A patient has an extremely high T3 and T4 level. Which of the following signs and symptoms DO NOT present with this condition?
A. Weight loss
B. Intolerance to heat
C. Smooth skin
D. Hair loss
D. Hair loss
High T3 and T4 levels indicate a state of hyperthyroidism. Weight loss, heat intolerance, and smooth, silky skin are all S/S of hyperthyroidism (Norris, p 1058).
Why is it important to educate diabetic patients to inspect their feet often?
Diabetic patients can experience neuropathies and venous insufficiency. Due to this they may not feel if they injure their feet or get a blister from their shoes. Venous insufficiency leads to a decrease in healing of these wounds (Norris, p 1082-1083).
A patient with a new onset of Type 2 DM has been keeping a food journal. This is the breakfast entry for today: 2 boiled eggs with biscuits and gravy and orange juice. What part of this breakfast meets criteria for a diabetic diet?
The boiled eggs.
Biscuits and gravy are carbohydrates which need to be limited in diabetic patients. Orange juice has a high sugar content.
A patient is being discharged home for treatment of hypothyroidism. Which medication is most commonly prescribed for this condition?
A. Tapazole
B. PTU (Propylthiouracil)
C. Synthroid
D. Inderal
C. Synthroid
Tapazole is used to treat hyperthyroidism. PTU is used to treat hyperthyroidism. Inderal is a betablocker used to treat blood pressure, tachycardia, and other cardiac abnormalities.
Your patient is suffering from hypothyroidism? What nursing intervention is most suitable for this patient?
A. Providing an extra blanket
B. Providing a meal tray that is high in cholesterol
C. Ambulating the patient TID
D. Educating the patient to slow down their respirations.
A. Providing an extra blanket.
Patient's with hypothyroidism often suffer from cold intolerance. Hypothyroidism often causes hyperlipidemia so their diet needs to limit cholesterol. Ambulating plays no role in this scenario. Hypothyroidism causes decreased respiration rate so you would not want to educate them to decrease their respiration rate further (Norris, p 1058-1059).
Based on signs evidenced in this picture, what disease would you expect for this patient to have?
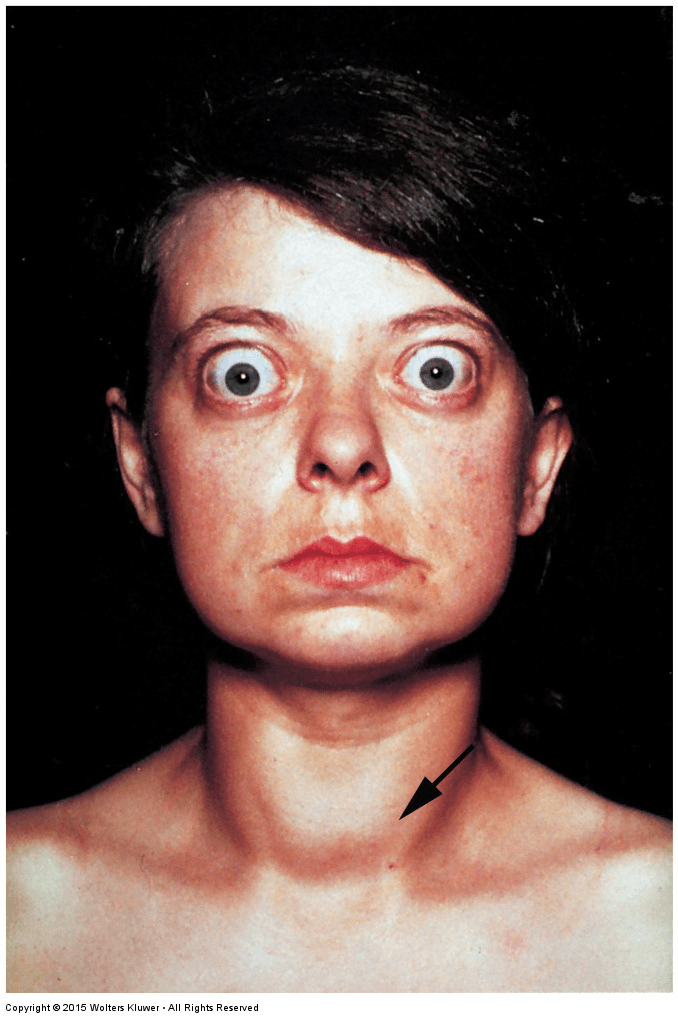
Graves Disease
"Graves Disease is a state of hyperthyroidism, goiter, and ophthalmopathy" (Norris, p 1061).
