What is movement of individuals into a population
This eats dead animals. A vulture is an example.
What is a scavenger?
The difference between weather and climate.
What is weather = day-to-day conditions and climate = long-term average patterns?
Three types of diversity.
What is genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity?
What percentage of energy is transferred from trophic level to trophic level?
What is 10%?
The most common population distribution. This is seen in schools of fish, herds of animals, or flocks of birds. (Clumped, Random, or Uniform)
What is clumped?
The difference between food web and food chain.
What is a food chain shows a single path of energy flow and a food web shows interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
This zone supports photosynthesis. (Aphotic or photic?)
What is photic?
Found only in a specific geographic area (example: lemurs are only in Madagascar).
(Endemic or extirpation?)
What is endemic?
The leading cause of biodiversity loss.
What is habitat loss?
The six levels of ecological organization from smallest to largest.
What is Organism → Population → Community → Ecosystem → Biome → Biosphere?
Which takes longer – Primary or Secondary Succession?
Primary succession takes longer (starts with bare rock, no soil).
The four types of wetlands.
What is marsh, swamp, bog, and fen?
Local disappearance of a species from an area; extinction = global disappearance.
(Endemic or extirpation)
What is extirpation?
Which of the following is an example of uniform distribution?
A school of fish
Elephants in the savannah
Wildflowers in a field
Trees at an apple farm
What is 4?
The graph shows exponential growth or logistic growth...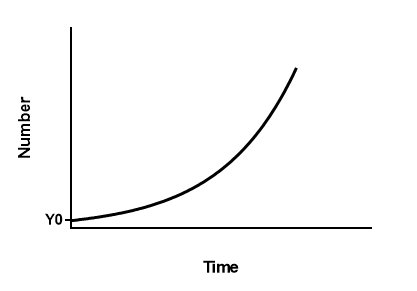
What is exponential growth?
These are the first organisms to colonize barren environments. Lichen is an example.
What is pioneer species?
Permanently frozen soil layer, common in tundra biomes.
What is permafrost?
Three causes of biodiversity loss.
What is habitat destruction (greatest cause), invasive species, pollution, overexploitation, climate change?
True or False? Biodiversity tends to decrease closer to the equator.
What is false?
Increases closer to the equator (remember where tropical rainforests are located).
The difference between density-dependent and density-independent.
Density-dependent factors are influenced by population size (more intense as population grows) where density-independent factors affect a population regardless of its size.
The species with a disproportionately large impact on an ecosystem (example: sea otter keeps sea urchin populations low, protecting kelp forests).
What is a keystone species?
Area where freshwater meets saltwater (river meets ocean); high productivity due to nutrient inputs from land and mixing of water.
What is an estuary?
Describe two pros and two cons of conservation efforts, using specific examples.
What is ...
Pros: protects species and ecosystems (e.g., protected areas preserve habitats), supports sustainability and ecosystem services.
Cons: can be expensive, may limit land use or economic development; may create conflicts over resource use.
TEST QUESTION!
The difference between mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
TEST QUESTION!
What is... Mutualism = both species benefit, Commensalism = one species benefits and the other is unaffected, and Parasitism = one species benefits and other is harmed.