What does “anthropocence” mean?
“The age of man”
What three things determine global climate patterns?
The sun, Global wind patterns, ocean currents.
What happens in the “intolerance” zone on the Goldilocks Curve?:
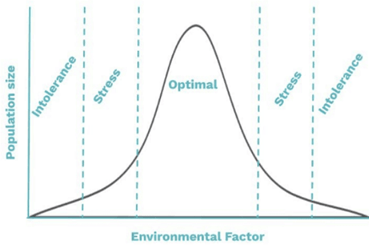
the population dies out, extinction or does not exist
What occurs when a new ecosystem develops where there was none before?
Primary Succession
Which biome has large amount of rain and little variation in temperature; forests near equator; greatest diversity of organisms on earth?
-tropical rainforest
WHAT ARE THE 3 CONSERVATION METHODS?
saving one species at a time, preserving habitats and ecosystems, legislation and treaties
What are the main ways humans have impacted the environment over the ages
- Hunter gatherers
- Agricultural revolution
- Industrial revolution
What are the 5 soil forming factors and which one is most important?
Parent material, climate, time, relief, biology. The Climate is most important
This level of ecological organization includes all the populations of different species that live in the same place at the same time.
What is community?
What is a Feedback Loop?
Feedback Loops any process that increases (positive feedback) or decreases (negative feedback) a change to a system
Which biome contains coniferous forests and has a short growing season?
Boreal forest
What is the extinction of a large percentage of all species in a relatively short period of time
Mass extinction
What are the three world views of environmental ethics. Put them in order of most anthropocentric to most ecocentric
-planetary management worldview-
-stewardship worldview
-ecocentric worldview
Label which steps points A and B are in the water cycle
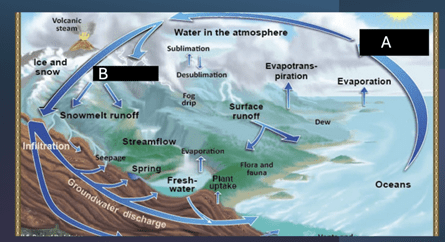
A=CONDENSATION
B=PRECIPITATION
According to island biogeography, islands with these two characteristics have the highest species richness
What are “large size” and “being near the mainland”?
If a keystone species is removed from community, what are three possible effects of its loss on the ecosystem
What is Food web crashes, population crashes, extinction
Which biome has hot, dry, summers, and mild, wet winters; primarily in coastal areas
-Chaparral
What are animals that have been identified to be in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant part of its range
Endangered species
What is the study of the interaction of humans with the natural environment
- Environmental Science
Soil varies in what physical properties?
Texture, porosity, permeability, and structure
Name the 5 levels of organization in order from smallest to largest
Organism, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biosphere
When the competition occurs within members the same species
What is intraspecific?
Which biome is the driest place on earth?
-deserts
What is the number of species in an area
Species richness
Mark-Recapture estimates what?
Population size
WHAT ARE THE MAJOR RESERVOIRS OF THE PHOSPHORUS CYCLE?
rocks, water, sediments, soil
Name the three types of reproductive isolation, bonus: which is the most important?
What is Geographic, Behavioral, and Temporal Isolation (Bonus: Geographic is most important)
What are some examples of predator strategies?
Structural: Natural Weapons such as fangs and claws and they have flexible bodies and larger size
Ambush Technique: Stalk a victim, Gape and Suck, Keen eyesight, and venom
A large region with a specific climate, plants, and animals.
What is a biome?
Three impacts of the bottleneck effect?
Interbreeding, more genetic diseases, and low survival rate