Give an example of a producer.
trees, grass, flowering plants, algae, etc.
What does the rat eat?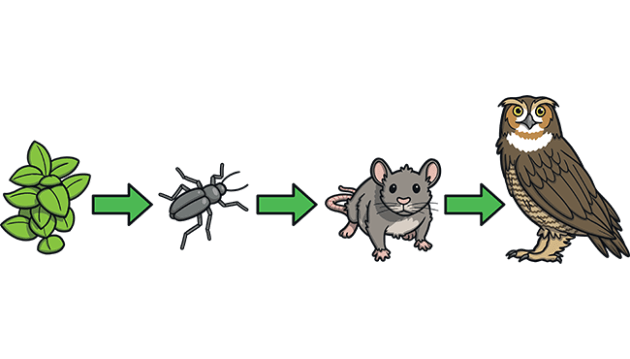
insects
What does the mouse eat?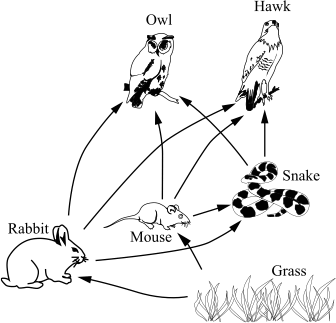
grass
Where are producers found on an energy pyramid?
the bottom
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain shows one path of energy flow. A food web is many overlapping food chains.
What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph?
Autotrophs make their own food. Heterotrophs consume other organisms.
What energy role always begins a food chain?
producer
Name all of the krill's predators.
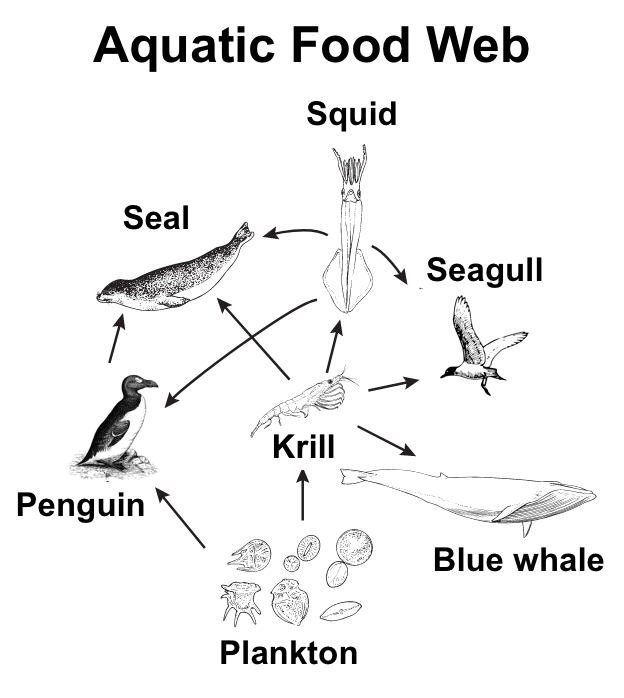
seal, squid, seagull, blue whale
What % of energy is transferred between trophic levels?
10%
Give an example of a decomposer.
What is the rhino's energy role?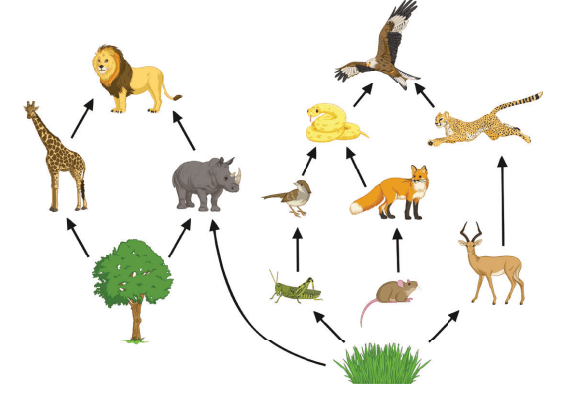
herbivore
How would the mouse population be affected if the owl was removed from the ecosystem? Why?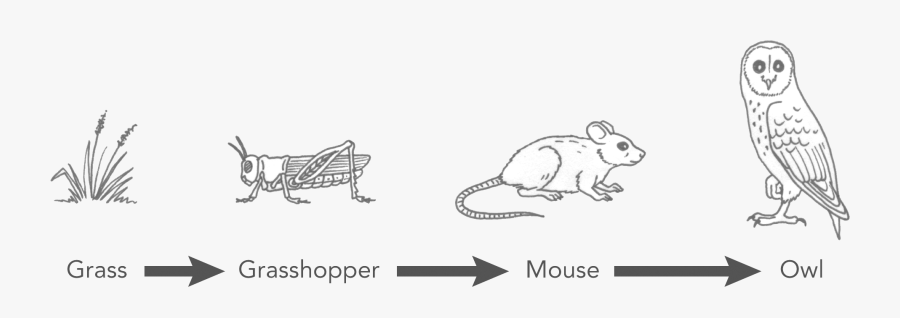
The mouse population will increase because they have no predators.
