Energy?
Energy?
Energy
Transformations
Grab bag
Learn?
Ability to do work or cause change.
What is Energy?
The form of energy associated with the position or shape of an object.
What is potential energy?
Define energy transformation.
What is
The change of one energy form into another energy form?
The type of energy stored in fossil fuels such as the coal pictured below.

What is chemical energy?
The 3 fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas all contain chemical energy.
The Law of the Conservation of Energy.
What is?
The scientific law that states:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed it can only be transformed into other forms of energy.
Energy due to motion and an example
What is kinetic energy?
Example: any moving object.
The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom.
What is nuclear energy?
An example of a single energy transformation.
What is?
1. A toaster transforming electrical energy into heat energy to toast bread.
2. A cell phone transforming electrical energy into electromagnetic energy to send your text message.
3. The chemical energy in food transforming into thermal energy to keep you warm.
4. The mechanical energy of rubbing your hands together transforms into thermal energy to warm your hands.
5. And many more examples.
Hand saw VS. Chain saw
Identify the saw with more power and explain why that saw has more power.
What is the chain saw?
The chain saw has more power because it can do the same amount of work in less time.
Name two factors that determine which of two objects has more potential energy.
What is shape (stretched or compressed) and position (the height of the object)?
Name the type of energy shown here and describe its characteristics.

What is elastic potential energy?
The elastic of the slingshot is stretched, changing its shape and giving the slingshot potential energy.
Compressed items also have elastic potential energy.
The energy of microwaves, X-rays, light and heat.
What is electromagnetic energy?
In this example, pictures were taken at equal intervals at the speed of 20 pictures per second. Explain how this picture provides evidence that the kinetic energy of falling objects increases as the object falls.

What is:
Since the pictures are taken at equal time intervals and the space between the basketballs is larger with each successive picture, the basket ball is picking up speed which means the kinetic energy of the basketball is increasing.
The energy transformation at the top of a waterfall.
Be specific.

Gravitational potential energy transforming into kinetic energy.
Both the water in the river and the water in the fall have mechanical energy, when considered together. However, the energy transformation is gravitational potential energy transforming into kinetic energy.
Name two factors that determine which of two objects has more kinetic energy.
What is mass and speed?
The rate that one form of energy is changed into another form of energy.
What is power?
The total potential and kinetic energy of the PARTICLES in an object.
What is thermal energy?
An example of a multiple energy transformation
(Two or more steps).
What is?
1. The chemical energy in a battery transforming into the electrical energy in the wires of a flashlight transforming into the electromagnetic energy of the light and heat released from the flashlight.
2. The nuclear energy in the sun is transformed into electromagnetic energy that travels to earth, which is then transformed by a plant into chemical energy during photosynthesis, which creates food to be eaten changing the chemical energy into mechanical energy to allow body movement.
3. And many more examples.
Identify 3 energy transformations that are happening as the roller coaster moves around the track. Be specific.

What is:
1. Gravitational potential energy transforming in to kinetic energy.
2. Kinetic energy transforming into gravitational potential energy.
3. Mechanical energy transformed into thermal energy.
4. For the first hill, electrical energy is transformed into kinetic energy to move the roller coaster car to the top of the hill.
Identify the energy transfer that occurs when two object slide or rub against each other.
What is thermal energy?
Thermal energy is released as the result of friction.
Identify these locations in the drawing of the diver:
A. the most potential energy
B. least potential energy
C. most kinetic energy
D. the 2 points of least kinetic energy
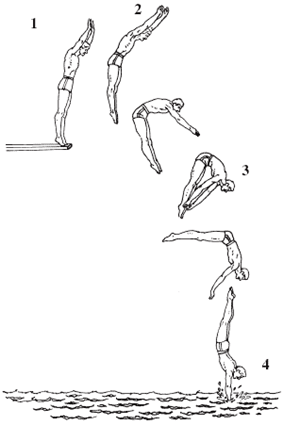
What are points?:
A. 2 most potential energy
B. 4 least potential energy
C. 4 most kinetic energy
D. 1 and 2 least kinetic energy
The energy associated with the motion AND position of an object.
Identify the formula to calculate this type of energy.
What is mechanical energy?
potential energy + kinetic energy
= mechanical energy
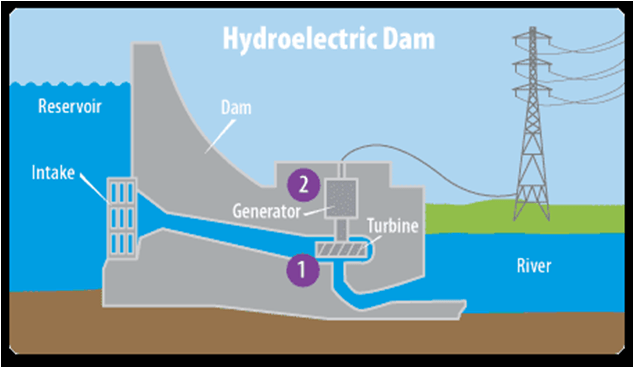
Identify the type of energy at the intake, and locations 1 and 2.
What is?
Intake: mechanical energy
Location 1: mechanical energy
Location 2: electrical energy.
Consider the energy of a pendulum.
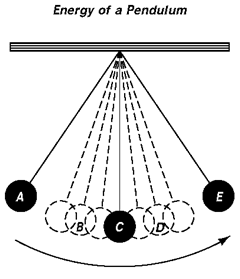
Identify the energy form at locations A. B. C. D and E. Be sure to describe the energy transformations happening at points B and D. Note: according to the arrow, the pendulum is moving from point A to point E.
What is the energy at location:
A. Gravitational potential energy. This is one point, along with point E, of the most gravitational potential energy.
B. Gravitational potential energy transforming into kinetic energy.
C. Kinetic energy. Pont C is where the pendulum has its most kinetic energy.
D. Kinetic energy transforming into gravitational potential energy.
E. Gravitational potential energy. This is one point, along with point A, of the most gravitational potential energy.
In the drawing of the basketball, identify the points of
1. Least kinetic energy 2. Most kinetic energy.
3 Least potential energy. 4. Most potential energy.
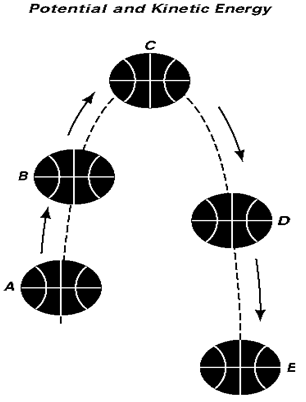
What is?
1. Point C: least kinetic energy (The ball is not moving).
2. Point E: most kinetic energy. The ball gains speed as it falls so the kinetic energy increases the closer the ball gets to the floor.
3. Point E: least potential energy. The ball is at its lowest point, so has the least gravitational potential energy.
4. Point C: most potential energy. The ball is at its highest point at point C, so has the most gravitational potential energy.