Describe the difference between microevolution and macroevolution.
Microevolution- when changes affect specific genes and occur over shorter time scales
Macroevolution- large-scale changes that occur over extended periods of time that can form new species or groups
Who created the current hierarchy of taxonomy?
Carl Linnaeus
The amount of extinctions recorded
What is 5?
The definition of a cladogram
A visual representation of evolutionary relationships using lines, animals and derived traits.
Define adaptation.
Structures that have the same function but different structures.

Analogous Structures
Who is known as the "father of Evolutionary Theory"?
Charles Darwin
The organisms that survived the Ordovician- Silurian Extinction
What are BONY FISHES?
Which trait is shared by both reptiles and birds?

The egg shell
Define "fitness"
The ability to survive and reproduce
Same structure, different function

Homologous structures
What is the most specific "rung" of the taxonomy ladder?
Species
The % of species that died at the end of the Permian - Triassic Extinction.
96%
Which is the closest relative to the crocodile? 
The bird
Does natural selection act upon phenotypes or genotypes. Explain.
Phenotypes- selection occurs on physical features, not actual genes.
Structures that used to have a function but no longer serve a purpose.
Vestigial Structures
What is the broadest "rung" of the taxonomy ladder?
Domain
The organisms that are direct descendants of the now extinct dinosaurs.
Birds
What trait do the Elasmobranchs possess that the lampreys do not?

JAWS
Describe the difference between R-selected and K-selected species. Give examples for full credit.
R-selected - Lots of offspring, short life spans (ex. rabbits, bacteria, bumblebees)
K-selected- Fewer offspring, typically longer life spans (elephants, humans, crocodiles, sharks)
Compare a bat, moth and bird wing. Describe their analogous and homologous features.
Bats and birds= homologous features
Moth and bats= analogous features
What is the suffix of words indicating species belong to the same family?
-idae
The cause of the Cretaceous - Tertiary Extinction
An asteroid hit the Yucatan peninsula in Mexico causing the atmosphere to heat up, smoke and dust blocked the sunlight which led to no photosynthesis and an eventual collapse of almost all food webs.
What did the tetrapods evolve that these groups of fishes did not have?
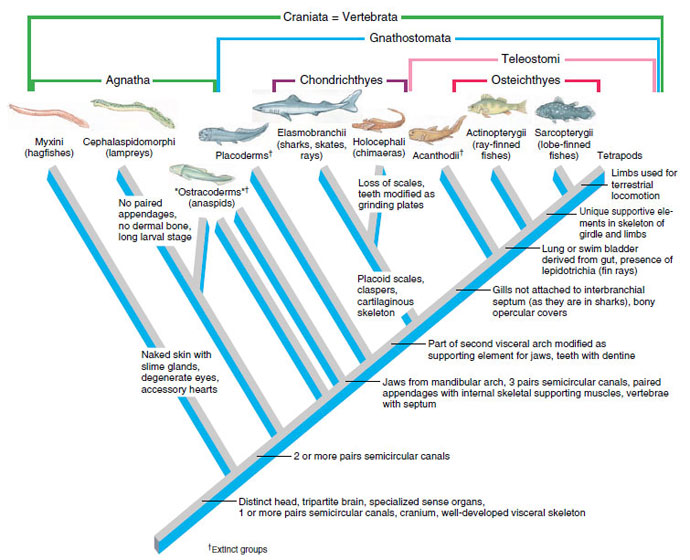
Limbs used for terrestrial locomotion
Describe the legacy of Francis Galton's Eugenics movement.
Let to scientific racism and affects people today due to policies and laws that were written in the 1900s.