This term describes the period in European history between 500 and 1500 CE.

What is the Middle Ages (or Medieval Period)?
This system of government was based on land ownership and personal loyalty.

What is feudalism?
Knights received these grants of land from their lords in exchange for military service.
What are fiefs?
This man was crowned Emperor by the Pope in 800 CE, on Christmas day, showing the Church’s growing power.

Who was Charlemagne?
The decline of cities and learning led to the loss of this shared means of communication in Europe.
What is Latin (or a common language)?
Religious communities where monks and nuns lived and worked.
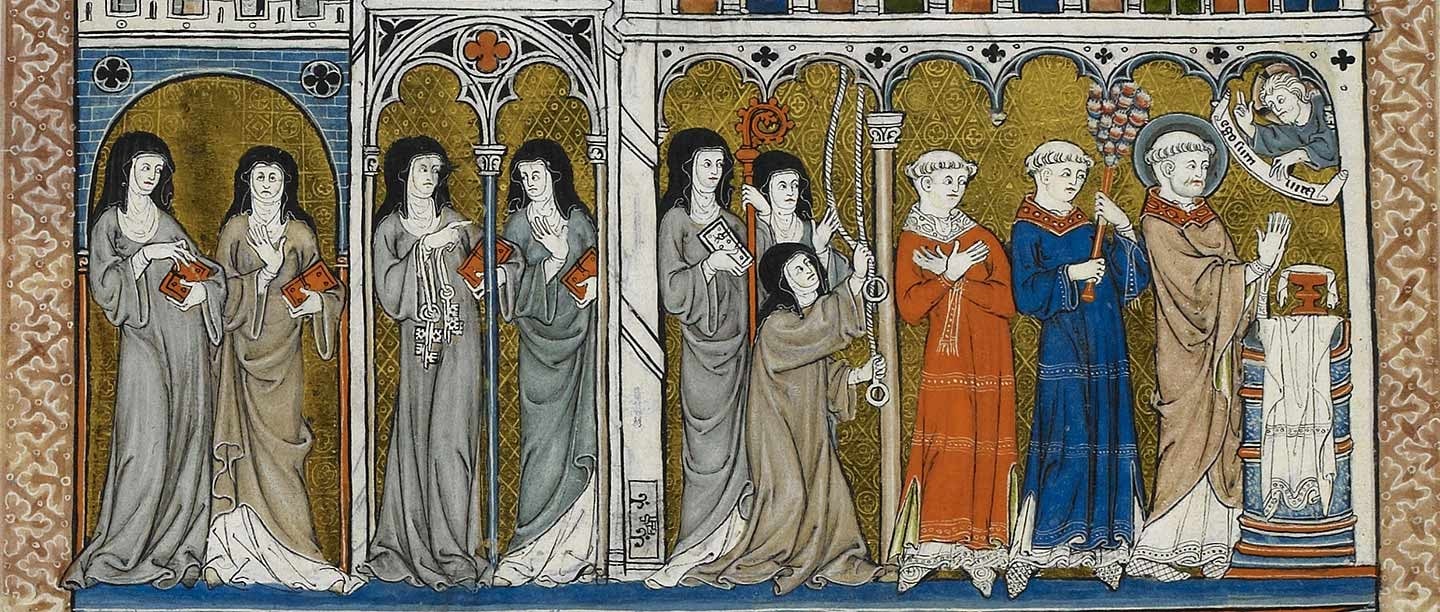

What are monasteries and convents?
At the bottom of the medieval social order/system were these agricultural laborers who were tied to the land.

Who were serfs?
This was the code of ideals that required knights to be loyal, brave, and courteous.

What is chivalry?
This ceremony, banned by Pope Gregory VII, allowed kings to appoint church officials.

What is lay investiture?
A lord granted land to this [specific] type of person.
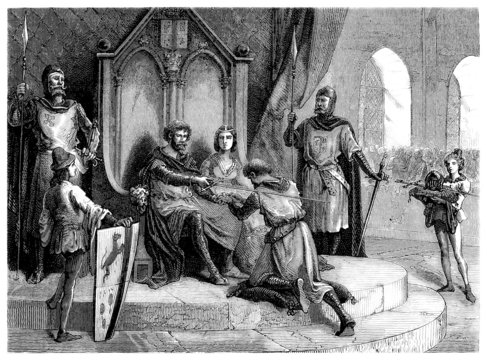
Who was a vassal?
This Frankish leader defeated Muslim forces at the Battle of Tours in 732, saving Western Europe from conquest.

