Sheathed Bacteria
This type of organism prefers a temperature < 20 degrees C
What is a Psychrophile
Are all Fungus aerobic or anaerobic?
All are aerobic, but some are facultative
What does it mean to be Enteric?
Exists in Intestines
Has nuclear bound DNA
What is a Eukaryote
What is the most Common terminal electron acceptor and what are organisms called that use it as a TEA
Oxygen, aerobic organisms
This step in the C/O cycle turns inorganic carbon into organic carbon
Hints:
CO2 + H2O → CH2O + O2
Fixes Carbon: CO2 → Organic Carbon
Or, formation of reduced carbon (foundation of the food web)
Solar energy → chemical energy
What is Photosynthesis?
Uses Light as energy
Phototroph
Most algae are ________ (what do they consume?)
photoautotrophs (light and inorganic carbon)
Protozoa are classified based on _______
Motility
Cyanobacteria (blue green algae) are the only type of prokaryotes to use this process
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
Spherotilus can cause what in WWTP sludge and why?
Poorly settling sludge because the filaments they grow are spread out and float on the surface
Nitrogen is important because it is a major component of________ (name one)
What are: Nucleic Acids, Amino Acids, and Proteins (enzymes)
These types of organism prefer a temperature range of (two answers)
20- 45 degrees C
T > 45 degrees C
What is a
- Mesophile
- Thermophile
Fungus are usually saprotrophs, these are...
organisms that decay dead organic matter
Fecal Coliform Ferments ______ at 44.5 degrees Celsius
Lactose
Has a Size of 0.5 - 2 um (1)
Has a Size of 2 - 200 um (2)
1. Prokaryote
2. Eukaryote
This type of organism does not use O2 as a TEA (1) and instead uses (name one TEA that is not O2)
1. Anaerobic Organism
2. Nitrate (NO3 -), Sulfate (SO4 2-), Fe 3+, Fe 2+, other inorganic elements
This stage in the C/O cycle Converts fixed carbon into CO2
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat (Δ)
Releases Energy
Aerobic Respiration
Uses Chemical Energy : Organic Molecules
chemoorganotroph
Can be non-motile, or flagellated, none are ____
ciliated
The class Mastigophora use ________ to move. Many are parasites, including Giardia
Flagellum 
True or false:
Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic Phototrophic Bacteria that can fix nitrogen gas
True, Cyanobacteria can fix nitrogen gas
This is a group of spiral-shaped/helically coiled bacteria that can cause diseases such as syphilis and Lyme disease
What are Spirochetes?
First step in the Nitrogen Cycle. Carried out by microbes such as Cyanobacteria
Consumes H+, so _____ pH
Typically occurs at a ____ O2 level
Nitrogen Fixation,
increase,
low
An organism that prefers saline conditions
What is a Halophile
True or False: Many Fungi are parasites
True-- Fungi can be parasites for both animals and plants
Fecal Coliform is traditionally used to monitor pathogen levels as it is an indicator organism, what does Fecal Coliform indicate?
DNA has several chromosomes (1)
DNA is a single molecule (2)
1. Eukaryotes
2. Prokaryotes
This organism prefers non-O2 TEA but can use O2
Facultative Anaerobe
This stage in the C/O cycle that is carried out by saprotrophs
What is Decay?
Uses Chemical Energy: inorganic molecules
chemolithotroph
Can be planktonic or benthic, what does this mean?
(in suspension in water)
(in sediments/soil)
The class _________ move by pseudopodia and can cause amoebic dysentery (through Entamoeba histolytica) and eat using phagocytosis
Sarcodina (Amoeba)
True or false:
Cyanobacteria does not cause problematic blooms in eutrophic environments
False, Cyanobacteria can cause harmful blooms and produces cyanotoxins
This process differentiates bacteria based on the thickness of their peptidoglycan layer– the thicker this is the harder it is to penetrate the cell wall. The stain colors the cell depending on this thickness. Leves cells purple, blue, or red– negative or gram positive
What is a Gram Stain?
Biological assimilation is the ___ step in the nitrogen cycle and turns NO3- into _____
2nd, Organic-Nitrogen
These organisms prefer a pH range of (three answers)
1) 5 < pH < 9
2) pH < 5
3) pH > 9
What is a...
Neutrophile
Acidophile
- Alkaliphile
Fungi Cell walls are made out of _____, this allows them to maintain moisture in dry environments and gives them competitive advantage over________ _______
Chitin, heterotrophic bacteria
True or False: Humans are loaded with E.coli
True
Can be unicellular, multicellular, or colonial (2)
1. Prokaryote
2. Eukaryote
This type of Organism has to have O2
What is an obligate aerobe
This process within the C/O cycle converts CO2 → CH4
Fixes carbon
and is carried out by archaebacteria
What is Methanogenesis
Give one example of an inorganic molecule that is commonly used as an energy source
NH4+/NH3 (ammonium/ammonia), H2S (hydrogen Sulfide)
Most Algae preform what type of photosynthesis?
oxygenic photosynthesis
Ciliophora move through hairlike projections called _______
cilia
Purple vs Green Photosynthetic sulfur bacteria:
Which stores sulfur intracellularly?
