Enzymes belong to which category of organic molecules?
Proteins
What happens to enzyme activity at very high temperatures?
The enzyme denatures
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
Chloroplast
What part of the chloroplast contains the thylakoids stacked into grana?
Thylakoid membranes
Which stage of photosynthesis takes place in the stroma?
Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions)
What is the role of an enzyme’s active site?
Binds to the substrate
In an experiment, catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide. Which products are released?
Water and oxygen
During which stage of photosynthesis is oxygen produced?
Light-dependent Reaction
What product of the light-dependent reactions is needed by the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH
What does P and Q represent?
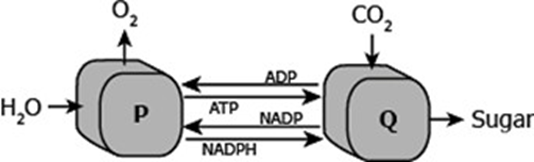
P- light-dependent reaction
Q- Calvin Cycle (light-independent reaction)
Identify a and c

a. enzyme
c. substrate
A graph shows enzyme activity vs. temperature. What is the optimum pH and temperature?
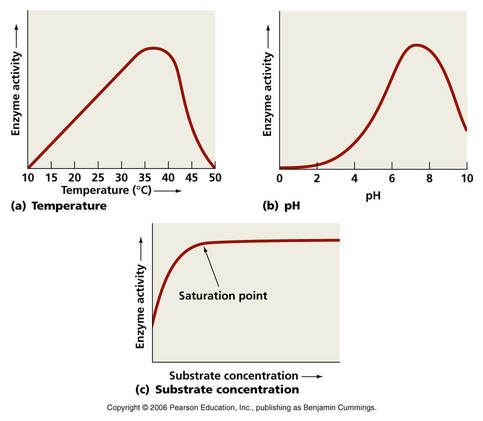
Temp 35-40
pH 7-8
What is the main product of the Calvin cycle?
Glucose
Which waste product of the light-dependent reactions is released into the atmosphere?
Oxygen
The light-dependent reactions create two energy-storing molecules. Name them.
ATP and NADPH
Why are enzymes specific for only one substrate?
The active site has a unique shape (lock-and-key)
What is happening to the enzyme at low temperature?
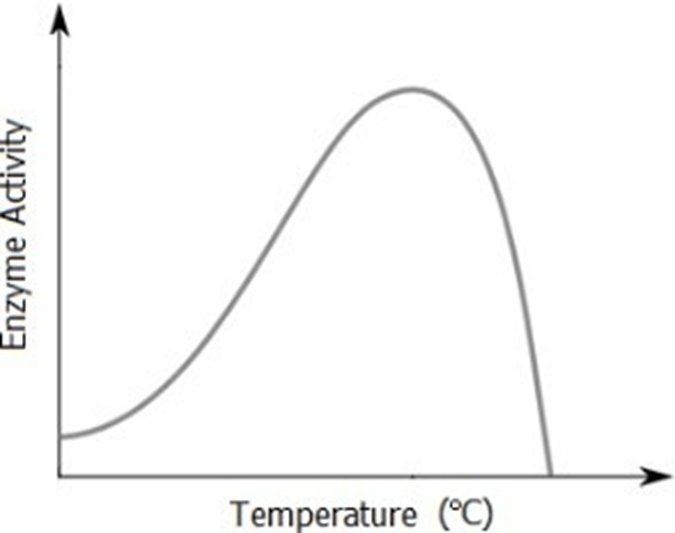
Molecules (enzyme and substrates) are moving slower causing less collisions so fewer products are produced
What is the overall photosynthesis equation.
CO2 + H2O (sunlight) → Glucose + O2
What do the light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle have in common?
Both are needed for photosynthesis; products of one are used in the other.
Why are enzymes not considered reactants in a chemical reaction?
They speed up reactions but are not consumed.
Glucose isomerase converts glucose into fructose in the body. Can another enzyme perform the same reaction? Why/Why not?
No, enzymes are specific for their substrate.
At what pH do both enzymes work?
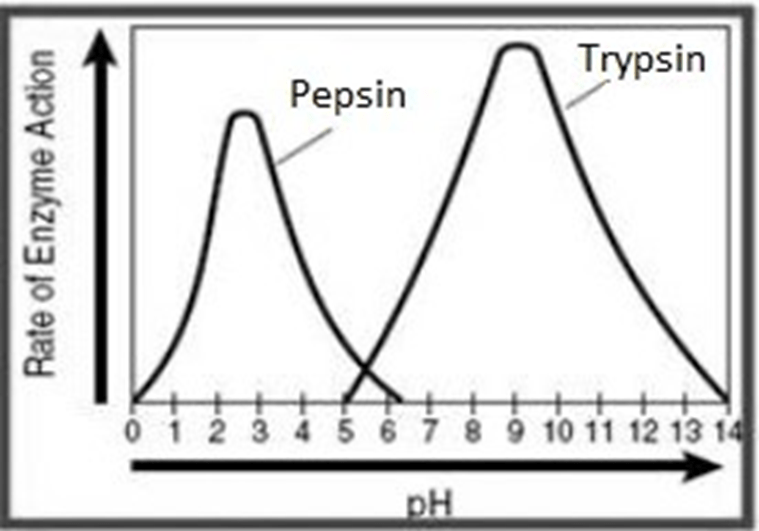
5.5
If photosynthesis stopped worldwide, what would happen?
No oxygen would be produced, no glucose would form, food chains would collapse, and most life would die.
In an experiment with pondweed, photosynthesis was fastest at 30°C. What does this suggest about temperature’s effect?
Photosynthesis has an optimal temperature; too low or too high slows the rate.
How do light and temperature interact to affect photosynthesis?
Both must be at optimal levels; insufficient light or extreme temperatures limit the rate.