A type of muscle contraction where the muscle shortens while producing force. This occurs when the muscle contracts against resistance, such as lifting a weight or pushing against an object.
Concentric contrations
Involves active movements that gradually increase ROM and prepare the body for exercise or activity
Dynamic
What muscle group allows for flexion of the knee?
Hamstrings
What muscle is this?

Latissimus Dorsi
the lengthening phase of a muscle contraction, where the muscle is contracting while it is being stretched
Eccentric contraction
This involves holding a stretch in a stationary position, improving flexibility and aiding recovery
Static
What muscle group is the primary extensor of the Hip?
Hamstrings
What muscle is this?
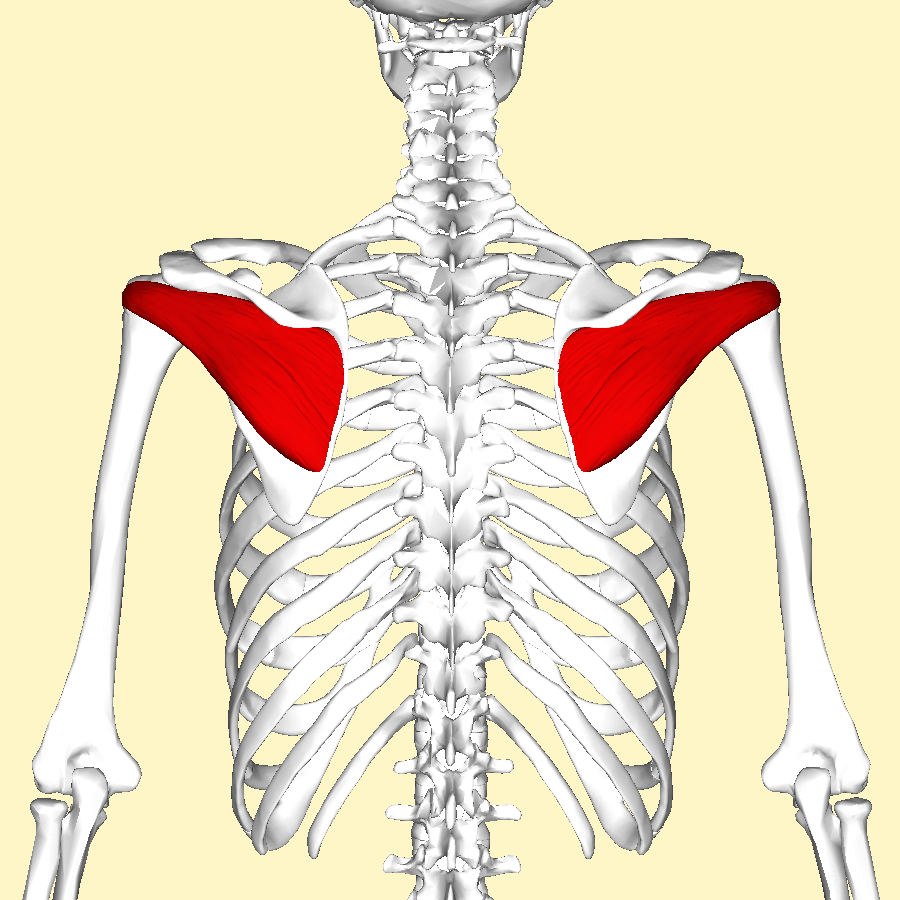
Teres Minor
A type of exercise that refers to movement at a constant speed regardless of the amount of resistance applied. Muscles contract at a constant speed in isokinetic contraction. This consistency allows muscles to gain strength uniformly all through the range of movement
Isokenetic
Involves a partner or resistance to stretch a muscle, followed by a contraction of that muscle, and then a deeper stretch, aiming to increase flexibility and range of motion.
PNF
What is the primary muscle group that extendes the Knee?
Quadriceps
What Muscle is this?

Supraspinatus
The contracting of muscles against a stationary object or force, without changing the length of the muscle or the angle of the joint, promoting strength and endurance.
Isometric
Involves using momentum to extend muscles and joints beyond their normal range of motion. It is characterized by quick, bouncing movements that create force and acceleration.
Ballistic
Which muscle group assists with internal and external rotation of the hip?
Gluteal muscles
This involves muscle contractions where the tension remains constant while the muscle length changes, meaning the muscle either shortens or lengthens during movement.
Isotonic
A technique where an external force is used to stretch a muscle without the individual's active contribution. It involves holding a stretched position for a period of time, typically 15-30 seconds.
Passive
Which muscle group allows for hip abduction?
gluteal muscles