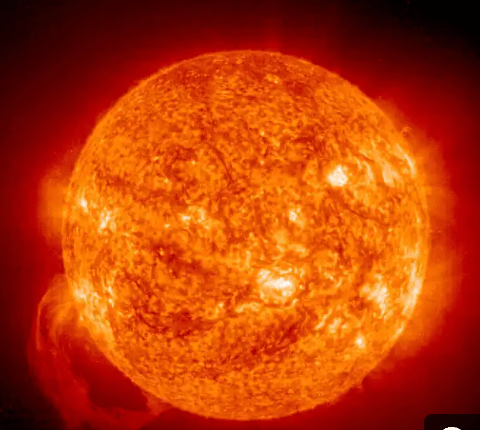
¿En qué etapa del ciclo de vida se encuentra nuestro Sol?
a) Nebulosa
b) Protoestrella
c) Estrella de la secuencia principal
d) Gigante roja
Which life cycle stage is our Sun in?
a.) Nebula
b.) Protostar
c.) Main Sequence Star
d.) Red Giant
e.)White Dwarf
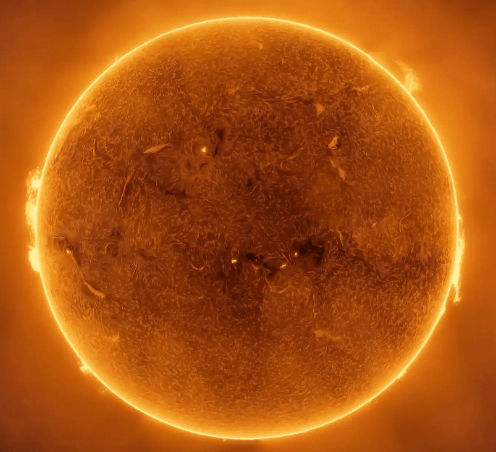
c.) Main Sequence Star
When hydrogen runs out, the star will then start to fuse what?
Cuando se agote el hidrógeno, la estrella comenzará a fusionar ¿qué?
Helium
La segunda ley de Kepler establece:
a) Las órbitas de los planetas son elipses con dos focos en el centro.
b) La distancia al Sol es proporcional a su período de revolución.
c) La velocidad orbital de los planetas varía según su distancia al Sol.
Kepler's SECOND law states
a.) the orbits of planets are ellipses with two focus points in the middle.
b.) the distance from the sun is proportional to its period of revolution.
c.) the orbital speed of the planets changes base on the distance from the sun.
c.) the orbital speed of the planets changes base on the distance from the sun.
TRUE OR FALSE: Planetary Motion is the movement of planets around a star.
VERDADERO O FALSO: El movimiento planetario es el movimiento de los planetas alrededor de una estrella.
TRUE
Cuando una estrella joven se "enciende", ¿cómo se llama ese proceso?
a) Nebulosa
b) Protoestrella
c) Supernova
d) Agujero negro
When a baby star "turns on" we call that a what?
a.) Nebula
b.) Protostar
c.) Supernova
d.) Black hole
b.) Protostar
Nuclear Fusion takes place where in the star?
¿Dónde tiene lugar la fusión nuclear en la estrella?
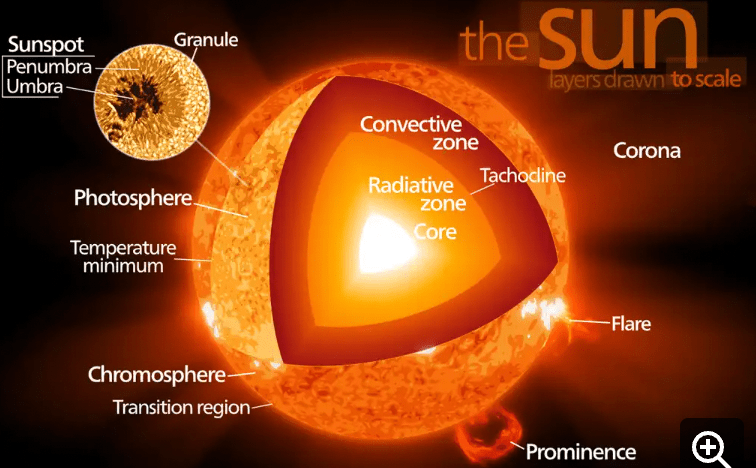
Core
Centro
La excentricidad de la órbita elíptica de un planeta es una forma de medir cuánto se desvía la órbita __________________
a) de un círculo perfecto a una elipse alargada
b) de una elipse alargada a un círculo perfecto
c) de una elipse a una línea recta
d) de un círculo perfecto a una línea recta
The eccentricity of a planet's elliptical orbit is a way of measuring how much the orbit deviates __________________
a.) from a perfect circle to an elongated ellipse
b.) from an elongated ellipse to a perfect circle
c.) from an ellipse to a straight line
d.) from a perfect circle to a straight line.
