German meteorologist and physicist known as the "Father of Plate Tectonics"
Alfred Wegener
A form of the mineral halite (NaCl) is actively used as a food ingredient/seasoning and is better known by this, more commonly used, name.
Salt
This is the term used for the position on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake source.
Epicenter
The approximate age of the Earth
4.6 billion years
This is the area of the glacier below the snowline in the image below:
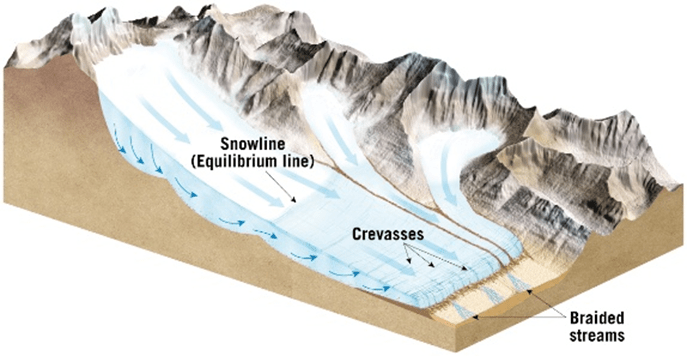
Zone of ablation/wastage
This portion of the atmosphere protects us from harmful UV radiation
Ozone layer
The largest layer of the Earth's interior
Mantle
This is the most abundant mineral group found in the Earth's crust
Silicates
This type of seismic wave arrives first at a seismograph station.
P waves
Fossils are only found in these types of rocks.
Sedimentary
This is an irregular ridge of till laid down at the terminus of a retreating glacier.
End moraine
This is what happens to atmospheric pressure as you go up in elevation/altitude
It decreases
The asthenosphere is part of this layer of the Earth
Mantle
Diamond
This type of lava flow has smooth surfaces and often looks like ribbons or braids of rope
Pahoehoe
This is the definition of an unconformity
A gap in the geologic record
In the image below the North Pole is tilted 23.5 degrees towards the Sun, known as this 'special day' in the Northern Hemisphere.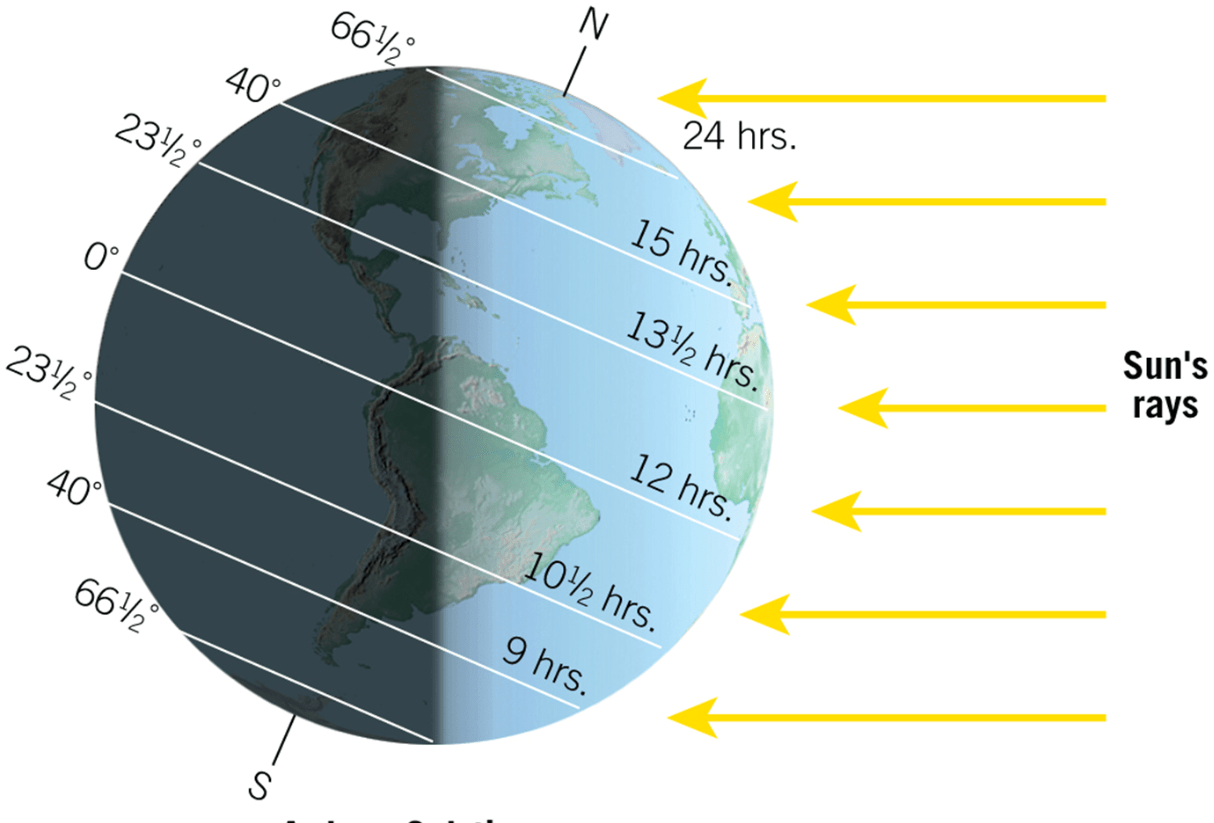
Summer Solstice
This type of fault is shown in the illustration below:
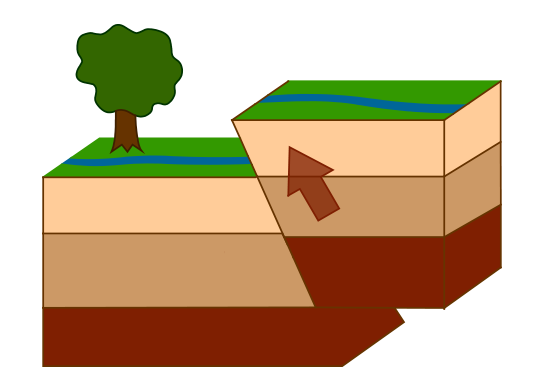
Reverse fault.
This is the process by which sediments are turned into sedimentary rocks.
