Substrate is rate limiting in this order of kinetics
What is first order kinetics?
This enzyme can be increased in cardiac and muscle disorders and has 3 isoenzymes
What is creatine kinase?
This enzyme is a specific hepatocellular marker
What is ALT?
In animals, amylase attacks this kind of bond in polysaccharides
What is an alpha 1,4 linkage?
This is the optimum pH for ACP
What is 4.5-7?
This class of enzyme adds water, ammonia or carbon dioxide across double bonds to break them
What are lyases?
Enzyme is rate limiting in this order of kinetics
What is zero order kinetics?
This molecule damages artery walls and promotes atherosclerosis
What is homocysteine?
ALT belongs to this class of enzymes
What is transferase?
Lipase is this class of enzyme
What is a hydrolase?
This disease caused by a disorder of fat metabolism results in a high ACP level, but is not a prostatic condition
What is Gaucher's disease?
Inorganic enzyme cofactors are also known as this
What are activators?
The name for this kind of graph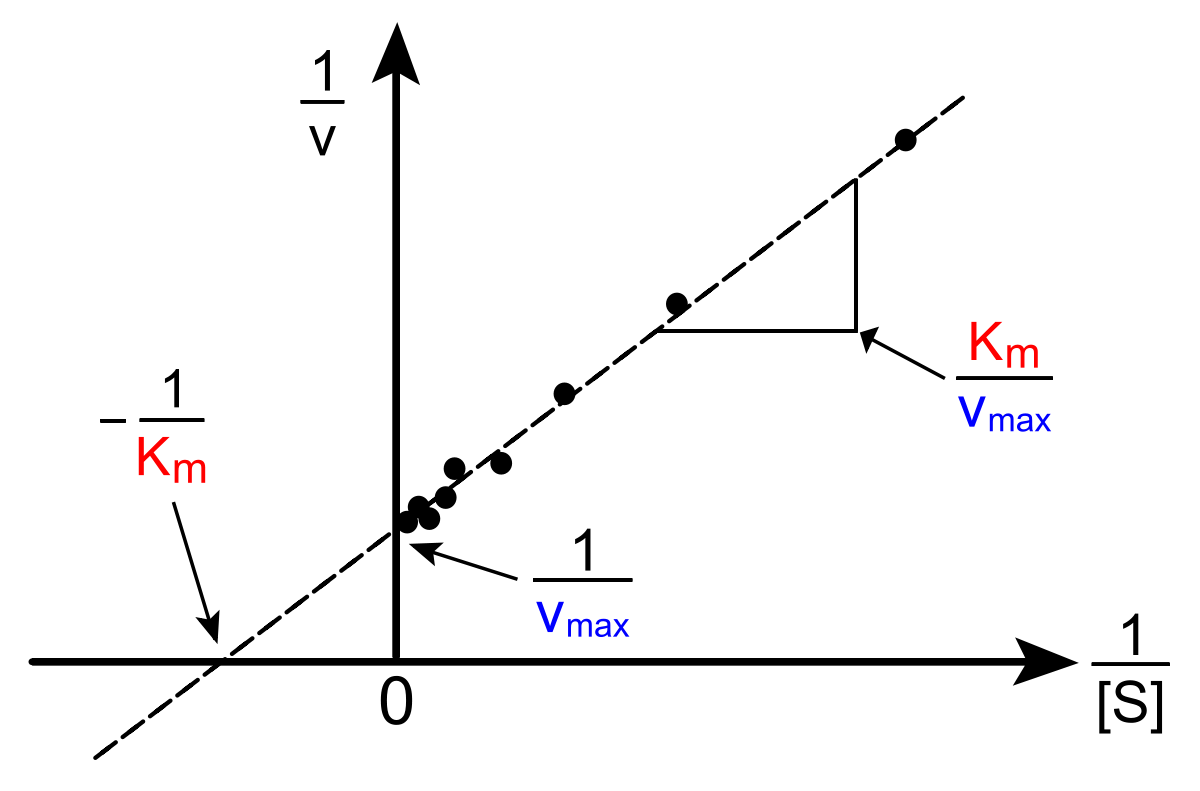
What is a Lineweaver-Burk plot?
This analyte would be ordered to monitor the severity of CHF
What is BNP?
This enzyme is increased in alcoholics
What is GGT?
This enzyme is more specific for the pancreas
What is lipase?
This enzyme exists as either a free or a complexed form
What is PSA?
In a coupled enzymatic reaction, this is the name of the reaction that we can directly measure (the final step)
What is the indicator reaction?
The kind of inhibition where increased substrate leads to increased inhibition
What is uncompetitive inhibition?
This is the activator required for CK
What is magnesium?
This enzyme has abnormal types called Regan and Nagao
What is ALP?
These compounds inhibit AMS activity
What are triglycerides?
PSA is considered abnormal when it goes above this concentration
What is 4.0 ng/mL?
This protein increases in inflammatory conditions and promotes atherosclerosis
What is CRP?
The kind of inhibition where Km is unaffected but Vmax cannot be reached
What is noncompetitive inhibition?
Hemolytic anemias would result in an increase of these 2 isoenzymes of LD
What are LD1 and LD2?
This is the coenzyme required for AST
What is pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)?
These are two of the methods for measuring serum amylase
What are Amyoloclastic, Saccharogenic, Chromogenic and continuous monitoring?
ACP belongs to this class of enzyme
What is hydrolase?
This enzyme can be measured by inhibition with tartrate
What is ACP?