What level/order consumer is the fox?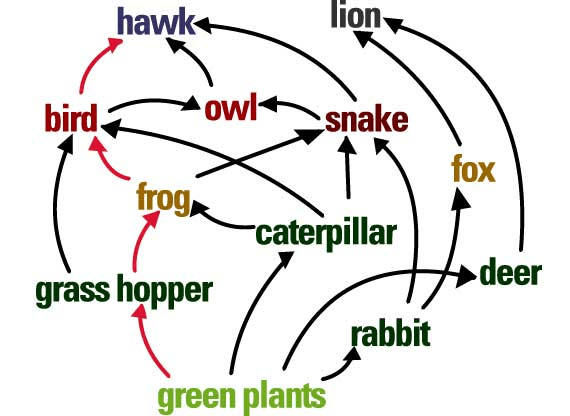
secondary consumer
Name one 2nd order heterotroph.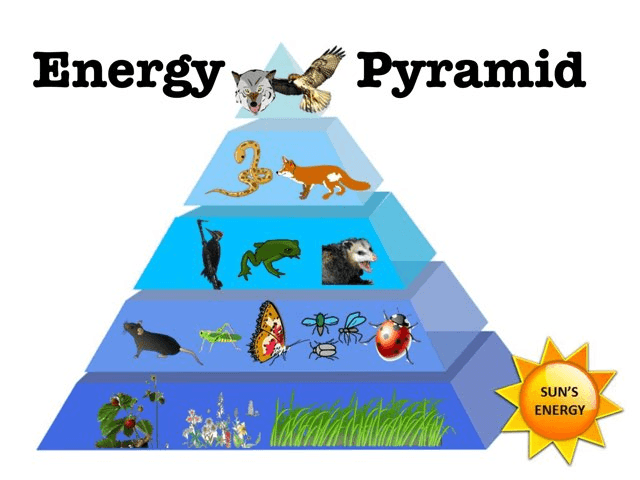
bird, frog, opossum
What is an apex predator (top carnivore)?
an animal at the top of the food chain that has no predators
Name 3 types of consumers and explain the difference between each.
herbivore: eat only plants
carnivore: eat only meat
omnivore: eat plants and meat
Which population's extinction would have the greatest catastrophic effect on this food chain? Explain.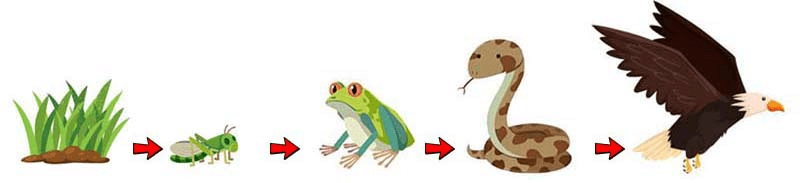
The grass. Producers are the foundation of all energy that flows through an ecosystem.
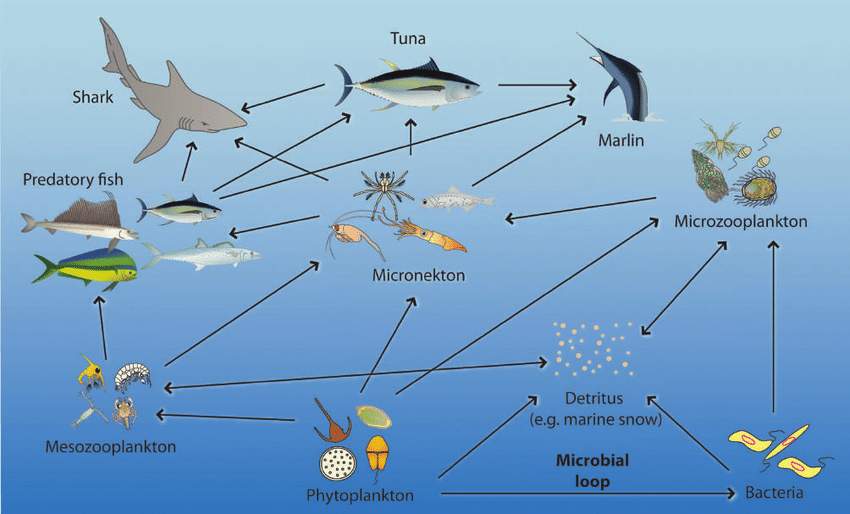
Name one food chain with at least 4 organisms from this food web.
example: phytoplankton > micronekton > predatory fish > shark
How many kcals of energy is available in the tertiary consumer level if the producer level has 10,000 kcals of energy?
