At the top of a rollercoaster, there is a maximum of kinetic or potential energy?
Potential
Give an example of a multicellular organism
Any plant/ animal
What is classification?
Sorting or organising things into groups.
What is the independent variable in this experiment? yellow (not placed in water), red (salt water, left overnight), green (plain water, left overnight)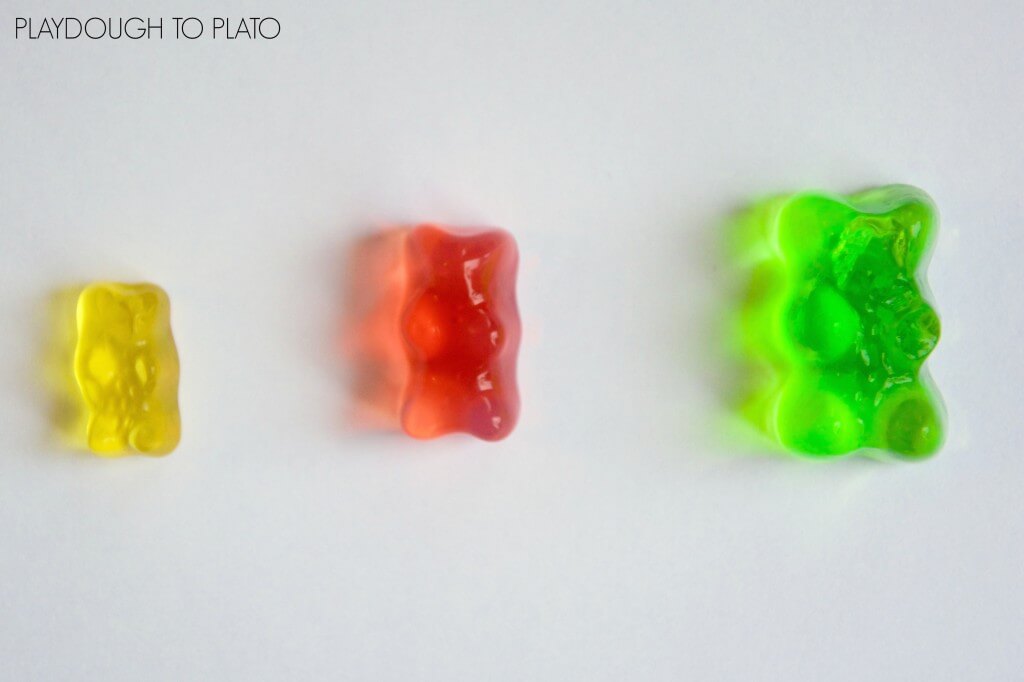
What the gummies are placed in (nothing, salt water, plain water)
Define kinetic energy
Moving energy
What is an energy transformation?
Where the energy turns into another type of energy
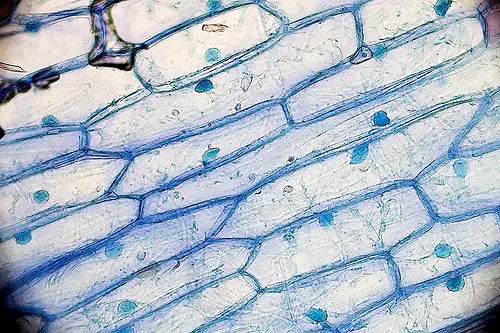
Is this a plant or animal cell?
Why do scientists use keys?
Scientists use keys because they:
• are easier to use than detailed descriptions of each group
• show at a glance what distinguishing characteristics each group has
• make it easier to identify objects that have never been seen before
• always give consistent answers, regardless of who is using them
What is the dependent variable of this experiment? yellow (not placed in water), red (salt water, left overnight), green (plain water, left overnight)

The size of the gummy
Define potential energy
Stored energy (e.g. elastic, chemical, food, raising object to a height)
Give an example of kinetic energy
Name three organelles that are only in plant cells
Cell wall (structure of cell), chloroplasts (photosynthesis), large vacuole (water storage)
What is a dichotomous key?
The most common type of branching key is a dichotomous key. Dichotomous keys have two choices at every branch. They start at the top with one large group and slowly subdivide into smaller and smaller groups until no more choices are possible.
What are 3 controlled variables?
yellow (not placed in water), red (salt water, left overnight), green (plain water, left overnight)

1. the size of the gummy
2. the amount of water it is placed in
3. the size of the container they are soaked in
Define organelles and give 3 examples
A small structure in a cell that is surrounded by a membrane and has a specific function. e.g. nucleus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, chloroplast, cell membrane, cell wall
What is energy conservation?
Energy can never be created or destroyed. It can be changed only from one form to another.
What is the job of the
1. Mitochondria
2. Nucleus
3. Cell membrane
1. Mitochondria- energy created from cellular respiration
2. Nucleus- contains DNA, controls cell
3. Cell membrane- controls what enters and leaves the cell
What is a tabular key?
Like branching keys, the idea is to start at the top and work your way down. Tabular keys can also be dichotomous, having two choices at each level in the key.
What is the independent variable?
Time
Define dichotomous key
Dichotomous keys have two choices at every branch.
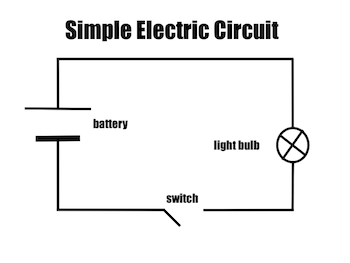
Draw this as a circuit diagram

What are the three parts to the cell theory?
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
3. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Use the key to identify H.
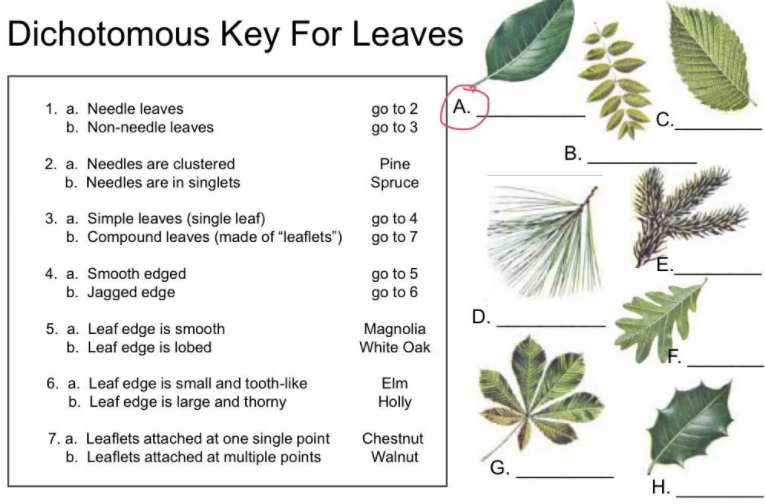
Holly
What are the features of this graph?
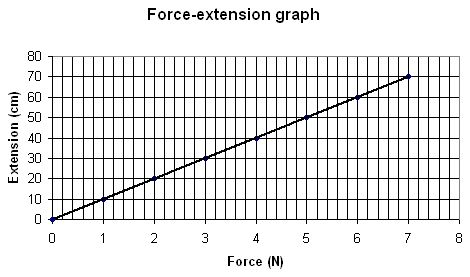
1. Title
2. Even scale
3. Labelled x- and y- axis, with units
4. Points plotted5. Line of best fit
What is classification?
Classification is the organisation of different things into groups of related types.The process that sorts all living things into groups is called taxonomy.