The minimum energy required for reactants to reach the transition state.
What is activation energy?
Two environmental factors that can affect reaction rates.
What are pH and temperature?
When a molecule binds to this type of site, it causes a change in enzyme shape and activity.
What is an allosteric site?
This statement best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme.

What is C?

The temporary structure formed when an enzyme binds its substrate.
What is the enzyme–substrate complex?
Increasing temperature initially increases enzyme activity because it increases this form of energy.
What is kinectic energy?
Increasing substrate concentration restores enzyme activity when this type of inhibitor is present.
What is a competitive inhibitor?

This statement best explains how the enzyme speeds up the reaction.
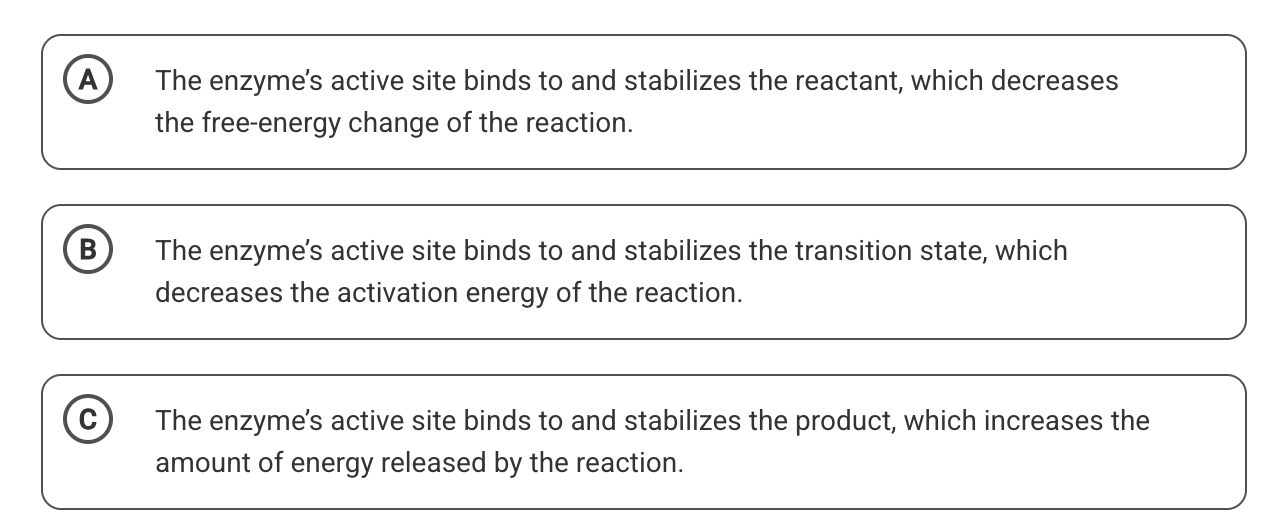
What is B?

A loss of enzyme shape and function caused by changes in temperature or pH.
What is denaturation?
A change in pH alters enzyme activity by disrupting these bonds that maintain enzyme shape?
What are ionic and hydrogen bonds?
When this type of inhibitor is present, Enzyme activity decreases even when substrate concentration is high.
What is a non-competitive inhibitor?

This statement best predicts the effects of increasing the substrate concentration while keeping the inhibitor concentration constant.

What is D?

This term describes the inactive protein portion of an enzyme that lacks its required helper component.
What is an apoenzyme?
An enzyme functions optimally at pH 2. This suggests the enzyme is most likely adapted to this kind of environment.
What is acidic?
This regulatory mechanism occurs when the final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme earlier in the pathway.
What is feedback inihibition?

This statement best helps justify the researcher's claim.

What is B?

This type of cofactor is an organic molecule, often derived from vitamins, that assists enzyme function.
What is a coenzyme?
This regulatory mechanism occurs when the final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme earlier in the pathway.
What is feedback inhibition?
Feedback inhibition is this type of inhibition.
What is allosteric?

This must remain the same for all trials of the experiment.
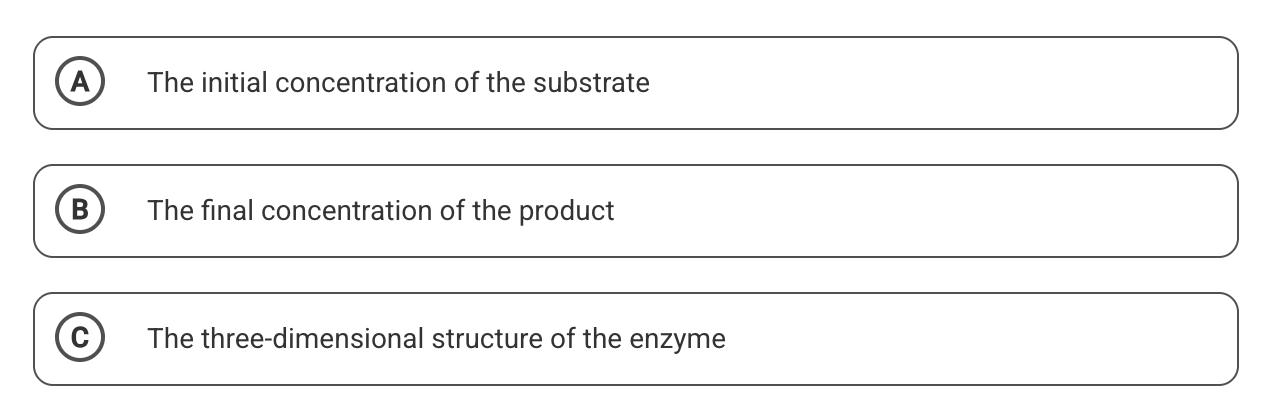
What is A?