A patient has a Hemoglobin A1C of 10.7 mg/dL. What is a priority teaching plan for this patient?
Diabetic Diet Education
"Hemoglobin A1C is a test that measures the quantity of a subtype of hemoglobin that has been glycated, meaning the glucose molecules have become bound to the hemoglobin molecule." The can measure the glucose level back 120 days because that is the lifespan of the RBC's. A result of 10 shows a 3 month average blood glucose of 240 (Norris, p 1075).
A patient reports they do not eat enough iodine in their diet. What condition are they most susceptible to?
Hypothyroidism
Iodine stimulates the thyroid gland to produce hormones. Eating a diet low in iodine can lead to hypothyroidism because there is not enough stimulation of the thyroid gland to produce hormones.
What route is Insulin most commonly given?
Subcutaneous
Insulin is most commonly injected into the adipose tissue via a subcutaneous injection. Insulin can sometimes be given via an IV route.
A patient is admitted for hyperthyroidism with a large multinodular goiter, a nurse knows that all of the following things should be assessed except:
A. Difficulty in swallowing
B. Inspiratory stridor
C. A choking sensation
D. The patient's ability to turn their head
D. The patient's ability to turn their head
The degree of thyroid enlargement is usually proportional to the extent and duration of thyroid deficiency. Multinodular goiters produce the largest thyroid enlargements. When sufficiently enlarged, they may compress the esophagus and trachea, causing difficulty in swallowing, a choking sensation, and inspiratory stridor. (Norris, p 1058). Although the patient's ability to turn their head is important the priority is the patient's airway and ability to swallow without choking.
This disorder is commonly manifested by polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia.
Diabetes
"Polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia are the most commonly identified signs and symptoms of diabetes" (Norris, p 1078).
What might the nurse educate the patient to do to decrease tissue damage and pain at the site of insulin injections?
Rotate Insulin Injection Sites
"Rotate sites when the patient is to receive repeated injections. Injections in the same site may cause undue discomfort, irritation, or abcesses in the tissues" (Taylor, Lynn, & Bartlett p. 850).
A newly diagnosed diabetic is experiencing frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. What might you educate the patient to carry in their pocket incase this occurs while they are not at home?
A piece of candy
Having a piece of candy in a patient's pocket is a safe guard against a hypoglycemic episode.
A diabetic patient is receiving education related to their medications. Which medication should the nurse educate this client on to help control their blood sugar levels?
A. Metalazone
B. Metoprolol
C. Metformin
D. Manitol
C. Metformin
Metalazone is a diuretic used to treat fluid volume overload. Metoprolol is a betablocker used to treat tachycardia, hypertension, and other cardiac abnormalities. Manitol is an osmotic diuretic.
A diabetic patient has a blood glucose of 297. The patient is not symptomatic and you have a sliding scale protocol to treat the blood glucose with Humalog. What is the most important intervention to be performed at this time.
A. Call the MD immediately
B. Record and treat the blood glucose level
C. Educate the patient about a diabetic diet
D. Call a rapid response
B. Record and treat the blood glucose level
A glucose level of 297 is elevated but not critical. This patient is known to be diabetic so a high glucose level is to be expected if the glucose is not well controlled or in times of high stress or illness. You have a sliding scale to treat the glucose and the patient is not symptomatic. There is no need to notify the MD or call a rapid response. Although you should educate the patient related to a diabetic diet the most important intervention at this time is to record and treat the blood glucose level.
You enter your patient's room to do intentional rounding. You find your patient laying in bed stating that they feel weak. You begin assessing your patient and find them cool, pale, and clammy. Using your nursing judgement and physical assessment, what process do you think is going on with this patient?
Hypoglycemia
"Because the brain relies on glucose as its main energy source, hypoglycemia produces behaviors related to altered brain function. Headache, difficulty in problem solving, disturbed or altered behavior, coma, and seizures may occur. The parasympathetic nervous system often causes hunger followed by anxiety, tachycardia, sweating, and constriction of the skin vessels (i.e. the skin is cool and clammy)" (Norris, p 1081).