Purple Photosynthetic Bacteria
This Genus of prokaryotic Sheathed Bacteria is very good at degrading Xenobiotics and is important in WWTP and remediation
What are Pseudomonads
Mineralization in the __ step of the nitrogen cycle, is anaerobic or aerobic, and turns Org-N into _____
3rd, NH4+
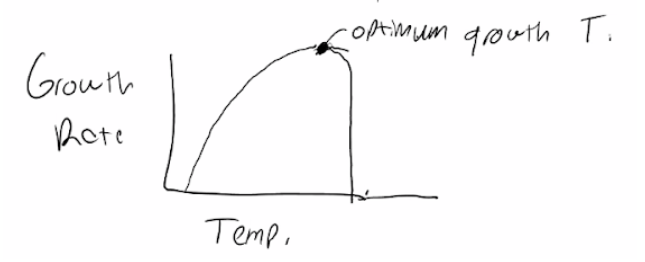
The Q10 rule states that organisms will double for every ___ degrees Celcius
What is 10?
Energy in fungi is primarily stored as _______
glycogen
Gram Negative chemolithotrophs require inorganic energy sources, name one inorganic energy source
NH4+/NH3, H2S, Fe 2+, etc.
Where does ATP production happen in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes: At the cell membrane
Eukaryote: Within the cell itself
A that system has > 2 mg/L dissolved Oxygen
What is an aerobic system
CO2 + H2O → CH2O + O2
Photosynthesis
Organic Molecules are...
Any carbon containing molecule (some exceptions)
Many are primary producers but can cause problems such as.... (name one)
Eutrophication , DO depletion, toxin production
This class of Protozoa are non-mobile and are obligate parasites
Sporozoa (Apicomplexa)
Purple vs Green photosynthetic sulfur bacteria:
Carries out anoxygenic Photosynthesis
Both
This Pseudomonad is the 2nd most studied bacteria after e.coli and can be found in the lungs of persons with cystic fibrosis
What is P. aeruginosa
The 4th step of the Nitrogen Cycle
Oxidation of ammonia to nitrite then nitrate
Nitrification
Within these years Von Leeuwenhoek identified ‘animalcules’ with an early microscope
1670 - 1680
Fungi are important in industry. Which, if any, of the bellow are bacteria and not Fungi?
Penicillin- penicillium candidum
Alcohol and bread Production- Saccharomyces cerveseria, Brettanomyces
Cheese- many (penicillium roqueforti)
No!
Nitrifying bacteria are Gram Negative Chemolithotrophs that include Nitrobacteraceae:
What are the two group that make up Nitrobacteraceae and what process in the nitrogen cycle are they a part of?
NH4+ → NO2- (nitrosomonas, nitrosospira, Nitrosococcus)
Nitrification
NO2- → NO3- (Nitrobacter, Nitrospira, Nitrococcus)
(nitrification)
A system that has < 2 mg DO/L
What is an anaerobic system
CO2 → CH4
What is Methanogenesis
Name the three carbon containing molecules that are not considered Organic Molecules
Carbonates (H2CO3, HCO3-, CO32-), Carbon dioxide, and Carbides
What Phylum of Algae does this describe:
Chlorophyll a & b. Carbs stored as starch
Cellulosic cell wall
Freshwater, marine, or terrestrial
Can have harmful algae blooms
E.g. cladophora- filamentous algae
What is Chlorophyta/ Green Algae
Plasmodium belongs to what class of Protozoa and causes what disease
Sporozoa (Apicomplexa)
Plasmodium- causes malaria
Purple vs. green photosynthetic sulfur bacteria:
Can tolerate lower levels of light and a higher concentration of H2S2
Green photosynthetic sulfur bacteria
Aztobacer and Rhizobacteria are ______ fixing bacteria
Nitrogen
Reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas
is an _______ process
Denitrification, Aerobic
(Carried out by Pseudomonas, Thiobacillus)
What early 1800s event in Ireland forced people to think about microbiology?
Irish potato Blight– caused by fungus (Phytophthora infestans) , killed about one million people from starvation
True or False: Fungi are mostly Aquatic
False:
Most terrestrial, some aquatic
Colorless Sulfur Bacteria is colorless because.....
