Organisms that share very similar structures may provide evidence of a ________________ common ancestor.
What is "recent"?
Structures that are similar due to a recent common ancestor.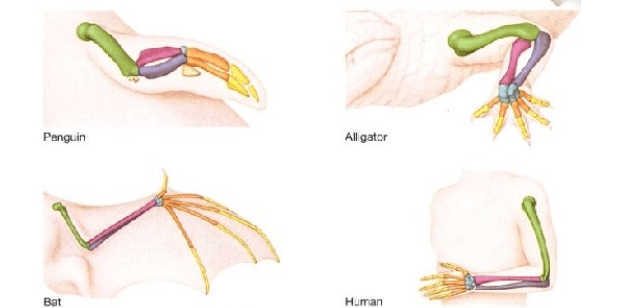
What is homologous?
The 2 types of nucleic acids.
What is DNA/RNA?
Short-term, immediate energy.
What are carbohydrates?
Which layer would have the oldest fossils?

What is the bottom layer?
Structures that have similar functions but are not related to a common ancestor.
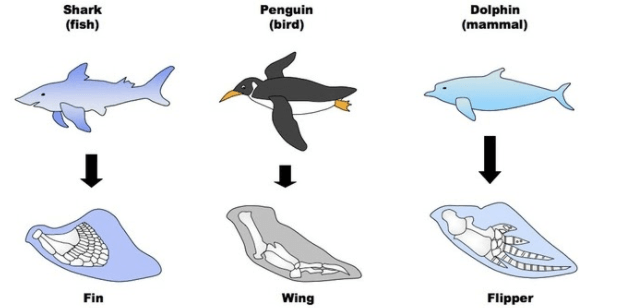
What are analogous structures?
DNA codes for __________________, a macromolecule (ex: enzyme)
What is proteins?
Made up of long chains of amino acids.
What are proteins?
The tree of life represents that all organisms originated from a _______________ ________________.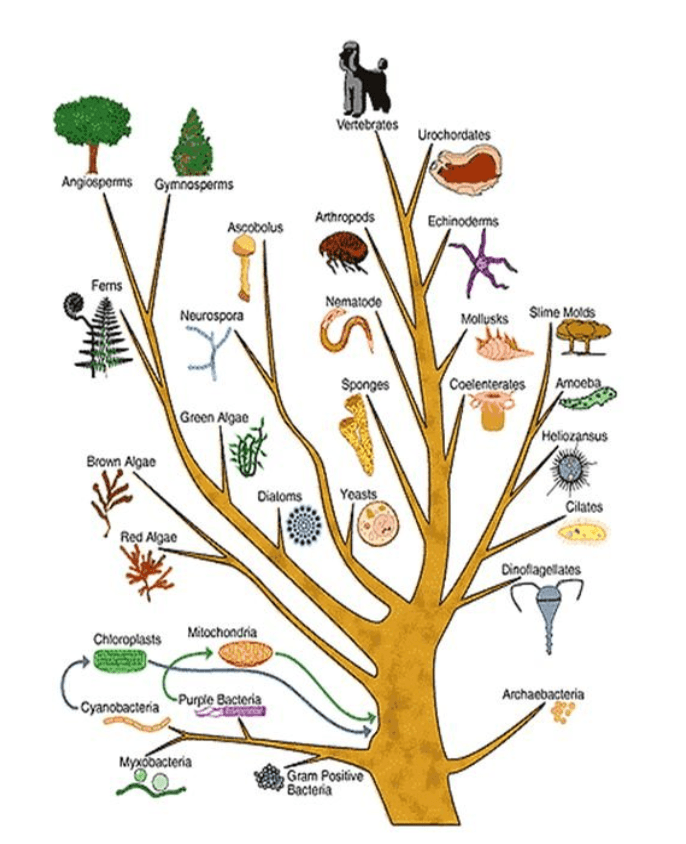
What is "common ancestor"?
Structures that no longer serve a function in an organism.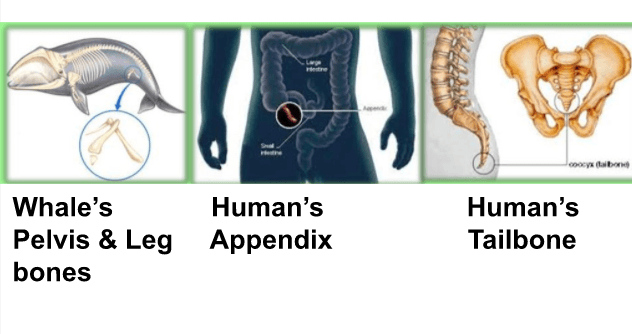
What is vestigial?
Based on the protein cytochrome c amino acid sequences, which organisms are most closely related?

Stores genetic information.
What are nucleic acids?
Tetrapods, organisms that have characteristics of both fish and land animals, are called _______________ fossils.
What is transitional?
The picture shows that the study of ____________ can also provide evidence of evolution.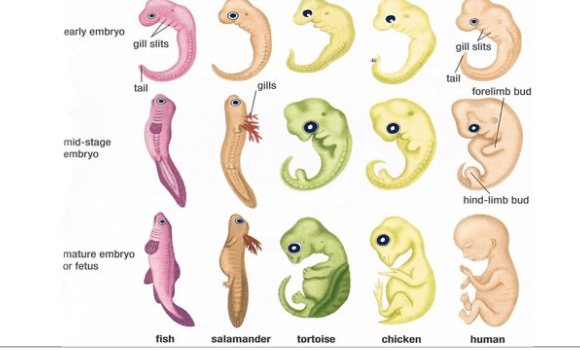
What is embryos?
Based on the image, which organism is most closely related to the chimpanzee?
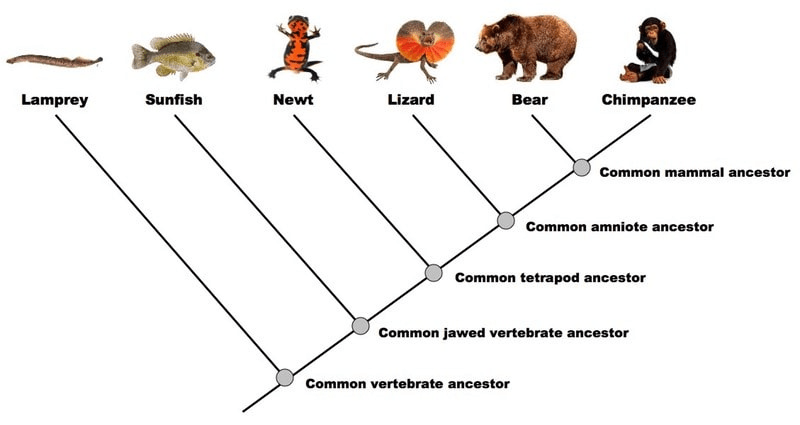
What is bear?
Long-term energy storage (think polar bear hibernating).
What are lipids?
True or false: the fossil record is the most accurate evidence of evolution.
What is false?
True/False: Comparative anatomy is the most reliable evidence of evolution.
What is false?
True/False: Molecular evidence is the most reliable evidence of evolution.
What is true?
Monosaccharides, Amino acids, Nucleotides.
What are monomers?