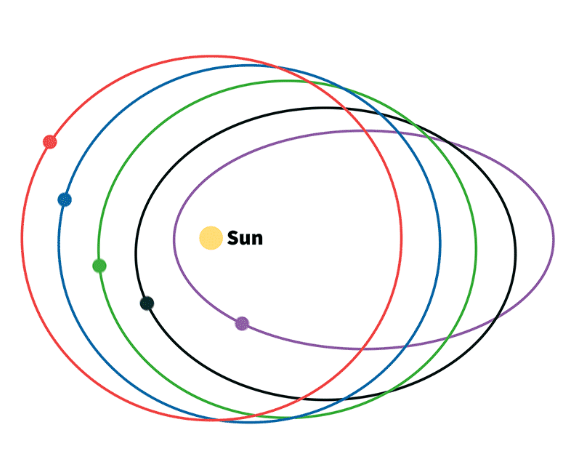
a.) from a perfect circle to an elongated ellipse
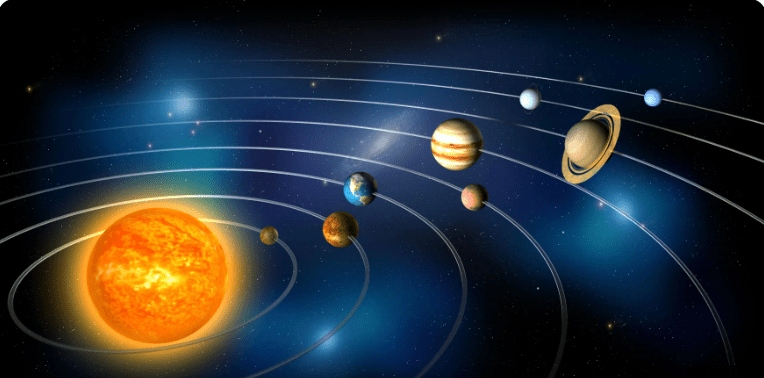
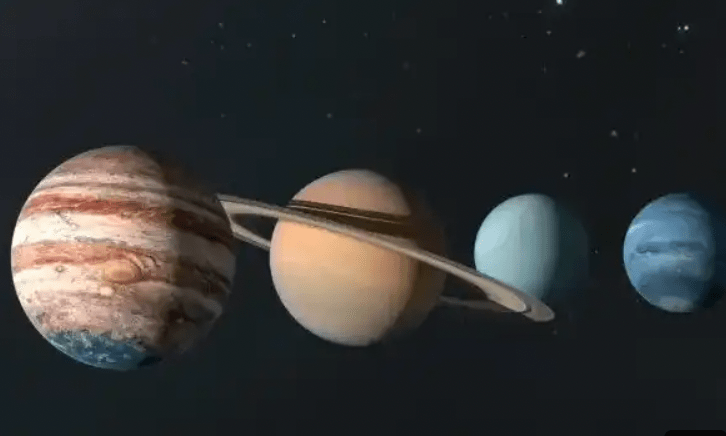
The 4 outer planets are also known as
Los 4 planetas exteriores también se conocen como
Joviano

Cuando nuestro Sol se expanda hasta engullir todos los planetas interiores, ¿en qué etapa de su vida se encontrará?
a) Protoestrella
b) Secuencia principal
c) Gigante roja
d) Enana blanca
When our sun expands to consume all the inner planets, it will be at what stage of its life?
a.) Protostar
b.) Main Sequence
c.) Red Giant
d.) White Dwarf
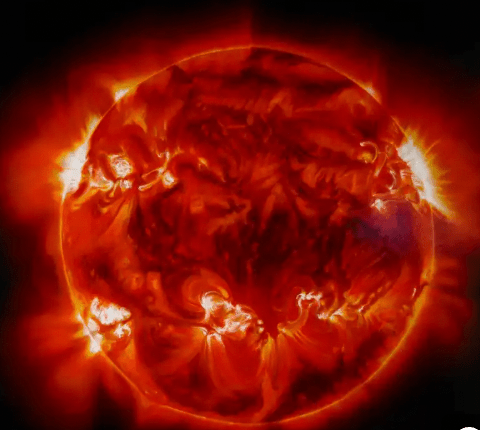
c.) Red Giant
¿Qué ocurre cuando los átomos se fusionan para formar elementos más pesados en la estrella?
a) Se contrae
b) Se expande
c) Permanece igual
d) Se vuelve invisible
When fusing atoms together to make heavier elements, the outer layer of the star does what?
a). Shrinks
b.) Expands
c.) Stays the same
d.) Turns invisible
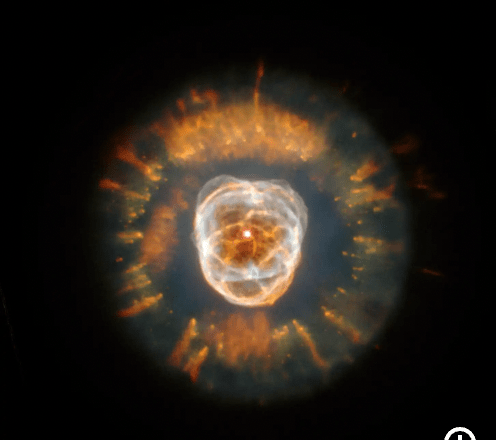
b.) Expands
¿Cuál de las siguientes opciones no se debe a la revolución de la Tierra?
