In this mechanism of evolution, individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to the gradual increase of those traits within a population.
What is natural selection?
A branching diagram that shows evolutionary relationships between species
What is a cladogram or phylogenetic tree
This is any evidence of prehistoric life found in the rock record.
What is a fossil
The image below shows examples of these kinds of structures
What are homologous Structures
DAILY DOUBLE
The process by which genetic information is passed on from parent to child, and a CRUCIAL part of Evolution.
What is inheritance
This mechanism of evolution occurs when random events lead to changes in allele frequencies within a population, often resulting in a loss of genetic diversity.
What is genetic drift?
DAILY DOUBLE!
The direction that "time" goes in evolutionary tree diagrams
From the bottom up (bottom is oldest, top is youngest)
With fossils, we are able to ____________ the anatomy of ancient organisms with their modern descendants, tracing back the evolution of traits and characteristics
Compare
Body parts of different species that have a similar function, but evolved independently of each other and are NOT structurally similar
What are analogous structures
An inherited trait that increases an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is an adaptation?
In this mechanism of evolution, the movement of individuals or gametes between populations can result in the transfer of alleles, altering the genetic composition of both populations.
What is gene flow?
Evolutionary tree diagrams can be created using animal characteristics as well as this other precious source of information.
An organisms' DNA or genetic code
DAILY DOUBLE
A type of fossil that shows evidence of behaviors, but not exactly of the organism itself (like footprints or burrows)
What are trace fossils?
This pattern of evolution is when a species evolves into one of more sizes more over time
What is divergent evolution
The organisms Charles Darwin observed in the Galapagos that had specialized body parts better suited for certain types of food in specific environments.
What are finches?
This phenomenon occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population, leading to a loss of genetic variation compared to the original population.
What is the founder effect?
An organism where more than one species can trace its ancestry back to
What is a common ancestor?
Explain how fossils provide evidence for evolution
Fossils provide actual PHYSICAL evidence of past life and support the theory of evolution by showing the changes in the physical traits and characteristics of species over long timespans.
Structures similar in form but not necessarily in function show what style of evolution?
What is divergent evolution?
In evolutionary biology, this describes how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is fitness?
This effect, which is caused by a drastic reduction in population size either by natural disasters, leads to a significant decrease in genetic diversity.
What is the bottleneck effect
On the tree below, circle where all hypothetical "common ancestors" are.
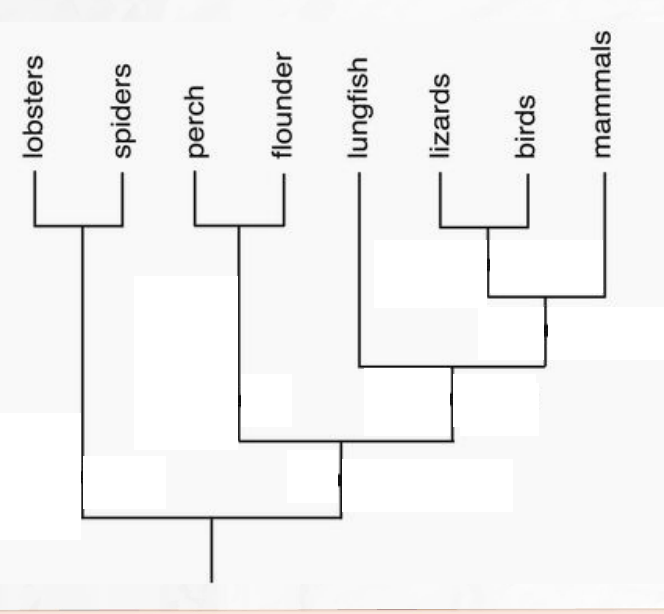
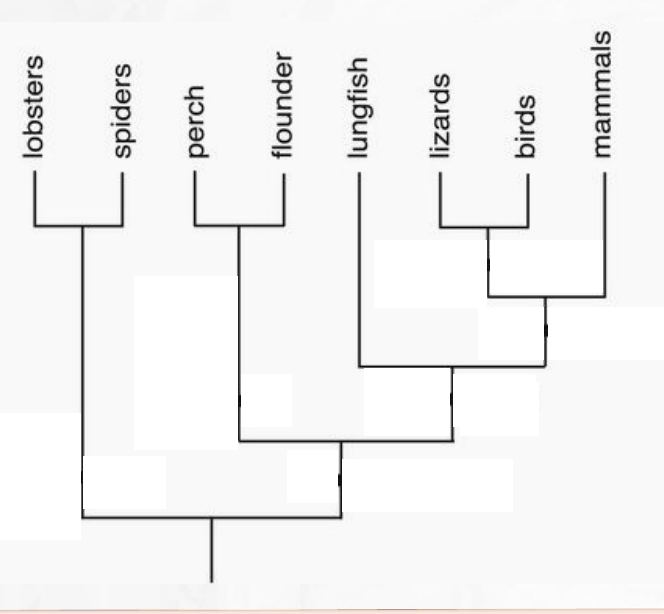
The discovery of Tiktaalik, a transitional fossil between fish and tetrapods (4-limbed animals), provides evidence for which major event in the evolution of life on Earth?
The transition of animals from living in water to on land
How does embryology show evidence of evolution?
Embryology provides evidence of evolution by showing similarities in early developmental stages of different species, suggesting a common ancestry.
Please name and briefly describe the three mechanisms of evolution
- Natural Selection: Favorable adaptations increase survival and reproduction.
- Genetic Drift: Random chance affects population allele frequencies.
- Gene Flow: Genetic exchange occurs between different populations/migration.