It does not use photosynthesis
DO < 2 mg/L AND NO3- (nitrate) is present
Anoxic System
Converts fixed carbon to CO2
Aerobic Restoration
CO2 dissolved in water becomes this
H2CO3
(H2O + CO2 = H2CO3)
What Phylum of algae does this describe?
Includes yellow-green, golden-brown, and diatoms
yellow - green and golden-brown
Chlorophyll A and C
Store energy as lipids- unsaturated
Mainly freshwater, some marine
Diatoms
Ubiquitous: freshwater, marine, and terrestrialCell wall contains silica
Shell called ‘frustule’
Dead diatoms constitute ‘diatomaceous earth’
Importance primary producers
Chrysophyta
Vorticella are stalked protozoa that help clean bulk water in WWTP, what class do they belong to?
Ciliophora (ciliates)
Which type of Prokaryotic Purple/Green photosynthetic bacteria is this describing:
1. Can only tolerate low levels of H2S
2. Is a Facultative Anaerobe
Purple/Green photosynthetic non-sulfur bacteria
Azotobacter is found in _____
Soil
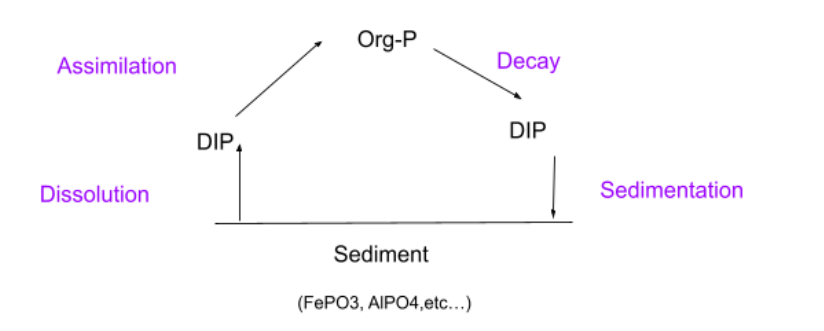
Name all the steps of the Phosphorous cycle
In the 1800s the French chemist Louis Pasteur invented this ground breaking way to keep food fresh
What is Pasteurization?
True or False: Fungi can be unicellular or multicellular
True
Colorless Sulfur Bacteria uses _______ ________ as energy
Reduced Sulfur
The process of turning inorganic carbon into organic carbon
What is Carbon Fixing
This organism uses Organic Carbon as a carbon source
Heterotroph
Classified as protozoa and alga
No cell wall, usually flagellated
Can live phototrophically or heterotrophically
Commonly found in freshwater with high organic content
Chlorophyll a and b
Store energy as paramylon
Euglenophyta
Least specialized of the four Classes of protozoa
Sarcodina (Amoeba)
Oxygen is toxic to Cyanobacteria (true or False)
False, Cyanobacteria uses oxygenic photosynthesis and needs oxygen- they are aerobic photoautotrophs
________ is found in root nodules in plants and fixes nitrogen
Rhizobacteria
A theory by Louis Pasteur in 1861 that theorized that living creatures could arise from non-living matter
What is the spontaneous generation of life theory
What Fungi is this describing:
Multicellular, reproduce via spores, have thread-like filaments called hyphae. (group of hyphae is called mycelium)
MOLD
What domain are Methane Forming archaebacteria in?
Archaebacteria-- Found in extreme environments, DNA difficult to denature
What is CH2O
What is a Carbohydrate?
This organism uses inorganic carbon for carbon source
Autotroph
Mainly marine, some freshwater
Typically planktonic
Generally bi-flagellated
Mainly heterotrophs, most are also phototrophs
Cellulose/silica cell wall (armor like)
Can cause harmful algal blooms (HABs)
Red Tides: Gonyaulax and others
Paralytic shellfish poisoning
Gonyaulax and pfiesteria
Dinoflagellates
which is false:
Protozoa are all unicellular
Protozoa cannot survive in low DO environments
Protozoa CAN survive in low DO environments
list the order of Prokaryotic Phototrophic bacteria that you would find in a lake's water column from top to bottom
1.Cyanobacteria
2. Purple/Green photosynthetic non-sulfur Bacteria
3. Purple photosynthetic sulfur bacteria
4. Green Photosynthetic sulfur bacteria
Amount of deaths annually that occur from lack of access to clean water
10 million
Methanogens are Strict________
and convert (CH3COOH) → CH4 + CO2 and are important in ______ ______ in WWTP
Anaerobes, anaerobic digestors
Eutrophication can cause
an overabundance of algae and plants. The excess algae and plant matter eventually decompose, producing large amounts of carbon dioxide. This lowers the pH of seawater, a process known as ocean acidification
Name all 4 classes of protozoa and their mobility type
Mastigophora: use flagellum
Sarcodina (amoeba): use pseudopodia
Ciliophora: move via cilia
Sporozoa: no movement