____________________ is described as a change in inherited traits in a population of organisms over time.
Evolution
Draw and label the three modes of selection.

When an organism completely dies out.
What is Extinction?
Identify two types or fields of science that could be used as evidence of evolution?
Paleontology, biochemistry, biogeography, morphology, and embryology.
What are phylogenetic trees/cladograms used for?
They are used to show evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
Look at the photo and identify which condition of Natural Selection does it represent AND why.

Variation because it shows butterflies can have wings that are different shapes, sizes, and colors!
In terms of the HWE, what do p and q represent?
q - recessive allele
If a population were to become separated or geographically isolated for a long period of time, this may lead to new species. What pattern is this?
Speciation
Some organisms evolve with structures that no longer serve a purpose or have no apparent function. These structures are called...
Vestigial structures
Looking at the cladogram, which trait does the lynx possess but the lizard does not?
Hair
What is it called if an organism or a population changes to become better suited to their environment in order to survive and reproduce?
Adaptation
In regard to evolution, what does "fitness" mean?
Fitness refers to how well you ca survive and reproduce in an environment.
Which type of pattern of evolution describes number of different species arise from one common ancestor.
Divergent Evolution
What vocabulary word best fits the descriptions below?
(1) Organisms who've evolved from a common ancestor will have similar structures but different functions.
(2) When unrelated organisms with no common ancestors have structures with the same functions.
(1) Homologous structures
(2) Analogous structures
Looking at the cladogram, what do ALL the organisms have in common?
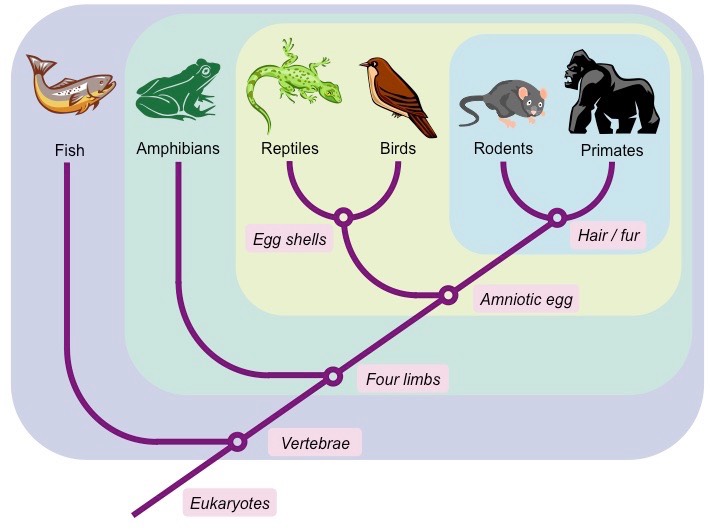
They are all Eukaryotes.
Which of the following IS a principle of Natural Selection?
A. Resources are readily available which mitigates competition in a population
B. Organisms overproduce offspring which causes competition for limited resources
C. Organisms have undifferentiated phenotypes in the population
D. All individuals in a population have the fitness to survive in their habitats
B. Because organisms do overproduce which causes competition.
If there are no mutations, no migration, random mating occurs, a large population occurs, and natural selection does not happen, what formula would you use to solve for their frequencies.
HWE!
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
What is convergent evolution? Give an example!
When unrelated species evolve similar characteristics because they live in similar environments.
- Bats and whales have echolocation
- Butterflies and birds have wings to fly
Explain why is it possible for a human to have DNA that is 48% similar to a rhino, but not be directly related.
It's because all living things share and are built from the same genetic information, which includes: genes, amino acids, and proteins.
Based on the amino acid differences, identify:
(1) The out group species AND how you know.
(2) The two species who would most likely be closely related AND how you know.
(1) Species A because it has the MOST differences when compared to the other species.
(2) Species B and C because those two species only have 3 amino acid differences.