Define adaptation.
An adaptation is a trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment.
Which scientist created the Theory of Acquired Characteristics?
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Which scientist created the Theory of Natural Selection?
Charles Darwin
True or False: All dogs are the same species.
True. Dogs can mate and reproduce to have offspring that can also reproduce.
Define evolution.
Evolution is change over time.
Humans have opposable thumbs. What type of adaptation is this?
structural
True or False: Lamarck believed that organisms never became extinct.
True. Lamarck believed that organisms would acquire whatever trait they needed in order to survive, and therefore never struggle and die out.
Some newly hatched turtles can swim faster than others of the same species. This is evidence of ____ within a species.
variations
What is another term for artificial selection?
selective breeding
What is the purpose of a line graph?
Line graphs show change over time.
Birds migrate south in the winter. What type of adaptation is this?
behavioral
Name one problem/error with the Theory of Acquired Characteristics.
Give an example of a trait that makes a shark fit. Explain.
sharp teeth to eat food, fins to swim fast, gills to swim underwater
In artificial selection, what determines which traits are passed on to the next generation? How is this different than natural selection?
In artificial selection, humans decide which traits get passed on. In natural selection, it is the environment (nature).
Name three characteristics/rules when creating a line graph.
title, labeled axes, even scales, use a ruler
Give an example of an adaptation that helps an organism survive in the Arctic. Explain.
thick fur to keep warm, white fur to blend in with snow, caves to hide for warmth
Name one statement that differentiates Lamarck and Darwin’s theories of evolution.
Lamarck said acquired traits are passed on and Darwin said only inherited traits, Lamarck said organisms cannot become extinct but Darwin said they could, Lamarck said individuals change and Darwin said populations change
In natural selection, what determines/selects which traits are passed on to the next generation?
the environment
Name one thing that artificial selection and natural selection have in common.
both cause populations to evolve, both involved inherited traits, both require variations within a species
Define species.
a group of organisms that can mate and reproduce and have offspring that can also reproduce
Give one example of each of the three types of adaptations.
Structural: rhinos' horns
Behavioral: bats are nocturnal
Physiological: snakes' venom
Name one statement that Lamarck and Darwin agreed on.
organisms change over time, the environment has something to do with why change happens, organisms that better fit into their environment have a better chance of surviving, evolution is still happening today
Explain the evolution of the peppered moth using these vocabulary words: variations, adaptation, competition, fit, survival of the fittest, evolution, natural selection
Most peppered moths were white, but there was some variation with a few dark moths. When the Industrial Revolution happened, the moths' environment turned dark from pollution and they competed to avoid being seen and eaten by the birds. The dark moths had an adaptation to blend in with the dark trees and were therefore more fit. The light mice struggled and died. Through survival of the fittest, the dark moths survived and reproduced to pass on their dark genes. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection explains how the changed environment selected the dark over the light moths causing the population to evolve to be mostly dark moths.
Give a real world example of artificial selection. Explain.
dog breeds, apple varieties, vegetables, livestock
Analyze this graph.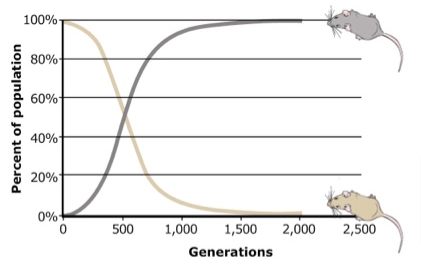
Almost 100% of the population of mice have light fur and very few have dark fur. Over time, the light decrease and the dark increase until they are about even after 500 generations. The population continues to evolve until almost 100% are dark mice after 2000 generations and very few are light.