Which EVS argues that technology provides solutions to environmental problems even when humans are pushing natural systems beyond their stable limits?
Technocentrism
Identify two transformations in the carbon cycle.
Respiration, photosynthesis, combustion of fossil fuels
What is the term for the evolutionary process sometimes referred to as 'survival of the fittest'?
Natural selection
Name three greenhouse gases.
carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour, fluorinated gases
Place these solid domestic waste management strategies in order from most sustainable to least sustainable.
Incineration, recycling, reuse, landfill
Landfill, incineration, recycling, reuse.
In which city was the 2015 climate agreement signed by nearly all 197 countries?
Paris
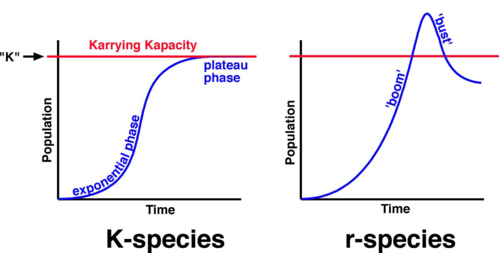
What is the term for the maximum number of species that can be sustainably supported by a given environment?
Carrying capacity
What is this the calculation for?

Simpsons Diversity Index
Of these countries, which produced most energy from nuclear and which produces most energy from fossil fuels? Denmark, France, Japan, Philippines, Malawi
France - 72% nuclear
Japan - 87% fossil fuels
Describe a countries population structure that is in stage 4 of the DTM.
Contracting base due to alow fertility rate (possibly below replacement level) and a stacked peak due to a high life expectancy. Most older economically active.
Who is the Swedish climate activist who initiated the global school strikes?
Greta Thunberg
What is the name of the cell that controls weather over the tropics?
Hadley cell
Identify three natural causes of past mass extinctions.
When considering mitigation approaches, what does CCS stand for?
Carbon capture and storage
Name the 5 values of nature.
intrinsic, scientific, sociocultural, economic, ecological
What are the names of the most extreme ecocentric and technocentric views?
Deep ecologist and cornucopian
What type of population growth curve is expected for r-selected species?
J population curve
Identify three factors that make species more prone to extinction.
small pop size, limited distribution, high degree of specialisation, low reproductive potential, non-competitive behaviour, high trophic level, long migration routes
Which greenhouse gas has the greatest warming potential?
Fluorinated gases
Distinguish between sustainability and sustainable development.
Sustainability looks at the rate of use of global resources, whereas SD looks at the ability to meet the needs of people now and in the future.
Which NGO's 'Save the Whale' campaign in 1977 led to the worldwide ban of commercial whaling in 1986?
Green Peace
What is the term given to producers that convert sunlight energy into chemical energy?
Photoautotrophs
What is the purpose of CITES?
international agreement to monitor and confiscate endangered species that are internationally traded.
Describe one negative feedback that affects the climate.
Cloud cover and atmospheric albedo
Changing vegetation and uptake of CO2
Distinguish between natural resource and natural capital.
Resource implies that it is there to be used by humans, capital refers to the stock of resources that are managed to provide ecosystem goods and services.