Name four types of energy.
Electrical, kinetic, light, sound ...
State the law of conservation of energy.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred or transformed.
Name three states of matter and the processes of changing from one state to another (four of them).

Solid - melting - liquid - boiling (evaporating) - gas.
Gas - condensation - liquid - freezing - solid.
What type of heat transfer occurs between two objects that are in direct contact with each other?
Conduction.

Name energy transfer type that happens when you walk barefoot on a hot sand.

Conduction.
Name at least 3 types of stored (potential) energy.
gravitational, elastic, chemical ...
In a light bulb only 10% of total energy is transferred as light. What is happening with the rest 90%?

The rest (90% of the energy) is transferred as heat into the surroundings.
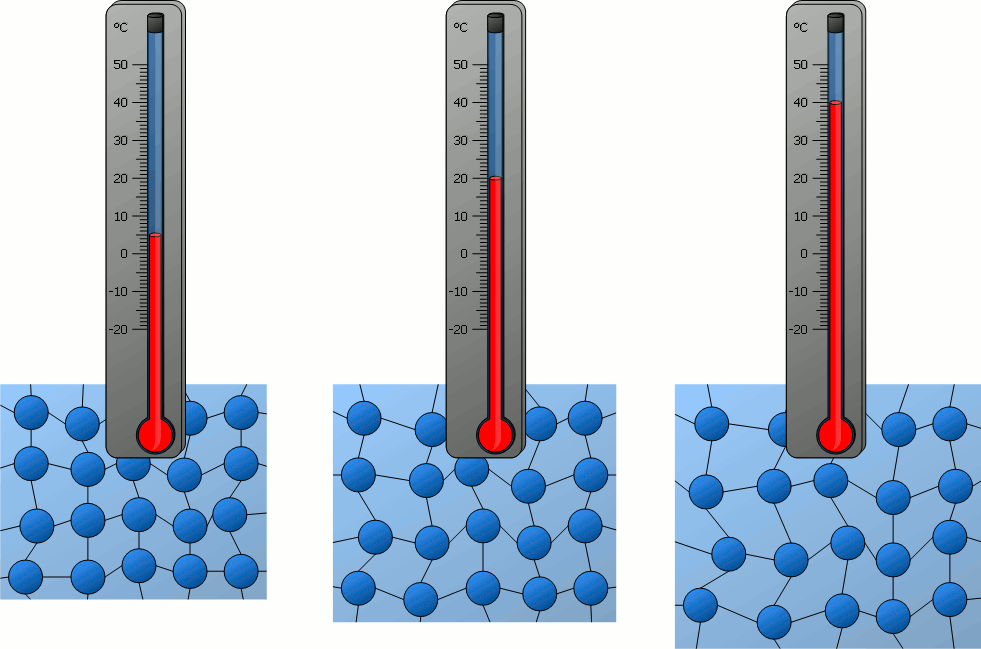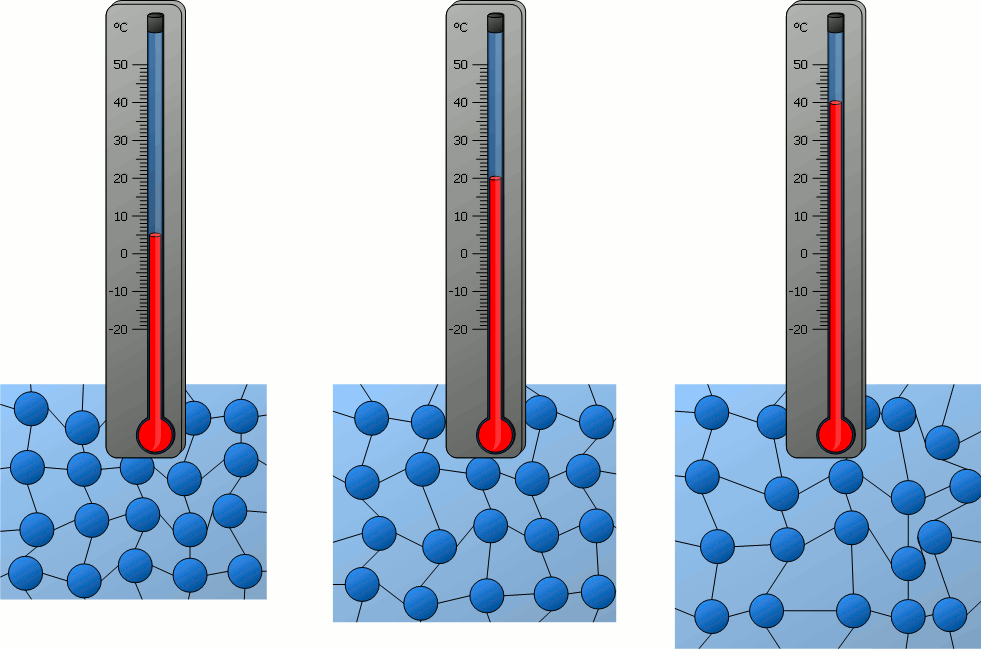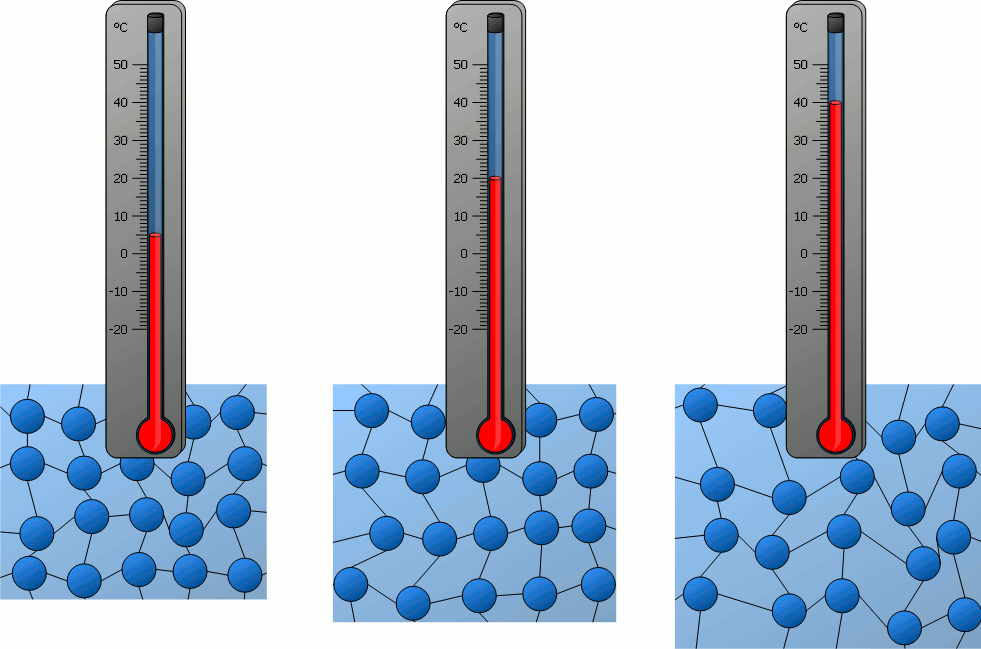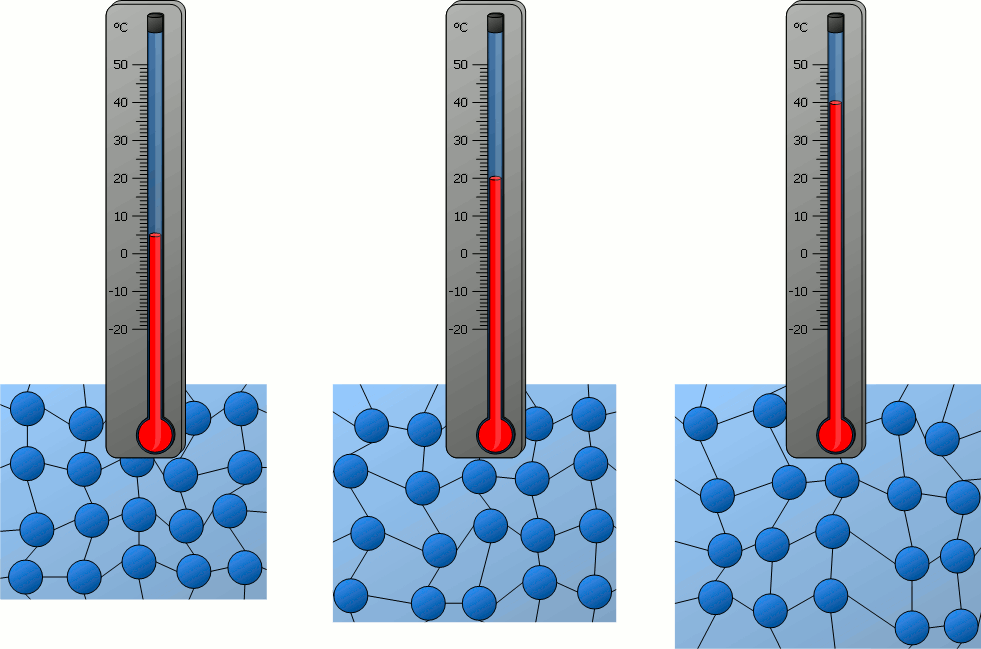
The temperature of an object is related to...?
