DKA is most often seen in this type of diabetes.
What is type 1?
This IV electrolyte is the drug of choice to prevent seizures in preeclampsia.
What is magnesium sulfate?
The type of ultrasound probe is used for central line placement.
What is a linear probe?
Torsades de pointes is treated acutely with IV administration of this electrolyte. 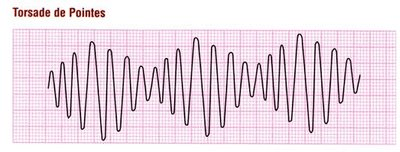
What is magnesium?
According to ATLS, a chest tube should be placed in this intercostal space.
What is the 5th?
This diabetes drug class is strongly associated with euglycemic DKA.
What are SGLT2 inhibitors?
This is the leading cause of postpartum hemorrhage
What is uterine atony?
This ultrasound view is most commonly used to rapidly assess for pericardial effusion in the ED or ICU.
What is the subxiphoid (subcostal) view?
This is the definitive treatment for refractory, life-threatening hyperkalemia.
What is hemodialysis?
A patient with referred right shoulder pain with suspected liver injury has this sign.
What is Kehrs sign?
This hormone injection can be given IM for severe hypoglycemia when IV access is not available.
What is glucagon?
This is the safest imaging modality to evaluate for pulmonary embolism in pregnancy if chest X-ray is normal.
What is ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan?
In a hypotensive trauma patient, this POCUS exam evaluates for free fluid in the abdomen and pericardial space.
What is the FAST exam (Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma)?
This beta-agonist inhaled medication helps shift potassium into cells.
What is albuterol?
This life-threatening diagnosis should be suspected in trauma patients with refractory hypoxemia, petechial rash, and neurologic changes.
What is fat embolism syndrome?
Unlike DKA, HHS typically does not have this key laboratory finding.
What is significant ketoacidosis?
A firm, high-rising uterus with sudden maternal collapse after delivery may indicate this rare but deadly complication.
What is amniotic fluid embolism?
A “barcode” or “stratosphere” sign on lung POCUS suggests this critical diagnosis.
What is a pneumothorax?
Loss of deep tendon reflexes and respiratory depression may indicate toxicity from this electrolyte.
What is hypermagnesemia?
This medication is often considered within 3 hours of trauma to reduce mortality in bleeding patients.
What is transexamic acid (TXA)?
This electrolyte must be monitored closely and replaced before giving insulin if severely low in DKA.
What is potassium?
This postpartum hypertensive emergency can present with seizures and may be complicated by intracerebral hemorrhage.
What is eclampsia?
This is the most sensitive lung POCUS finding for pulmonary edema in critically ill patients.
What are B-lines (comet-tail artifacts)?
This devastating neurological condition can occur if hyponatremia is corrected too rapidly
What is central pontine myelolysis (CPM) or osmotic demyelination syndrome?
In a patient with pelvic fracture and hemodynamic instability, this is the initial stabilization maneuver recommended.
What is application of a pelvic binder (pelvic sheet wrap)?