Who is Charles Martel (Charles the Hammer)?
This tax represented one-tenth (1/10) of a medieval farmer's income and was paid to the Church.

What is a tithe?
These TWO inventions—originally from Asia—changed European warfare around 700 CE.
What are the saddle and stirrup?
Pope Gelasius I described these two “swords” as symbols of authority — one spiritual, one political.

What are the Church and the state
(or religious and political powers)?
These traveling poet-musicians sang songs of courtly love and recited medieval poetry that celebrated heroic deeds and adventures.

Who were troubadours?
One of Charlemagne’s biggest achievements was encouraging this among clergy and nobles.

What is learning/education?
Peasants accepted their hardships because they believed this determined their place in society.

What is God, God's Will, or divine order?
This type of medieval poetry celebrated heroic deeds and adventures.
What is epic poetry?
The Church could punish rulers by excluding them from the sacraments — this was called ___.

What is excommunication?
This term refers to Church law that governed marriage and religious practices.

What is canon law?
Charlemagne’s empire was divided among his three grandsons by this 843 agreement.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-526779746-58fdece55f9b581d5995d961.jpg)
What is the Treaty of Verdun?
This economic system was based on rights & obligations between lords and serfs.
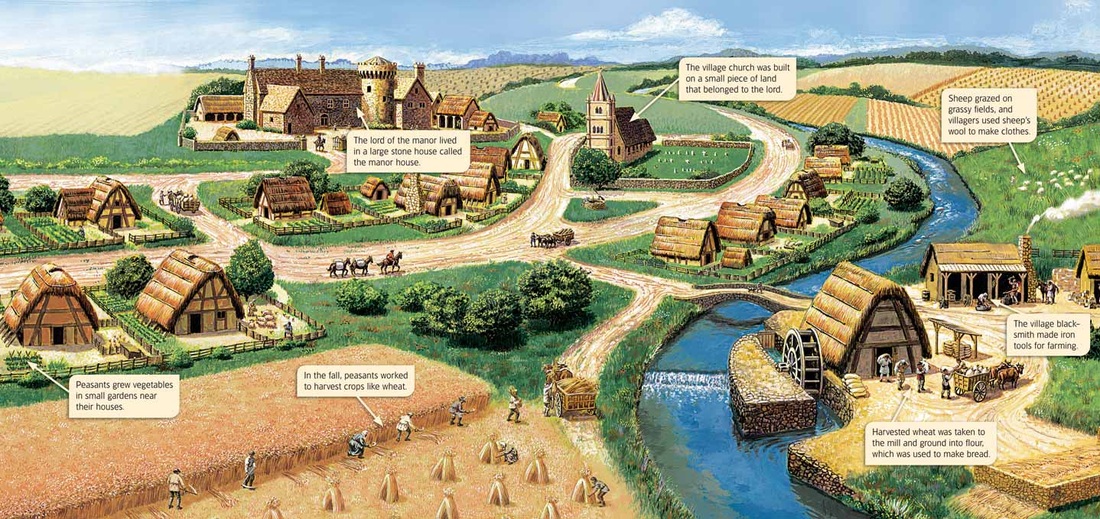
What is the Manor System?
A knight pledged loyalty to these three “masters”
Who are his feudal lord, heavenly Lord, & chosen lady?
The 1122 agreement that ended the lay investiture conflict was called ____________, and gave the pope power to appoint bishops, but allowed the emperor to ________ the appointments.
What are the Concordat of Worms and veto
This was the name of the empire Otto I helped create in 962 CE.
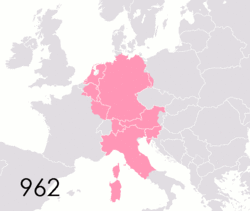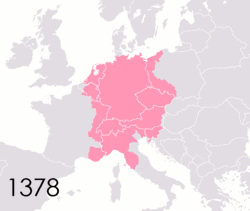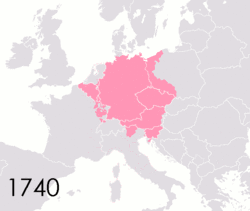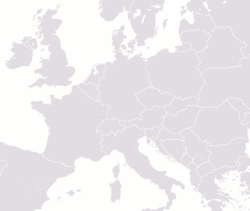
What is the Holy Roman Empire?