How fast the particles of the object move.
A type of heat transfer that does not need any matter to travel through.
Radiation.
Explain what is happening. What type of heat transfer do we observe?
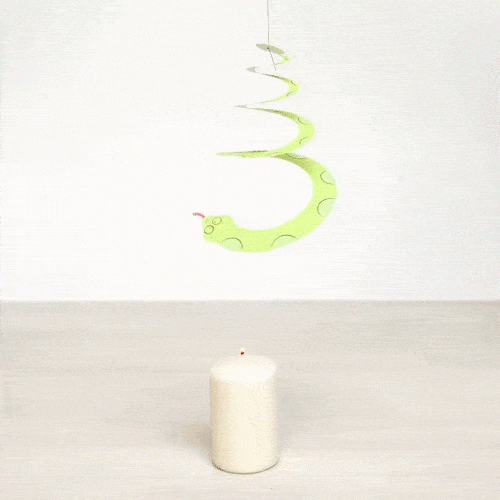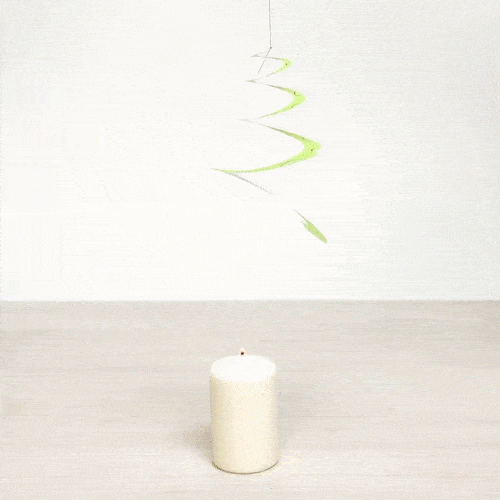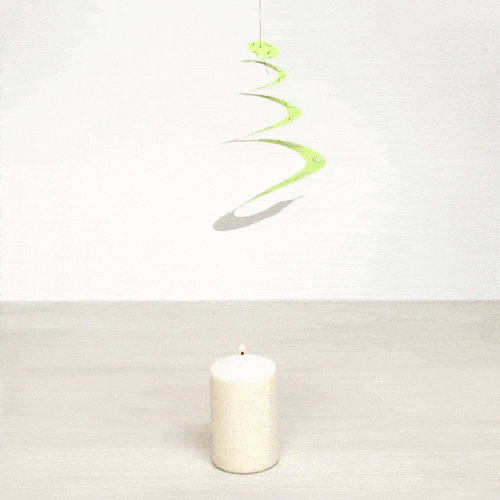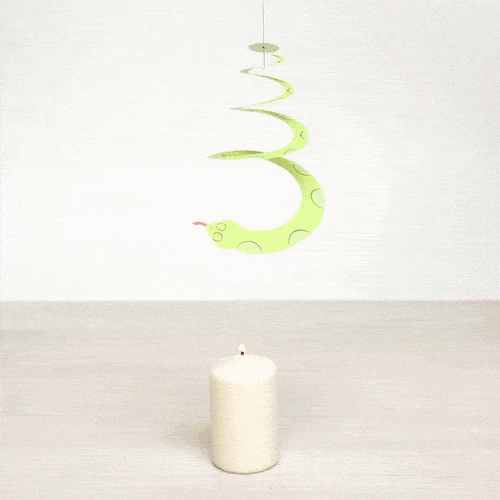
Air is heated with the candle and it flows upwards making the spiral rotate. This is an example of convection.
Name all energy types present in a working battery powered fan.

