If something has energy, then it has the ability to ___ ____________ or _______ ________.
DO WORK
CAUSE CHANGE
1) Energy of motion:
2) Energy due to position, structure, or arrangement:
1) Kinetic
2) Potential
2) Units of work (and abbreviation):
1)Force x Distance
2)joules (J)
What energy transformation occurs when you slide your phone on the desk and it stops?
Kinetic Energy --> Thermal Energy (and acoustic)
Turning on a fan
( _______________ --> _______________ )
electric energy transforms into kinetic energy
F = kx
(Hooke's Law)
Units of energy (name AND abbreviation)
joules (J)
The sum of potential and kinetic energies in a system.
MECHANICAL Energy
1) Lifting your friend
2) Carrying your friend
3) Dropping your friend
1) Y
2) N
3) Y
A ball is on top of a 1m shelf. At what height will it have an EQUAL amount of PE and KE once it falls?
0.5m (halfway down!)
Colliding metal spheres into paper
( _______________ --> _______________ & _______________)
Kinetic energy --> thermal energy & acoustic energy
What type of energy is associated with friction?
THERMAL energy
The velocity of a car changes by 3x and it climbs up a 10m mountain.
By how many times does it's KE change by?
9x
15J of work is done to move a large 10kg box across the floor of the classroom.
How much did its K.E. change during this process?
15J
The CHANGE in Kinetic Energy of the object is EQUAL to work.
The roller coaster is at rest at point A. AFTER point A, it is in motion. Zero-point is at the bottom of the structure. There IS friction!
Where is KE the GREATEST?
D (lowest point on the track)
At what point in the fall does KE become GREATER than PE?
After the half-way point
A spring with k=3N/m is stretched to a length of 9m. How much restoring force is the spring applying?
27N
Thermal energy transfer is also called...
HEAT
A bird flies from 100 to 500 feet.
By how many times does it's Potential Energy change by? (?x)
5x
A 800kg car slams on its brakes, stopping in 10m.
How much work was done?
-8,000J
(remember, NEGATIVE work is done if force is parallel to motion BUT in the opposite direction. Also, if KE decreases, work must be negative)
The roller coaster is at rest at point A. AFTER point A, it is in motion. Zero-point is at the bottom of the structure. There IS friction!
At what point(s) does the roller coaster have both P.E. and K.E.?
B, C, D, E
A skydiver jumps from a plane. They start with 392,000J of potential energy. (assume no friction or air resistance)
How much K.E. will the skydiver have 3/4 of the way down?
294,000J
(If the skydiver has fallen 3/4 of the way down, then they have lost 3/4 of their P.E. which has transformed into K.E. 3/4 x 392,000J = 294,000J)
A spring with k=3N/m is stretched to a length of 9m. How much work was done to stretch the spring?
121.5J
Elastic Potential Energy stored in a spring is equal to the work done on the spring.
FINAL JEOPARDY!
You may wager as little as zero (0) or as much as your current score!
Choose wisely! If you get the question wrong, you will lose the amount that you bet!
A campfire provides what THREE types of energy?
LIGHT
THERMAL
SOUND
A 2kg model airplane is flying at a height of 3 meters, moving at 5m/s.
How much MECHANICAL energy does it have?
25J of PE, 58.8J of KE
Total Mechanical Energy: 83.8J
A 10kg box falls off of a 2m shelf.
How much work was done on the box?
196J
(work = Fd and Fgrav = mg, so... work = mgd)
The roller coaster is at rest at point A. AFTER point A, it is in motion. Zero-point is at the bottom of the structure. There IS friction!
If the coaster system has 100,000J of total energy at A, how much total energy does the system have at E?
A) Less than 100,000J
B) 100,000J
C) More than 100,000J
B
A human with a mass of 90kg jumps off a diving platform that is 5m above the water.
What is their velocity at the moment of impact?
(Round to the nearest TENTH)
9.90m/s
A spring with k=3N/m is stretched to a length of 9m.
It is then hooked up to a 1kg cart.
What is the maximum velocity of the cart when pulled on by the spring? (assume no friction or air resistance)
15.59m/s
Elastic P.E. becomes K.E. If you know Elastic P.E., you can plug that in for K.E. and then solve for v.
1/2kx2 = 1/2mv2
0.5(3N/m)(9m)2 = 0.5(1kg)v2
v = 15.59m/s
A 60kg skater is atop a 6m hill. What is the maximum amount of work that friction could do for the skater to still make it to the top of the second hill (4m)?
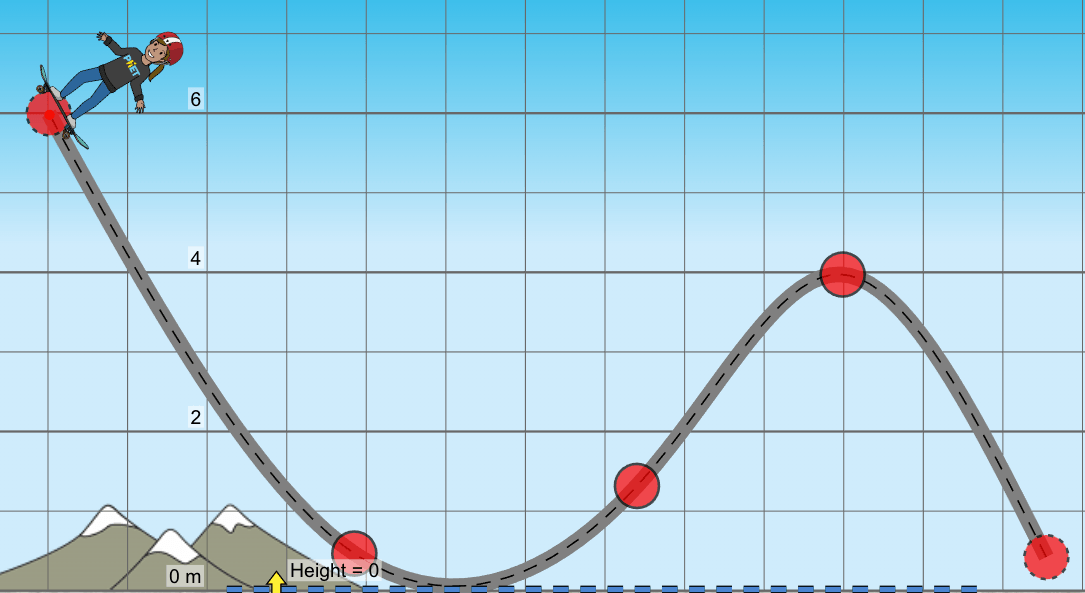
1,176J
The skater starts with 3,528J at 6m of height. They need 2,352J of kinetic to be able to reach a height of 4m (60kg x 9.8m/s2 x 4m = 2,352J). If they start with 3,528J, and only need 2,352J, then the difference, -1,176J, could be "lost" as thermal energy.