A cart is on an inclined ramp. Where will the cart have the most PE?
At the top of the ramp (highest place)
True or False: An object must move a distance to have work done on it.
True! W = Fd
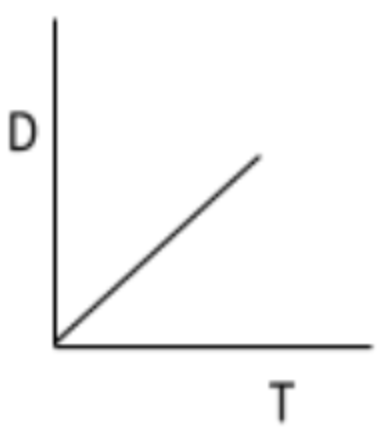
A object has as constant velocity. What would the D vs t graph look like for this object?
What is the equation for potential energy?
PE = mgh
The PE of an object is 100 J. If the object's height is doubled, what is the new PE?
PE = mgh KE = (1/2)mv2 W=Fd
g = 9.8 m/s2
200 J. If height doubles, PE will double.
PE = mgh
What must an object have in order to have potential energy?
A force applied to an object that causes it to move...
Work
The KE of the graph below is...

Increasing because velocity is increasing!
Calculate the kinetic energy of a 3 kg baseball rolling at a velocity of 4 m/s.
PE = mgh KE = (1/2)mv2 W=Fd
g = 9.8 m/s2
24 J
What is needed in order to be able to apply a force to an object?
Energy
What is the relationship between KE and PE?
Inverse (As KE goes up, PE goes down)
A polar bear pulls a fish upwards out of icy water. Did the polar bear do work?
Yes! A force was applied in the same direction as the movement.
What is happening to the KE of the graph below?
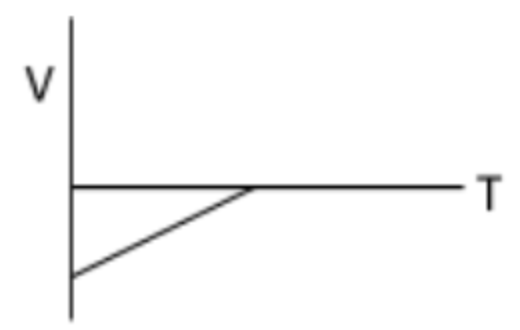
KE is decreasing because velocity is decreasing.
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
KE = (1/2)mv2
An object at a height of 10 m has a total energy of 200 J. If the object is moved to a height of 20 m, what happens to the total energy?
It doubles!
What must an object be doing in order to have kinetic energy?
Moving (be in motion)
Correct the statement: Work is done on an object when the force and distance are different directions.
Work is done on an object when the force and distance are SAME directions.
Describe what is happening to the KE in the following graph.

KE is increasing as velocity is increasing.
Calculate the potential energy of a 5 kg basketball that’s held 2 meters up in the air.
PE = mgh KE = (1/2)mv2 W=Fd
g = 9.8 m/s2
98 J
Energy is measured in the units of....
Joules (J)
A cart is on an inclined ramp. Where will the cart have the most KE?
At the bottom of the ramp (lowest point)
Ice skater A is holding ice skater B and carrying her across the ice for a show. Is ice skater A doing work?
No. The force (upward) is in a different direction than the motion.
How much work is done when you have to apply 25N of force to push a shopping cart up a 3m tall hill?
PE = mgh KE = (1/2)mv2 W=Fd
g = 9.8 m/s2
75 J
An object has 100 J of KE energy. If the velocity of the object is doubled, what happens to kinetic energy?
PE = mgh KE = (1/2)mv2 W=Fd
g = 9.8 m/s2
It increases by a factor of 4 so KE becomes 400 J due to square on velocity in KE Eq.