In a closed system, pressure and velocity make up
Total pressure
The two basic designs for inlet ducts
single entrance, divided entrance
Subsonic versus supersonic shape?
What causes a compressor stall?
Excessive compressor blade AOA.
A free or power turbine in a turbofan is
a turbine aft of the gas generator turbines, is not connected to the gas generator, may drive the fan
Pascal's Law
Pressure applied to an enclosed or confined liquid is transmitted equally in all directions without loss and acts with equal force on equal surfaces.
Transformer rectifiers produce what type of electric current?
DC from an AC input
The difference between volatility and flashpoint
Volatility: tendency of a fuel to vaporize
Flashpoint: minimum temperature at which a combustible liquid emits a sufficient quantity of vapor that ignition will occur during a momentary application of a flame.
Viscosity is ___ and can be affected by ___
resistance to flow, temperature
(temperature increases, viscosity decreases, and vice versa)
The start sequence
Compressor rpm, ignition, fuel
For subsonic air, the shapes of a diffuser and nozzle are
divergent, convergent
What does this mean for supersonic air?
Primary and secondary air are
Primary air= 25% mixes fuel for combustion Secondary air= 75% cooling and flame control
Indications of a compressor stall (5)
Mild pulsations, engine vibration, loud bangs, drop in RPMs, and rise in turbine temperature.
The sections of a turboshaft and its function
Gas generator: Provides exhaust gas to drive the free/power turbine.
Free/power turbine: Connected to the main transmission, it converts the heat energy to mechanical energy to drive the rotors.
The relationship between linear displacement and multiplied force in a hydraulic system
inverse
Provides a constant rotational input to the generator regardless of engine rpm
Constant Speed Drive (CSD)
The four major considerations in designing a fuel system
1. Operation at low atmospheric pressures.
2. Complexity of the piping system.
3. Cold weather starting.
4. High fuel flow pressure.
Gas turbine engines use a synthetic oil because ___ and the most common synthetic oil used by the military is ___
it is better suited for high temperatures
MIL-L-23699
The different types of starters
DC electric motor and air turbine starter (ATS)
Which is most commonly used on large gas turbine engines?
Three sections of a gas generator are
Compressor, Combustion chamber, turbine
The parts of an axial flow compressor and a centrifugal compressor are
axial flow: Rotors, stators
Centrifugal: impeller, diffuser, manifold
Angle of attack on a compressor blade is determined by
The angle between the chord line of the rotors and the relative wind. The relative wind is comprised of the inlet airflow and the compressor RPM.
For turbojets, turbofans, and turboprops, a majority of thrust comes from
Turbojets: exhaust gases
Turbofans: 30-60% of the total thrust from fan. 40-70% from the gas generator exhaust gases.
Turboprops: 90% from prop. 10% from exhaust gases.
The difference between the accumulator and the reservoir
Accumulator: System shock absorber, supplements system pressure during peak operations, one-time emergency use.
Reservoir: Store fluid, trap impurities, dissipate heat, and purge air bubbles.
Provides power to the start bus
External DC power, internal battery or APU
The three rated thrusts and their differences
Normal Rated Thrust (NRT): thrust @ maximum continuous turbine temperature with no time limitation. This rating serves for cruising speed
Military Rated Thrust (MRT): thrust @ maximum turbine temperature for a limited time (~30 minutes). This rating can serve for takeoff or when additional thrust is desired.
Combat Rated Thrust (CRT): thrust w/ the afterburner in operations. Not based on turbine temperature limitations.
The three subsystems of the engine lubrication system
-Pressure: supplies lubricating oil from the tank to the main engine bearings and the accessory drives
-Scavenge: removes the oil from the main bearings and accessory drives through the oil coolers and returns it to the tank, completing the oil flow cycle
-Breather Pressurizing: 1) minimizes internal oil leakage by encasing the oil sumps (located around the engine bearing) with pressurized air, 2) ensures proper spray patterns of oil across the bearings //connects the individual bearing compartments and the oil tank with the breather pressurizing valve to help minimize oil leakage
The two types of ignitor, which one is more common, and how many you would find in an engine
annular-gap type and constrained-gap plug, annular-gap type, two
Gross thrust and net thrust are different because
-Gross thrust is a measurement of thrust due solely from the velocity of the exhaust gases.
-Thrust that corrects for the effect of inlet airflow velocity is known as net thrust.
WHEN are they the same?
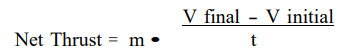
The three types of combustion chambers and their advantages/disadvantages?
Can- ease of maintenance, cause cold spots on turbine.
Annular- even heat, complicated maintenance.
Can-annular- even heat, ease of maintenance, expensive.
How can an exhaust nozzle can cause a compressor stall
(Only applies to variable exhaust nozzle) it could fail to open, causing a back pressure and reverse flow back through the compressor.
The four components of a turboprop and their function
Gas generator, reduction gearbox (keeps the blade tips subsonic. Converts high RPM to low torque and low RPM to high torque), torque meter assembly(torque shaft and reference shaft), and a propeller assembly.
The five valves discussed in this chapter are
Selector Control Valve
Pressure Regulator Valve
Unloader Valve
Check Valve
Relief Valve
The shared function of switches, fuses, and circuit breakers and their differences
used to provide manual and/or automatic control over the flow of electrical power.
Switches provide manual control of power. Located in the cockpit.
Circuit breakers provide a means to manually or automatically interrupt power.
Fuses provide automatic circuit protection in case of an over-load.
