Define natural selection.
Defina selección natural.
Population can change over generations if individuals with certain heritable traits produce more viable offspring than others.
Define divergent evolution.
Definir evolución divergente.
When a population becomes isolated from the rest of the species and becomes exposed to new selective pressures, causing it to evolve into a new species
Define mutation.
Defina mutación.
Mutation introduces new alleles in a species.
Define directional selection.
Definir selección direccional.
Favors traits that are at one extreme of a range of traits
Define generalist species.
Definir especies generalistas.
Species that are able to thrive in a wide variety of environments (Stable)
What are two claims that Darwin made about evolution?
¿Cuáles son dos afirmaciones que hizo Darwin sobre la evolución?
Modern species evolved from ancestral forms
Driving force of evolution is natural selection
Define convergent evolution.
Definir evolución convergente.
When unrelated species occupy the same environment and are subjected to similar selection pressures leading to similar adaptations
Explain how mutations drive evolution.
Explica cómo las mutaciones impulsan la evolución.
Mutations cause change in the genes of a species and their physical characteristics. If these physical characteristics thrive in an environment they are passed on and weaker traits will die out.
Give your own example of stabilizing selection.
Dé su propio ejemplo de selección estabilizadora.
Answers will vary.
Analogous structures arise from what kind of evolution?
¿De qué tipo de evolución surgen estructuras análogas?
Convergent evolution
State three evidence of evolution we have so far.
Enumere tres evidencias de evolución que tenemos hasta ahora.
Molecular homologies
Biogeography
Fossil Record
Comparative Anatomy
Give an example of divergent evolution.
Dé un ejemplo de evolución divergente.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/four-or-the-species-of-finch-observed-by-darwin-on-the-galapagos-islands-802464738-5c452bbbc9e77c0001d34a79.jpg)
Explain the founder effect.
Explique el efecto fundador.
Occurs when a small number of individuals travel away from their original population and become reproductively isolated
Explain the difference between allopatric and sympatric speciation.
Explicar la diferencia entre especiación alopátrica y simpátrica.
Allopatric speciation occurs when geographic isolation creates a reproductive barrier
Sympatric speciation occurs when a reproductive barrier is created by something other than geographic isolation
Explain the difference between a generalist species and specialist species. Give an example of a specialist species.
Explicar la diferencia entre una especie generalista y una especie especialista.
Generalist species are able to thrive in a wide variety of environments. Specialist species survive on narrow habitats and limited food sources. and similar functions.
Define homologous structures and give an example.
Variations of structure which show anatomical signs of evolution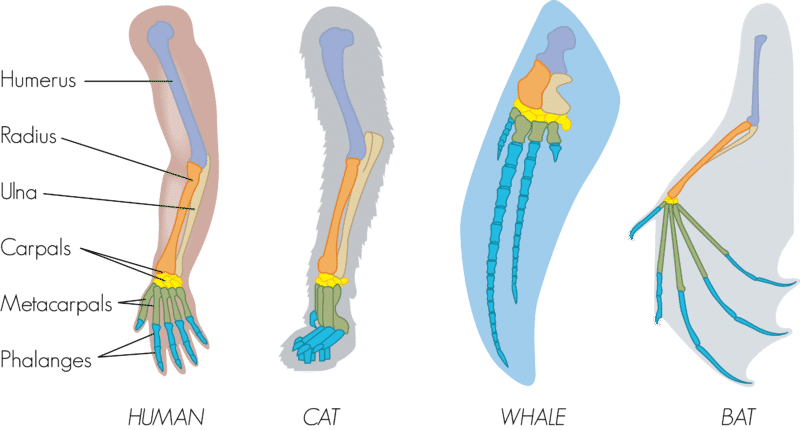
Give an example of convergent evolution.
Dé un ejemplo de evolución convergente.
Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype.
Explica la diferencia entre genotipo y fenotipo.
Genotype refers to the genes within the organisms DNA and phenotype refers to the physical appearance.
Name and explain three intrinsic reproductive isolating mechanisms.
Nombra y explica tres mecanismos intrínsecos de aislamiento reproductivo.
Hybrid inviability or infertility
Mechanical isolation
Gametic isolation
Behavioral isolation
Ecological isolation
Temporal isolation
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre estructuras homólogas y análogas?
Homologous structures has similar physical features with different functions. Analogous structures have different physical features and similar functions.
During the Darwin documentary that we watched, what was the organism that was on Darwin's desk when he was showing his daughter the microscope?
Durante el documental de Darwin que vimos, ¿cuál era el organismo que estaba en el escritorio de Darwin cuando le mostraba el microscopio a su hija?
Baby tortoise
Define coevolution and explain how birds and monarch butterflies drive each other's evolutions.
Defina la coevolución y explique cómo las aves y las mariposas monarca impulsan sus evoluciones mutuas.
Mutual evolutionary adaptations of two interacting species
Explain the bottleneck effect and how it causes genetic drift.
Explique el efecto cuello de botella y cómo provoca la deriva genética.
The bottleneck effect can be caused by a natural disaster. Species are randomly wiped from a population resulting in some genes being lost. This causes the population's gene pool to move in a different direction or "drift".
Think back to the documentary on Darwin and how it mentioned the HIV virus. Explain how natural selection relates to the HIV virus in the human body.
Piense en el documental sobre Darwin y en cómo mencionaba el virus del VIH. Explique cómo se relaciona la selección natural con el virus VIH en el cuerpo humano.
No matter how much antibiotics are used, the HIV population cannot be fully killed. There are always strands of HIV virus survives and reproduces showing natural selection at work.
Provide an example of analogous structures between two organisms of your choice.
Proporcione un ejemplo de estructuras análogas entre dos organismos de su elección.
Answers will vary.