A very common system is the Object and ______ System
Object and Earth System

If an object's velocity is tripled, its Kinetic Energy increases by this factor.

Other than the equation W = F * D, this is the definition of Work
Change in Energy

In the absence of friction and air resistance, this sum remains constant throughout an object's motion.

Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy (Total Mechanical Energy)
This is the standard SI unit for Power, defined as one Joule per second.
Watts
A closed system never ________
Loses or Gains Energy
Calculate the elastic potential energy stored in a spring with a constant k = 200 N/m that is compressed 0.1m
 Joule
Joule
This is the amount of work done by a waiter carrying a 5kg tray at a constant velocity across a 10m room.
None

A 1 kg ball is thrown upward with 50 J of kinetic energy. Calculate its maximum height (use g = 10 m/s^2).
 Meters
Meters
An engine does 12,000 J of work in one minute. Calculate its power output in Watts.
200 Watts
A block slides down a rough incline in a vacuum. If the system is defined as "The Block and the Earth," name the force that is considered "external" to this system.
Friction
On a graph of Gravitational Potential Energy (Ug) vs. Height (h), this specific physical constant represents the slope of the line (assuming mass is constant).
Weight (Mass * Acceleration due to Gravity)
On a Force vs. Position graph, this geometric feature represents the work done on the object.
Area under the Curve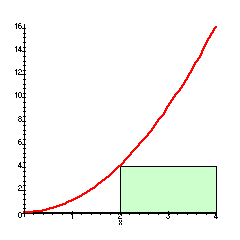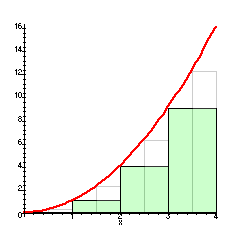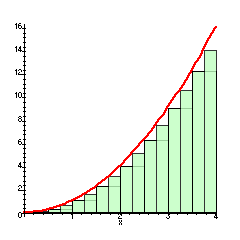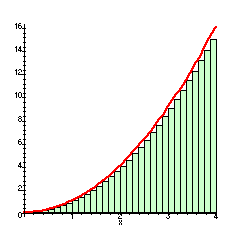
Transfer of your hand's Kinetic Energy to ____ as ____

To the Rocks (environment/outside the system)
A motor lifts a mass at a constant speed, this is the relationship between the power required and the velocity of the lift.
Power = Force (Weight) * Velocity
If he deploys a Parachute, in the Man, parachute, and Earth System the system does _____ work on the _____.

The System does positive Work on the Surroundings
The angle on the swing where PE and KE are equal

Less than halfway from the Horizontal (70ish degrees)

The two conditions that must be met for a force to be considered "doing work" on an object.
Force must be Applied, and Force must be in the same direction
Where energy goes in a bowling ball and earth system, when getting a strike

Some of the energy goes into the Pins and some continues as KE for the Bowling ball.
The amount of horse power an average horse has

(2/3)*746 = 497
When the Earth is NOT included in the object's system, this is what replaces Potential Energy
External Work
An object is dropped from rest. This is the type of relationship between its Kinetic Energy and the square of the time it has been falling.
Direct Relationship
A force of 50N is applied at a 60 degree angle to a box moving 4 m horizontally. Calculate the work done by this force.
 Joules
Joules
Ratio of work between a Force being applied to a block at an angle of 60 degrees across a surface, vs horizontally across a surface
1 : Square Root (3)
A 50kg car experiences a constant deceleration of -10m/s^2 while traveling at a constant 30 m/s. Calculate the power the engine must provide just to maintain this speed.
15,000 Watts