Lithification
Triangulation, a method used to locate the epicenter of an earthquake, requires data from this many seismic stations.
Three (3)
This relative dating principle refers to the idea that the oldest strata are at the bottom and the newest strata are on top
Principle of Superposition
The LGM, or Last Glacial Maximum, occurred approximately this many years ago.
20,000
This is the lowest layer of the atmosphere
Troposphere
Normal dip-slip fault
Why are intrusive igneous rocks often characterized as coarse-grained?
They cool slowly at depth (deep underground), allowing large crystals to grow
This is the measurement of a fluid's resistance to flow.
Viscosity
Paleozoic Era
This is the equation for stream discharge
Stream cross-sectional area multiplied by stream velocity
This mechanism of heat transfer is responsible for the circulation of heat INSIDE the cooking pot illustrated below.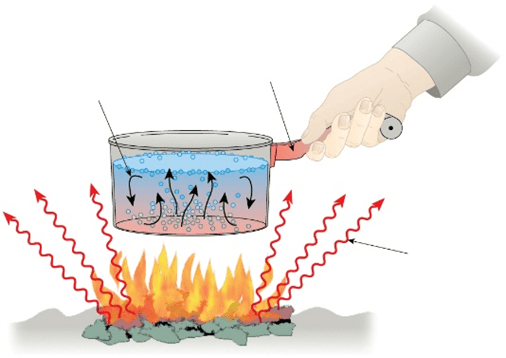
Convection
There are this many major tectonic plates on Earth
What is the chemical formula of the cave-forming mineral calcite?
CaCO3

Mauna Loa
90%
This term is used to describe when large pieces of ice break off a glacier, into the water.
Calving
These types of organisms drift with ocean currents and make up most of the Earth's biomass
Plankton
The San Andreas Fault is an example of this type of plate boundary
Transform
This is the most common mineral/mineral group in the Earth's crust.
Feldspars
Pyroclastic flows
This supercontinent existed during the late Paleozoic, and was the most recent supercontinent
Pangaea
Accumulation exceeds ablation
These types of air masses cause lake effect snows
Continental polar (cP)