10 kcals
In a forest ecosystem, are there more trees or more hawks? Explain.
There are more trees because there are always more producers than consumers.
What is the difference between a scavenger and a decomposer?
Scavengers eat freshly dead organisms. Decomposers break down decaying biotic matter.
Which direction does the arrow point in a food chain? Why?
What energy role is sometimes a primary consumer and sometimes a secondary consumer? Explain.
Omnivores. When feeding on plants, omnivores are primary consumers. When feeding on other consumers, omnivores are secondary consumers.
Why is a pyramid/triangle the appropriate shape for an energy pyramid? (Hint: two reasons!)
The wide bottom has the most energy and the greatest number of organisms. As you move to the top, the pyramid narrows because energy decreases and there are fewer organisms.
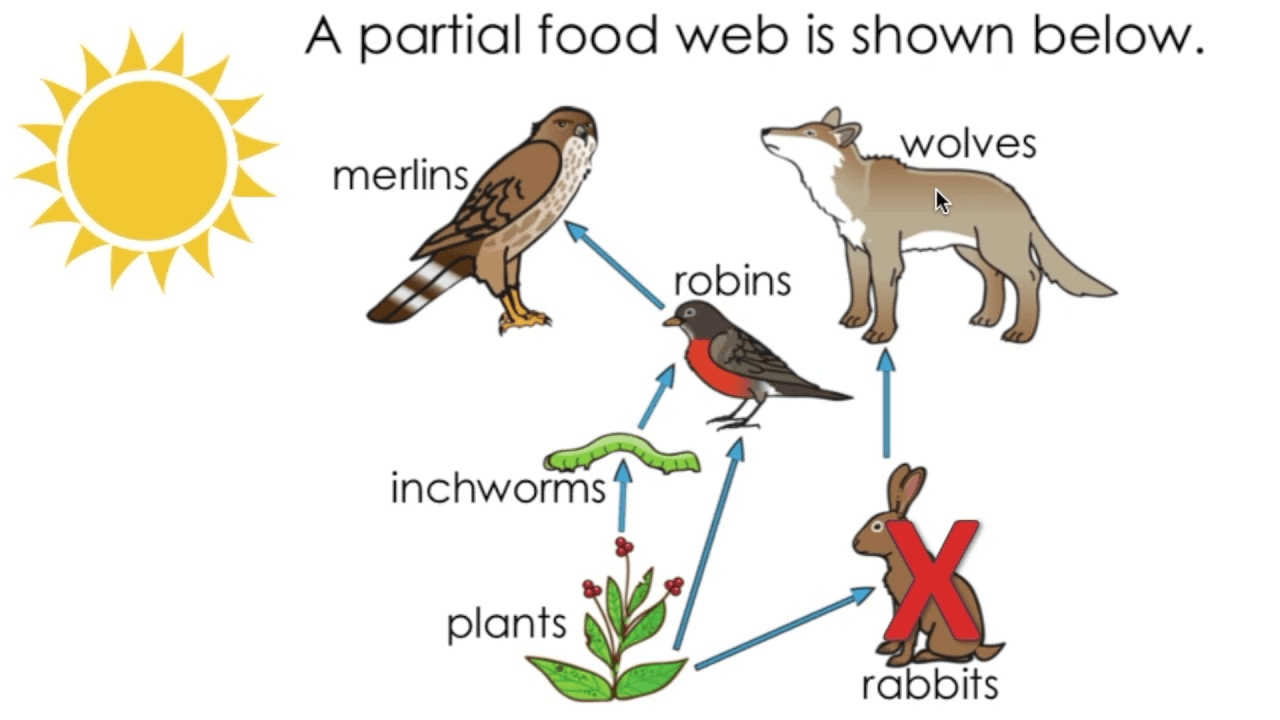 What would happen if the rabbits were removed from this ecosystem? Explain how all other organisms are affected.
What would happen if the rabbits were removed from this ecosystem? Explain how all other organisms are affected.
The plant population will increase because the rabbits are no longer eating them. With more plants, the inchworms have more food so they increase. Robins and merlins also increase due to having more prey. Wolves will decrease because they have no mood food.