical foramen within 1mm.
What is the Promark Apex locator
What is the sensor device used for taking multiple radiographs and aides in positioning.
RINN = This holder device helps keep the sensor in the same location when taking multiple radiographs.
Archeological evidence shows that endodontics was performed as far back as....
What is second or third century B.C.
When referencing the acronym S.O.A.P from the Endodontic lecture- what does PCSB stand for with Heartland's treatment model for case presentation?
What is PCSB – Problem, Consequence, Solution, Benefit
The reasons for straightline access are: (name 2)
What are:
1. Less pressure/stress on file. Improve instrumentation
2. Easier delivery
3. Decreased procedural accident
The failure to excavate all caries and weak tooth structure results in ?
Recontaminate canal space via leakage or caries
Describe an Endodontic set-up that you learned about from this course and will implement for your practice:
What is:
Picture of the Sponge
Motor Calibration
4 Handed Dentistry- Team DDS/DA
This publication is highly regarded by Endodontists....
What is The Journal of Endodontics.
What does a Pre-Op access opening radiograph capture?
What are:
Insights into pulp chamber and root canal system:
- Location
-Length
- Size
- Shape
- Curves
- Obstructions
- Defective restorations
- Caries
Visually project pulp onto the external tooth surface
What are the results of a chemical burn

When should you clean and inspect files with cause moistened in alcohol or NaOCl?
What is
After EACH USE! 
Who recognized the modern root canal in 1963 ?
What is the American Dental Association.
How does the Mx CI pulp chamber differ in a young versus elderly patient?
What is
Young patient
- Wide pulp chamber M/D
- Three pulp horns
Older patient
- Oblong pulp chamber M/ D
- Pulp size/function decreases
- Age
- Restorations
- Calcifications
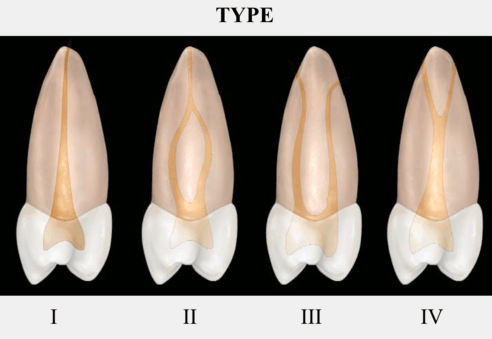
These are Weine's 4 classifications of canal systems. Describe each class?
What are:
Type I - 1 canal
Type 2 - 2 canals that join at the apex
Type 3 - 2 canals that do not join at the apex
Type 4 - one canal that bifurcates at the apical 1/3 (Difficult to treat).
Why is it important to remove any GP from the access cavity & how do you perform the procedure?
What is
GP material may discolor the tooth
USE cotton pellet and alcohol
Why not do a RCT? (Name 4 of 6 Contraindications)
What would be?
1. Non restorable teeth
2. Inadequate periodontal support (mobility 3)
3. Vertical root fractures
4. Canal instrumentation not possible.
5. Dam not possible
6. Tooth cannot be sealed