a) Las estaciones
b) 365 días
c) Los meses
d) El día y la noche
Which of the following is not due to Earth's revolution?
a.) seasons
b.) 365 days
c.) months
d.) day and night
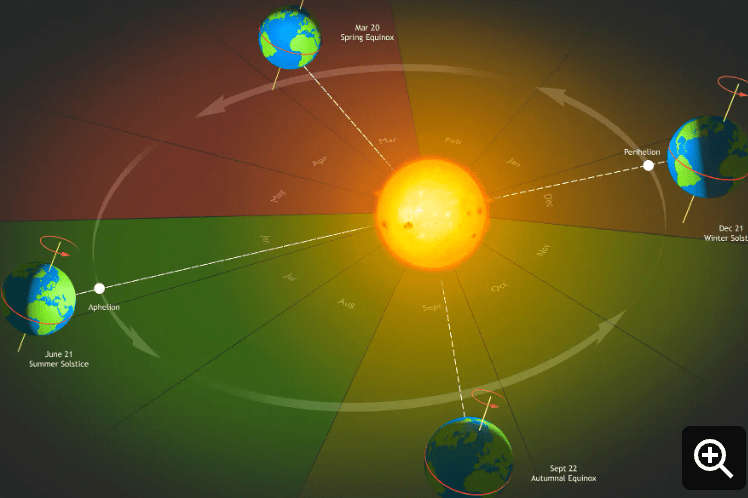
d.) day and night
Betelgeuse es una estrella gigante roja, 12 veces más grande que el Sol; al final de su vida se convertirá en:
a - agujero negro
b - enana blanca
c - estrella de neutrones
d - enana negra
Betelgeuse is Red Giant star, 12x the size of the Sun; at the end of its life cycle it will turn into a
a - black hole
b. white dwarf
c - neutron star
d - black dwarf
c. neutron star
Al final de su vida, el núcleo de una estrella del tamaño de nuestro Sol se convertirá en:
a) una protoestrella
b) una nebulosa
c) una gigante roja
d) una enana blanca
At the very end the core of a star the size of our sun will become a what?
a.) protostar
b.) nebula
c.) red giant
d.) white dwarf

d.) white dwarf
Cuando la capa exterior se desprende del sol al final de su vida, ¿qué ocurre con la fuerza de gravedad?
a) Se debilita
b) Permanece igual
c) Aumenta
d) Cambia de color
As the outer layer sheds off the sun at the end of its life the force of gravity gets?
a.) Weaker
b.) Remains the same
c.) Stronger
d.) Changes color
c.) Stronger
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones no se debe a la rotación de la Tierra sobre su eje?
a) Día y noche
b) La Tierra gira sobre su eje
c) Tarda 24 horas en completar un ciclo
d) Tarda 365 días en completar un ciclo
Which of the following is not due to Earth rotating on it's axis?
a.) day and night
b.) Earth spins on an axis
c.) Takes 24 hours to complete one cycle
d.) Takes 365 days to complete one cycle
d.) Takes 365 days to complete one cycle
Rigel es una estrella gigante azul, 79 veces más grande que el Sol; al final de su vida se convertirá en:
a - agujero negro
b - enana blanca
c - estrella de neutrones
d - enana negra
Rigel is Blue Giant star, 79x the size of the Sun; at the end of it's life cycle it will turn into a
a - black hole
b - white dwarf
c- neutron star
d - black dwaf
a - black hole
Los científicos teorizan que las estrellas más grandes explotan como supernovas y su núcleo se transforma en:
a) estrella de neutrones
b) agujero negro
c) enana blanca
d) planeta
Scientists theorize that the largest stars go supernova and their core turns into what?
a.) neutron star
b) black hole
c.) white dwarf
d.) planet
b) black hole
Cuando una estrella pasa de la secuencia principal a la fase de gigante roja, ¿qué ocurre con su fuerza de gravedad?
a) Se debilita
b) Permanece igual
c) Aumenta
d) Cambia de color
As a star moves from the main sequence stage to the red giant stage, the force of gravity gets?
a.) Weaker
b.) Remains the same
c.) Stronger
d.) Changes color
a.) Weaker
La tercera ley de Kepler establece:
a) Las órbitas de los planetas son elipses con dos focos en el centro.
b) La distancia al Sol es proporcional a su período de revolución.
c) La velocidad orbital de los planetas varía en función de su distancia al Sol.
Kepler's THIRD law states:
a.) the orbits of planets are ellipses with two focus points in the middle.
b.) the distance from the sun is proportional to its period of revolution
c.) the orbital speed of the planets changes base on the distance from the sun.
b.) the distance from the sun is proportional to its period of revolution
¿Qué factor al nacer determinará cómo termina la vida de una estrella?
a - sabor
b - color
c - masa
d - redondez
What factor at birth will determine how a star ends its life?
a - flavor
b - color
c - mass
d - roundness
c - mass