At what point on a roller coaster does the roller coaster have the most potential energy?
At the highest point
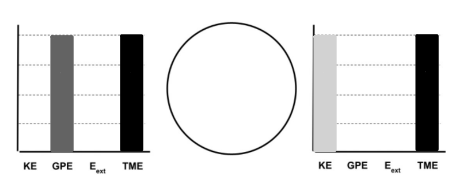
Draw an Energy Chart for a ball that started at rest at the top of a hill, then picked up speed and rolled to the bottom of the hill.
The third floor of a house is 7.93 meters above street level. How much work is needed to move a 1646.4 N refrigerator to the third floor?
W = 13055.95 J
What are the units for power?
Watts
Quick Fire Math:
If a 10 kg object is moving at 5 m/s, what is its kinetic energy?
125 J
Aside from mass, changing what will impact your gravitational potential energy?
height
What energy is present at the point at which a ball bounced to its max height after being dropped
Gravitational Potential Energy
Mr. Urbain plans to attend the 2024 cheese rolling event this spring and plans to use physics to win. He knows the mass of the cheese is 6kg and the height of the hill is 200m tall.
What is his KE at the bottom of the hill? Is his winning?
(Assume no energy loss)

KE = 11,760J
You are pushing a table and exert 30 J of work over 2 seconds. How much power did you apply?
15 W
Why does a pendulum never swing higher than its initial release point. (ignore friction and air resistance)
Because of the conservation of energy: the pendulum’s potential energy at its highest point is entirely converted to kinetic energy and then back to potential energy. No energy is added, so it can’t exceed its initial height.
Aside from mass, changing what value will impact your kinetic energy?
velocity
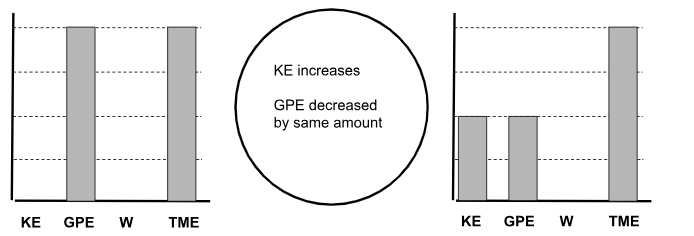
Draw the Initial and Final Energies on an Energy Chart of a skier starting from rest on a snow hill and gaining speed to the halfway point down the hill.
Mr. Urbain decides to add power cleans to his workout routine. HE snatches 125kg bringing the barbell 1.3m off the ground
Calculate the work on the barbell

1,592.5 J
Grabbing a 2 kg weight off the ground, you lift it 1.5 meters off the ground in 2 seconds. How much power did you exert while lifting the weight?
14.7 W
A skier slides down a snowy hill without pushing off. The skier starts with 2000 J of gravitational potential energy. By the time they reach the bottom (height of zero), their kinetic energy is 1500 J. In terms of energy conservation, why is the KE not 2,000J?
Some energy is lost to friction, which dissipates as thermal energy into the ground. The earth-skier system' energy is conserved, but the skier itself looses energy because work was done on him by the snow.
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Instead, all forms of energy can be converted or transformed into other forms.
If a cart of mass 289 kg were to fall down from rest, calculate the KE at point B
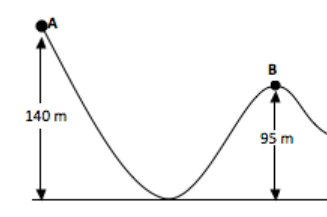
KE = 127,449 J
A sled with a mass of 20 kg starts from rest at the top of a hill that is 15 meters high. Assume the hill is frictionless.
a) Using the conservation of energy, calculate the sled’s kinetic energy when it has traveled one-third of the way down the hill. (15*2/3 = 10m)
b) What is the sled's speed at this point?
a) KE=980J
b) v=9.9m/s
5 seconds
If a person climbs a mountain twice as high as another, does the gravitational potential energy they gain double, triple, or quadruple? Explain your reasoning.
doubles!
When is work present in a system?
When there is an outside force acting on the system (friction, pressing on a gas pedal, etc.). This will cause a change in total energy.
Draw an Energy Chart of a car moving and then rolling to a stop. EXPLAIN!!!
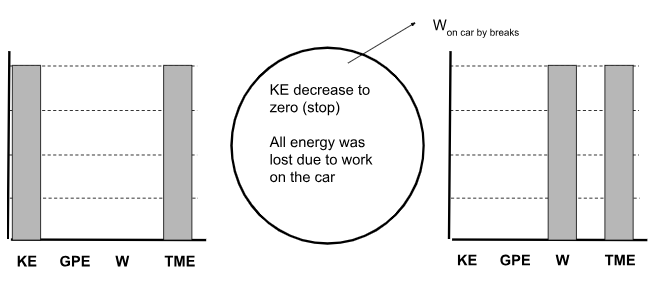
*All energy was lost to work done by the force of the breaks.
*There was a change in KE and total energy
HARD! A boy is pulling a wagon along the sidewalk. It has a kinetic energy of 18.3 Joules. The boy then applies a forward force of 23.6 Newtons for 3.92 meters. What is the final kinetic energy of the wagon?
(HINT: Use W=ΔKE , Where W=Fd)
KEf = 110.81 J
An X-Wing has a mass of about 18,000 kg. If the ship accelerates from rest to 291 m/s in 5 seconds, how much power do it's thrusters exert?
243,881,280 Watts
A skier with a mass of 70 kg starts at the top of a hill (point 1) with a height of 15 m from rest. The skier wants to reach the top of a ramp that is 25 m high (point 5). Assume there is no friction or air resistance. Will he be able to make it to the top of the ramp on the other side?
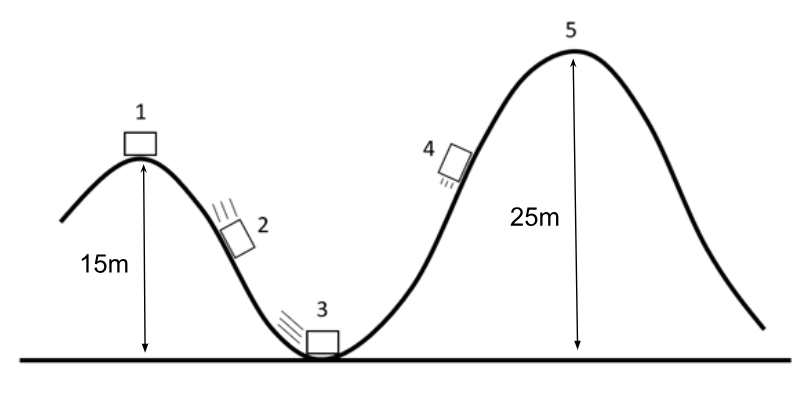
no!
More height means more energy.
The skier does not have enough energy to make it to the top.
If the skier started with an an initial velocity, or had jetpacks, this could have raised the total energy available and maybe he could have made it.