A patient with hypothyroidism has been started on Synthroid. What signs/symptoms would you educate your patient to report if they occur? (select all that apply)
A. Restlessness
B. Tachycardia
C. Weight gain
D. Heat intolerance
A. Restlessness
B. Tachycardia
D. Heat intolerance
All of these could indicate that the Synthroid dose is too high and is causing the thyroid to become overactive (Norris, p. 1058).
Which of the following is part of a diabetic diet?
A. Peach Cobbler
B. Sweet tea (sweetened with Splenda)
C. Fried Potatoes
D. White bread
B. Sweet tea (sweetened with Splenda)
Splenda is a sugar substitute used to sweeten the food and drink of diabetic patients. Peach cobbler has a high sugar content. Fried potatoes and white bread are loaded with carbohydrates which should be limited in a diabetic diet.
Your patient is newly diagnosed diabetic. As the nurse you are educating your patient on ways to decrease the blood glucose level. You choose to educate your patient on which of the following (select all that apply):
A. Exercise
B. Eating a diet high in carbohydrates
C. Taking their metformin as prescribed
D. Consulting with a dietitian to help create a meal plan.
A. Exercise
C. Taking their metformin as prescribed
D. Consulting with a dietitian to help create a meal plan.
Exercise, compliance with medication, and nutrition counselling are all ways to help decrease a patient's blood glucose levels. A diabetic diet should limit carbohydrates.
A patient with diabetes has a morning glucose of 50. The patient is sweaty, cold, and clammy. The patient is not NPO. Which of the following nursing interventions is the MOST important?
A. Recheck the glucose level
B. Give the patient ½ cup (4 oz) of fruit juice
C. Call the doctor
D. Keep the patient nothing by mouth
B. Give the patient 1/2 cup (4 oz) of fruit juice
The patient has a glucose of 50 and is symptomatic. The initial nursing intervention should be to provide carbohydrates to the patient to elevate the blood glucose as long as the patient is not NPO. If the patient is NPO you may have to call the doctor for an injection of D50.
Your patient presents in a state of stupor. They are lethargic but complaining of abdominal pain. Their breath smells fruity. HR is 115 and BP is 88/64. Respirations are 24 and deep. What are these signs/symptoms indicative of?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
"A day or more of polyuria, polydipsia, nausea, vomiting, and marked fatigue, with eventual stupor than can progress to coma commonly precedes DKA. Abdominal pain and tenderness may be experienced. The breath is often fruity because of the presence of the volatile keto acids. Hypotension and tachycardia may be present due to a decrease in blood volume. Kussmaul respirations occur as a compensatory mechanism to prevent further decrease in pH" (Norris, p 1080).
You are performing discharge teaching with a patient who is going home on Synthroid. Which statement by the patient causes you to re-educate the patient about this medication?
A. “I will take this medication at bedtime with a snack.”
B. “I will never stop taking the medication abruptly.”
C. “If I have palpitations, chest pain, intolerance to heat, or feel restless, I will notify the doctor.”
D. “I will not take this medication at the same time I take my Carafate.”
A. "I will take this medication at bedtime with a snack."
Thyroid medication works best if taken at the same time every day on an empty stomach. For this reason it is usually taken first thing in the morning about an hour before breakfast. Stopping the medication abruptly can cause a dangerous state of hypothyroidism. Palpitations, chest pain, heat intolerance and restlessness are all signs of hyperthyroidism and should be reported to the MD. Carafate can affect the absorption of multiple drugs including Synthroid.
A patient eats a diet that consists of a large amount of shrimp, eggs, and seaweed. Is this patient more likely to suffer from hypo or hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism.
These foods are high in Iodine. Iodine causes the thyroid to be over productive which can cause a state of hyperthyroidism.
Which of the following are treatment options for hyperthyroidism? Please select all that apply:
A. Thyroidectomy
B. Methimazole
C. Liothyronine Sodium “Cytomel”
D. Radioactive Iodine
A. Thyroidectomy
B. Methimazole
D. Radioactive Iodine
Cytomel is a treatment for hypothyroidism.
Your patient calls and states that they feel like they are going to pass out. You notice that they are pale, cool, and diaphoretic. You note that they skipped their breakfast because they didn't like what was on the tray. What is the first thing you will do as the nurse?
Check a finger stick blood glucose level.
The patient skipped breakfast and is exhibiting signs of hypoglycemia. The initial nursing intervention should be to check a blood glucose level.