These two things affect Kinetic Energy
What is Mass and Speed?
These two things affect Gravitational Potential Energy
What is Mass and Distance?
What is an Elastic force?
An engine or piston uses this form of CPE
What is gasoline?
These two things must be present in order for there to be Potential Energy
What is Force and Distance?
This causes Kinetic Energy to increase rapidly.
This force exists in order to have GPE
There is distance between these two things when there is EPE
What is the Deformed State and the Original State of an object?
A motor uses this form of CPE
What is a battery?
What is deform and not break?
What is Kinetic Energy to Heat Energy?
What is GPE?
An object has the property of Elasticity when it is able to do this.
This energy transformation happens when gasoline is lit on fire in a piston
What is CPE to Heat, Light, and Kinetic Energy?
The force of friction from air
What is Air Resistance?
At what point in this diagram is the roller coaster moving fastest? Assume no friction.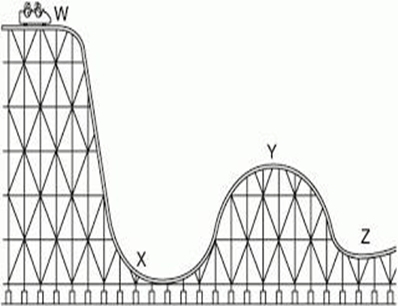
What is point X?
At what point is the GPE transforming into KE? Assume no friction.
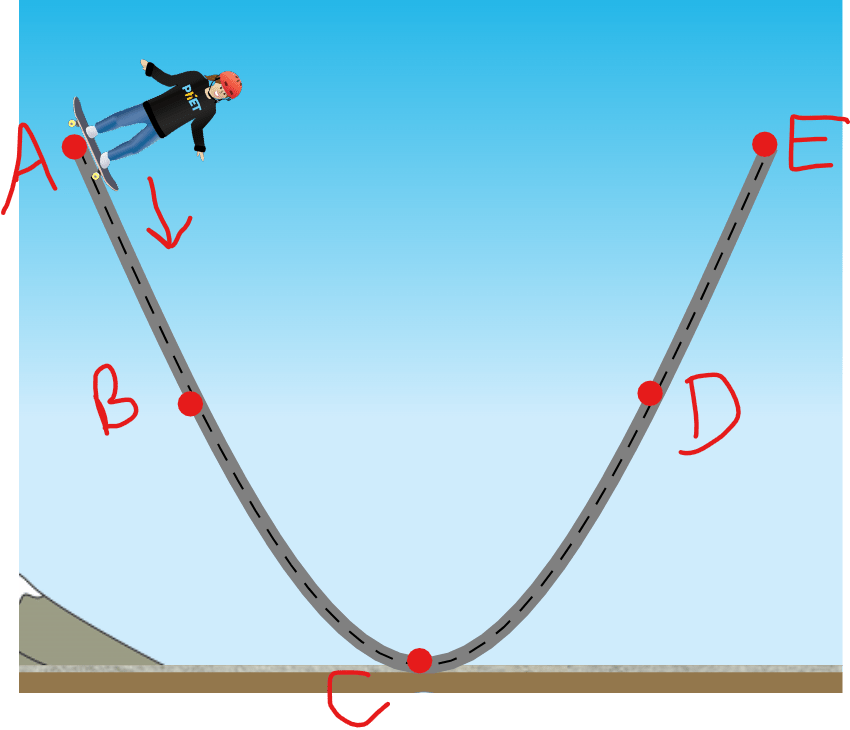
What is point B?
Does this spring have EPE? Why or why not?
No, because there is no distance between the original and deformed states. (Or, because there is no deformation)
These energy transformations happens in a motor
What is CPE to Electrical Energy to Kinetic Energy?
Why does Friction make objects slow down?
Friction causes KE to transform into HE which means that the KE is decreasing. When KE decreases, so does the speed of the object.