The three different kinds of military jet fuel, their respective users, and volatility/flashpoint
JP-4(none primary), highly volatile, low flashpoint -35 °F
JP-5(USMC, USN, USCG), low volatility, high flash point 140 °F
JP-8(USAF), high volatility, low flashpoint 100 °F
The various types of oil contamination, and the most common type of contamination
Metallic particles, carbon, sand, fuel, over age synthetic oil.
Metallic particles from engine wear.
The uses of compressor discharge air
To drive accessories, air conditioning, and cabin pressurization
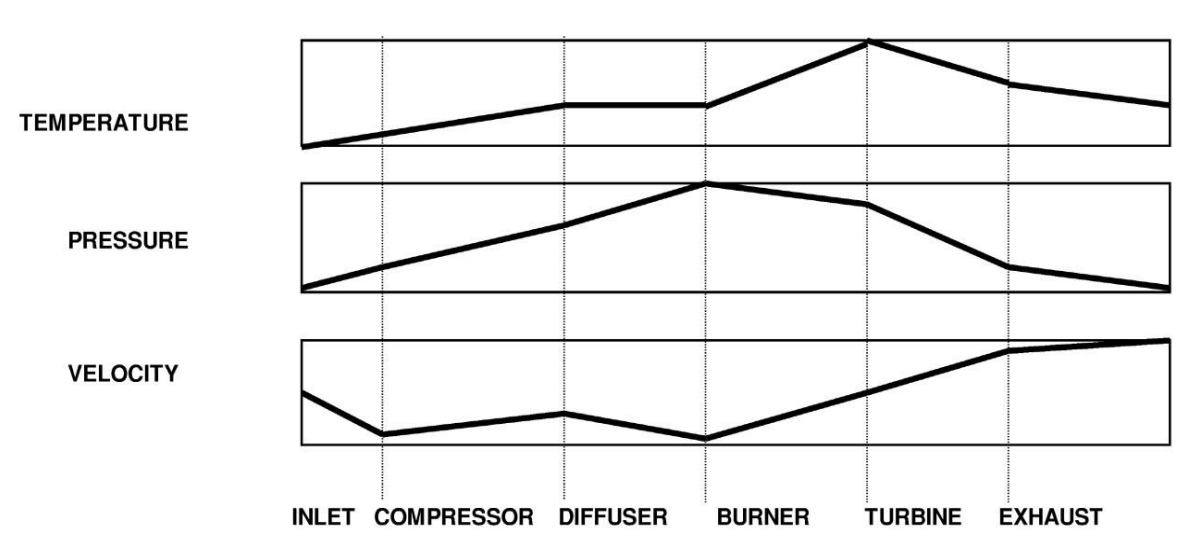
As air goes through a gas turbine, its pressure, velocity, and temperature...
(Inlet-Compressor-Diffuser-Burner-Turbine-Exhaust)
Temperature: Increase-Increase-Steady-Increase-Decrease-Decrease
Pressure: Increase-Increase-Increase-Decrease-Decrease-Decrease
Velocity: Decrease-Increase-Decrease-Increase-Increase-Increase
The parts of a turbine (2) and of an afterburner (4) are (and the function of each stage)
Turbine: stators and rotors... To turn the compressor and accessories.
Afterburner: Spray bars, flame holder, screech liner, variable exhaust nozzle... Secondary air from burner section along with bypassed air (turbofan) is mixed with fuel and ignited in the afterburner duct to augment thrust.
Some of the ways manufacturers decrease the possibility of stalls (4)
Incorporating Split-spool compressor, bleed air valves, variable inlet guide vanes, and variable exhaust nozzle.
The advantages and disadvantages of the turbofan, turboprop, turbojet...
Turbojet: +best high speed and high-altitude performance. -Highest TSFC. Longest takeoff rolls.
Turbofan: +Better TSFC than a turbojet, shorter take off distance, can lift larger weights. -Large frontal area, slower, and cannot fly as high as turbojet.
Turboprop: +Low TSFC, high thrust at low airspeed, able to carry more load requiring short runways. -Heavier and more complicated, limited to 450 knots.
Difference between hydraulic fuse and the actuator
Hydraulic fuse: safety device, installed at strategic locations. Helps guard against leaks by isolating a parts of the system.
Actuator: converts fluid under pressure into linear or reciprocating mechanical motion.
(They are not the same thing at all)
The four types of busses and the type of equipment that is supplied power
Essential bus - safety of flight;
Primary bus- mission equipment;
Monitor/ Secondary bus- convenience items;
Starter bus - starting circuits
Definition of the FCU, how the pilot communicates through it, and its four operational parameters
Fuel Control Unit, through the power control lever (PCL), and
1. PCL inputs. 2. Compressor inlet temperature. 3. Compressor RPM. 4. Turbine inlet temperature.
Generic components of a pressure subsystem
Oil tank (reservoir)
Oil Pump
Instrumentation (Pressure and temperature gauges)
Filters
Filter bypass valve
Oil pressure relief valve
The four kinds of abnormal starts
-"hot start" is defined as exceeding the maximum allowable temperature for the turbine section during start.
-"hung start" describes a situation where the temperature within the turbine section continues to rise, and the compressor rpm stabilizes below normal.
-"false start" occurs when compressor rpm stabilizes below normal, and the turbine temperature remains within limits.
-"wet start" is a situation in which the fuel-air mixture does not light off initially, but has the capability to eventually ignite. (most dangerous)