Chemical (battery), kinetic (rotating fan, motor), thermal (motor, wires).
Give the name of a diagram that is used to show energy transfer. What does the arrows' thickness show?
Sankey diagram. Arrow thickness shows the amount of energy being transferred.

The thermal energy of an object is related to...?
How fast the particles of the object move AND how many particles there are in the object.

This is the transfer of heat by physical upward movement of particles. What state of matter is needed for it to happen?
Convection. It happens in fluids (liquids or gases).
Watch the demonstration with a baloon. Explain what is happening. What type of heat transfer did we observe?

First demo: a baloon is heated and the rubber melts, that is why it pops.
Second demo: water in a baloon absorbs the heat transfereed from rubber, so the rubber temperature does not increase and it does not melt.
This is an example of conduction.
Describe why energy can be called "the money of physics"? Give 2 points of similarity.
Like money, energy can be:
1. Stored in different places.
2. Transferred between places.
3. But it will be the same total amount.
4. And it will be the same money (currency).
Define energy efficiency.
Energy efficiency is a measure of how much useful energy is transferred.
Explain why the temperature of solid matter is always less than the temperature of the same matter in liquid state.
The particles of matter will move slower (only vibrate) in a solid than in a liquid.
Describe how the three types of heat transfer occur in Earth's atmosphere heating.
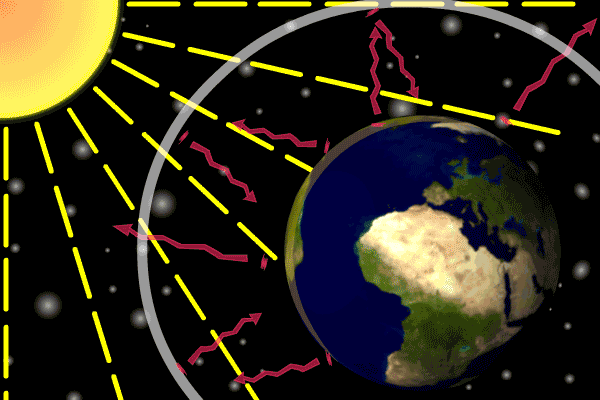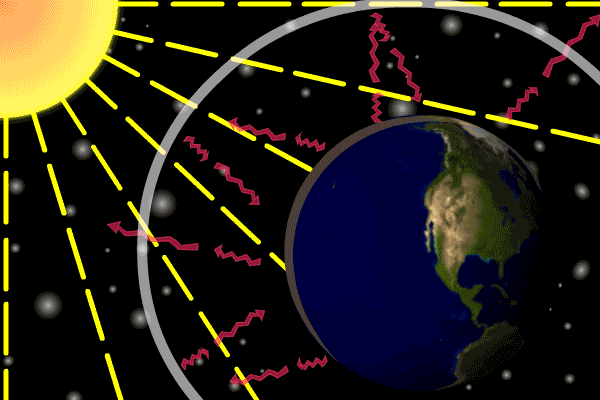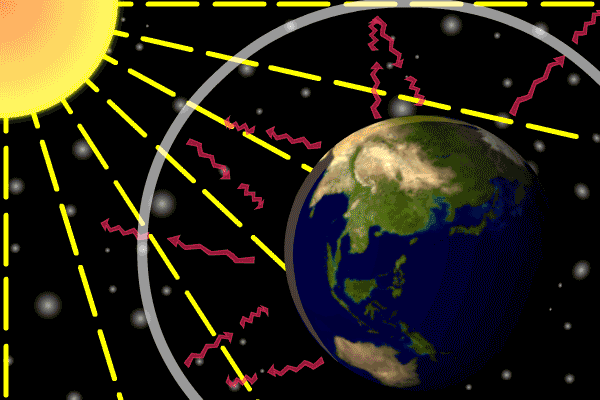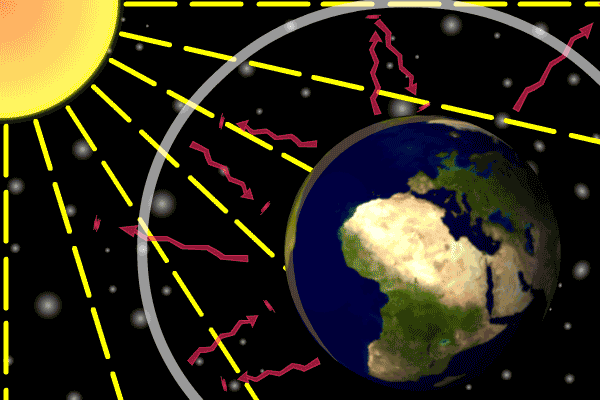
•Energy is transferred from the Sun as radiation.
•Earth’s surface absorbs this energy and transfers it via conduction.
•Energy is transferred from lower warm air to upper cold air with convection.
Watch the demonstration with a pencil lead. Explain what is happening. What types of energy stores and transfers were used?
Chemical store (battery) - electrical transfer - thermal store (pencil lead) - heating and light radiation - surroundings.
Name energy types in a working hydropower plant: it uses falling water to rotate turbine, that turns electrical generator, that gives away electricity we can use for our appliances.
Gravitational potential (water upstream) - kinetic energy (turning the turbine) - electrical transfer (generator transfers electricity to the network).
Calculate the efficiency of an electrical motor (in %) if it loses 300 J of 1000 J total energy input as heat and sound.
Input 1000 J = 100%, energy loss 300 J = 30%, useful energy 1000-300=700 J = 70%.
Describe why more time is needed in the same microwave to heat a larger glass of milk to the same temperature as a smaller one?
The larger glass contains more milk, that means we need to make more particles move faster. It takes more energy and so it takes more time (in the same microwave oven).
Why does jumping into a cold water make you feel cold? What transfer is occurring?

The heat is flowing out of the body into the cold water through conduction.
Give examples of four main types of energy transfer.
Some examples:
Electricity going from the power plant to the lamp in the room.
Spinning the bicycle pedals.
Drying out wet clothes on the heater.
Multimedia projector projecting the presentation on the screen.

